Killer Seaweed: The Extermination Of Marine Life In Australia

Table of Contents
The Invasive Species Threat
Identifying the Culprits
Several invasive seaweed species are wreaking havoc in Australian waters, outcompeting native flora and fauna. These "killer seaweed" species, often introduced accidentally through ballast water or aquaculture activities, rapidly colonize vast areas, transforming healthy ecosystems into barren landscapes.
- ** Caulerpa taxifolia (Killer Algae):** This species, originally from the Mediterranean, has spread aggressively along the Australian coast, forming dense mats that smother native seagrass beds.
- ** Undaria pinnatifida (Wakame):** Native to Asia, this brown seaweed is a highly invasive species that outcompetes native kelp forests and disrupts the delicate balance of coastal ecosystems.
- ** Rugulopteryx okamurae (Japanese seaweed):** This rapidly growing seaweed has spread along the coasts of Spain and France, and there are concerns about its potential invasion of Australian waters.
- ** Heterosiphonia japonica:** Another invasive species originating from Asia, this red seaweed can form dense mats, negatively impacting native seaweed communities and associated organisms.
- ** Gracilaria vermiculophylla:** This red seaweed is native to East Asia but has spread globally, potentially impacting native seaweed diversity and creating ecological imbalances.
[Insert images/links to images of each seaweed species here]
Mechanisms of Destruction
Invasive seaweed employs various strategies to dominate native ecosystems. Their aggressive growth and spread are facilitated by:
- Smothering of native plants: Dense mats of invasive seaweed prevent sunlight from reaching native seagrasses and algae, leading to their decline and death.
- Reduction of sunlight: The thick canopies of invasive seaweed drastically reduce the amount of light reaching the seafloor, impacting photosynthesis in native plants and reducing overall primary productivity.
- Alteration of habitat structure: The dense growth of invasive seaweed alters the physical structure of the seabed, destroying crucial habitats for many marine invertebrates and fish.
- Release of allelochemicals: Some invasive seaweed species release chemical compounds (allelochemicals) that inhibit the growth and reproduction of native species. This chemical warfare gives them a competitive advantage.
Scientific studies have consistently demonstrated the devastating impact of these mechanisms, highlighting the urgent need for effective management strategies.
Impact on Marine Biodiversity
Loss of Habitat and Biodiversity
The proliferation of killer seaweed has severe consequences for marine life. The displacement of native species leads to a decline in overall biodiversity and ecosystem stability.
- Affected species: Numerous fish species, invertebrates (like crustaceans and molluscs), and commercially important seagrasses are negatively affected by invasive seaweed.
- Consequences: This loss of habitat leads to population declines, disrupted food webs, and reduced resilience to environmental changes. For example, studies have shown significant declines in fish populations in areas heavily infested with Caulerpa taxifolia.
- Quantifiable impact: While precise figures are difficult to obtain, anecdotal evidence and localized studies indicate significant reductions in biodiversity and fish stocks in impacted areas, highlighting the urgent need for action.
Economic Consequences
The economic impact of invasive seaweed infestations is substantial, affecting various sectors.
- Fishing industry: Reduced fish populations lead to decreased catches and revenue for commercial fisheries.
- Tourism industry: The decline in marine biodiversity and the unsightly appearance of seaweed-infested areas negatively impact tourism, reducing visitor numbers and revenue.
- Aquaculture industry: Invasive seaweed can foul aquaculture infrastructure and compete with cultivated species, impacting yields and profitability.
- Management costs: The cost of control and eradication efforts is considerable, placing a significant burden on government budgets.
Current Management Strategies and Challenges
Control and Eradication Methods
Several methods are employed to manage invasive seaweed, each with its own advantages and limitations.
- Manual removal: This labor-intensive method involves physically removing the seaweed, but it is only effective in small, localized infestations.
- Chemical treatments: Herbicides can be used to control the spread of invasive seaweed, but their use can have negative impacts on other marine organisms.
- Biological control agents: Research is ongoing to identify and utilize natural enemies of invasive seaweed species, offering a potentially sustainable approach.
The Difficulties of Eradication
Eradicating invasive seaweed is incredibly challenging due to several factors:
- Rapid growth: Many invasive species exhibit rapid growth rates, making eradication efforts difficult to keep pace.
- Fragmentation: Small fragments of seaweed can easily disperse and establish new populations, hindering eradication efforts.
- Vastness of affected areas: The scale of infestations often makes complete eradication impractical and prohibitively expensive.
- Logistical hurdles: The logistical challenges of accessing and treating large, remote areas add to the difficulty and cost of control programs.
