Steepening Japanese Bond Curve: Investor Divisions And Economic Implications
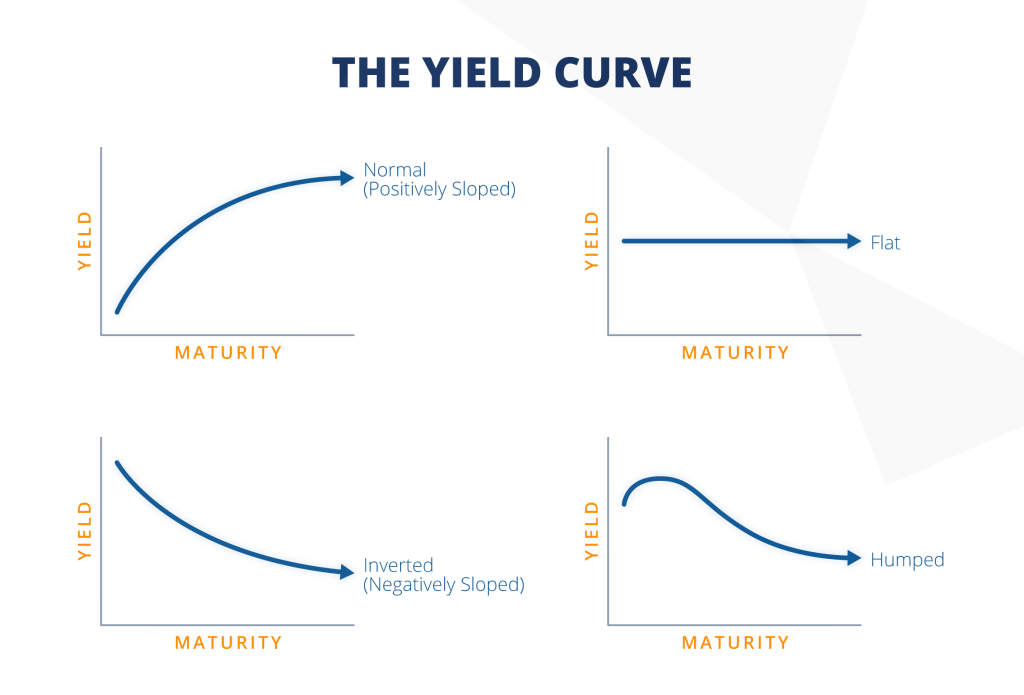
Table of Contents
2.1. Analyzing the Drivers of the Steepening JGB Yield Curve
Several intertwined factors contribute to the recent steepening of the Japanese government bond yield curve. The Bank of Japan's (BOJ) monetary policy adjustments play a central role. The BOJ's previous policy of yield curve control, aimed at keeping long-term interest rates low through aggressive quantitative easing, is undergoing a significant shift towards monetary policy normalization. This gradual tapering of quantitative easing has allowed long-term JGB yields to rise, contributing to the steepening curve.
The impact of rising global interest rates and inflation expectations further exacerbates this trend. Global inflation, fueled by factors such as supply chain disruptions and increased energy prices, has prompted central banks worldwide to raise interest rates. This has increased the attractiveness of higher-yielding assets globally, putting upward pressure on JGB yields. Consequently, JGBs are becoming less attractive as an inflation hedge, affecting investor sentiment. The widening interest rate differentials between Japan and other developed economies also play a significant role.
Finally, domestic and foreign investor sentiment plays a crucial role. Concerns about the sustainability of Japan's fiscal position, coupled with expectations of further BOJ policy adjustments, are affecting domestic JGB demand. Foreign investors, traditionally significant buyers of JGBs, are reevaluating their positions in light of higher global yields and the weakening yen.
- BOJ yield curve control adjustment: The BOJ's shift away from its yield curve control policy is a primary driver of the steepening curve.
- Rising global inflation and interest rates: Increased global inflation and interest rates make JGBs less attractive relative to other assets.
- Weakening investor sentiment: Uncertainty about Japan's fiscal outlook and BOJ policy is impacting both domestic and foreign investor confidence.
2.2. Conflicting Perspectives: How Investors View the Steepening Japanese Bond Curve
The steepening Japanese bond curve has created a significant division among investors. A bullish outlook prevails among those who anticipate further yield increases. Their arguments center on the continued adjustment of BOJ monetary policy, persistent inflationary pressures, and the potential for further weakening of the yen. They foresee continued upward pressure on JGB yields, making long-term bonds less attractive and further steepening the curve.
Conversely, a bearish outlook exists among those who believe the steepening is temporary. They highlight the potential for BOJ intervention to stabilize yields, the possibility of a global economic slowdown dampening inflation, and the continued demand for JGBs from domestic investors. This group anticipates a potential stabilization or even reversal of the yield curve steepening.
- Bullish JGB outlook: Further BOJ policy shifts, persistent inflation, and a weaker yen will continue to push yields higher.
- Bearish JGB outlook: BOJ intervention, economic slowdown, and sustained domestic demand will limit yield increases.
2.3. Macroeconomic Ramifications: The Economic Impact of a Steepening JGB Yield Curve
The steepening JGB yield curve has significant macroeconomic implications for Japan. Rising yields directly translate to increased borrowing costs for the Japanese government, impacting fiscal policy and potentially leading to reduced government spending or increased taxation.
The Japanese banking sector, a major holder of JGBs, is also affected. Higher yields can impact bank profitability, especially if the rise is rapid and unexpected. This could have implications for financial stability, although the impact depends on the banks’ hedging strategies and the pace of yield increases.
Finally, higher interest rates can influence investment and economic growth through the monetary transmission mechanism. Increased borrowing costs can dampen business investment and consumer spending, potentially leading to slower economic growth. However, higher yields might also attract foreign investment seeking higher returns.
- Increased government borrowing costs: Rising yields increase the cost of financing Japan's substantial government debt.
- Impact on Japanese banks: Higher yields can affect bank profitability and potentially impact financial stability.
- Influence on investment and economic growth: Higher interest rates can dampen investment and consumer spending, potentially slowing economic growth.
2.4. Looking Ahead: Forecasting the Future Trajectory of the Japanese Bond Curve
Several potential scenarios exist for the future trajectory of the JGB yield curve. Continued steepening remains a possibility if the BOJ continues its monetary policy normalization, inflation remains persistent, and global interest rates stay elevated. Conversely, a stabilization of the curve might occur if the BOJ intervenes more aggressively to control yields or if global economic conditions weaken, impacting inflation. A reversal is also possible, should inflation significantly subside and global interest rates decline.
Predicting the most likely outcome requires careful consideration of various factors, including the future path of BOJ policy, inflation dynamics, global economic conditions, and investor sentiment. The interplay of these factors will determine whether the steepening trend persists, stabilizes, or reverses.
- Continued steepening: Further BOJ policy adjustments, persistent inflation, and high global interest rates.
- Stabilization: BOJ intervention, a slowdown in global inflation, or a weaker global economy.
- Reversal: Significant decline in global and domestic inflation and lower global interest rates.
3. Conclusion: Navigating the Steepening Japanese Bond Curve
The steepening Japanese bond curve is driven by a complex interplay of factors, including BOJ policy shifts, global inflation, and evolving investor sentiment. This creates significant divisions among investors regarding the future trajectory of JGB yields. The economic implications are considerable, affecting government borrowing costs, the banking sector, and overall economic growth. Understanding the dynamics of the steepening Japanese bond curve is critical for investors and policymakers alike. While several scenarios are possible, careful monitoring of BOJ policy, inflation trends, and global economic conditions is necessary for navigating this evolving landscape. Stay updated on the evolving dynamics of the steepening Japanese bond curve to make informed investment decisions and effectively manage risk in this crucial market.

Featured Posts
-
 Ai Digest Transforming Repetitive Scatological Data Into Engaging Podcasts
May 17, 2025
Ai Digest Transforming Repetitive Scatological Data Into Engaging Podcasts
May 17, 2025 -
 Wga And Sag Aftra Strike What It Means For Hollywood
May 17, 2025
Wga And Sag Aftra Strike What It Means For Hollywood
May 17, 2025 -
 Cassie Venturas Testimony In Sean Combs Trial Details Emerge
May 17, 2025
Cassie Venturas Testimony In Sean Combs Trial Details Emerge
May 17, 2025 -
 Exclusive Access Investigation Into Trumps Donor Events At Military Installations
May 17, 2025
Exclusive Access Investigation Into Trumps Donor Events At Military Installations
May 17, 2025 -
 Angel Reeses Ss 25 Reebok Collaboration A First Look
May 17, 2025
Angel Reeses Ss 25 Reebok Collaboration A First Look
May 17, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Refinance Federal Student Loans When It Makes Sense
May 17, 2025
Refinance Federal Student Loans When It Makes Sense
May 17, 2025 -
 4 Cursos Com Nota Maxima Do Mec No Vale Do Nome Do Vale Veja Quais Sao
May 17, 2025
4 Cursos Com Nota Maxima Do Mec No Vale Do Nome Do Vale Veja Quais Sao
May 17, 2025 -
 The Ultimate Guide To Federal Student Loan Refinancing
May 17, 2025
The Ultimate Guide To Federal Student Loan Refinancing
May 17, 2025 -
 Financial Planning For Homeownership With Existing Student Loans
May 17, 2025
Financial Planning For Homeownership With Existing Student Loans
May 17, 2025 -
 Apenas 4 Cursos Superam Avaliacao Do Mec Com Nota Maxima No Vale E Regiao Confira A Lista
May 17, 2025
Apenas 4 Cursos Superam Avaliacao Do Mec Com Nota Maxima No Vale E Regiao Confira A Lista
May 17, 2025