Conclusion
The devastating impact of killer seaweed on Australia's marine environment and its economy cannot be overstated. The loss of biodiversity, the economic repercussions, and the challenges in controlling its spread highlight the urgency of the situation. Protecting Australia's unique marine ecosystems requires immediate action. Learn more about killer seaweed and how you can contribute to its control and the preservation of our coastal biodiversity. Support research efforts, participate in citizen science initiatives, and advocate for stricter regulations on the introduction of non-native species. Together, we can combat the spread of invasive seaweed and safeguard Australia's precious marine heritage. Let's work together to prevent further destruction caused by this destructive algae, protecting our oceans from harmful marine algae and other invasive species.

Featured Posts
-
 Guia De Programacion De Television Del Sabado 10 5 This Is Incorrect As The Keyword Is In Greek And This Is In Spanish
May 30, 2025
Guia De Programacion De Television Del Sabado 10 5 This Is Incorrect As The Keyword Is In Greek And This Is In Spanish
May 30, 2025 -
 Crisprs Next Generation Higher Precision Gene Editing
May 30, 2025
Crisprs Next Generation Higher Precision Gene Editing
May 30, 2025 -
 Experiencia De Fan Mejorada Setlist Fm Se Une A Ticketmaster
May 30, 2025
Experiencia De Fan Mejorada Setlist Fm Se Une A Ticketmaster
May 30, 2025 -
 Bts Comeback Speculation Soars After Reunion Teaser Release
May 30, 2025
Bts Comeback Speculation Soars After Reunion Teaser Release
May 30, 2025 -
 Deutsche Banks Fixed Income Currencies Traders Strategies For Market Leadership
May 30, 2025
Deutsche Banks Fixed Income Currencies Traders Strategies For Market Leadership
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
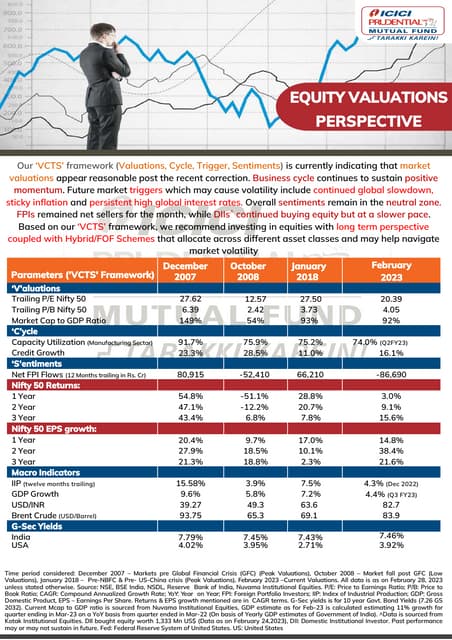 Understanding Elevated Stock Market Valuations A Bof A Perspective
May 31, 2025
Understanding Elevated Stock Market Valuations A Bof A Perspective
May 31, 2025 -
 High Stock Valuations And Investor Confidence A Bof A Analysis
May 31, 2025
High Stock Valuations And Investor Confidence A Bof A Analysis
May 31, 2025 -
 Addressing Investor Concerns Bof A On Elevated Stock Market Valuations
May 31, 2025
Addressing Investor Concerns Bof A On Elevated Stock Market Valuations
May 31, 2025 -
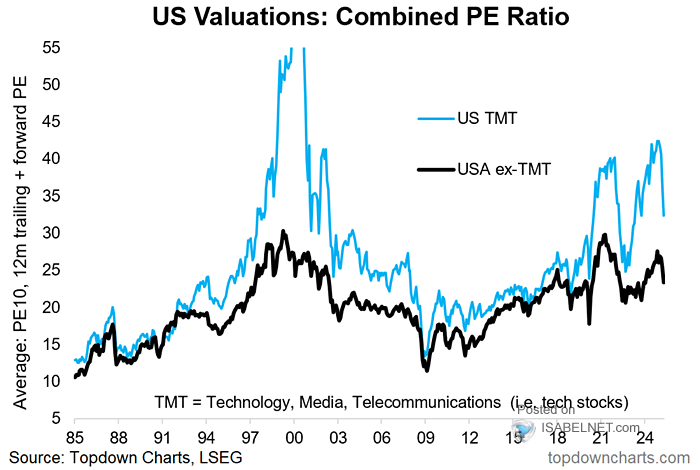 Stock Market Valuations Bof As Argument For Why Investors Shouldnt Worry
May 31, 2025
Stock Market Valuations Bof As Argument For Why Investors Shouldnt Worry
May 31, 2025 -
 Successfully Applying For Private Credit Jobs A 5 Point Guide
May 31, 2025
Successfully Applying For Private Credit Jobs A 5 Point Guide
May 31, 2025
