Combating The Killer Seaweed: Protecting Australia's Marine Biodiversity

Table of Contents
Identifying the Enemy: Types of Invasive Seaweed in Australia
Several invasive seaweed species are wreaking havoc on Australia's coastal waters. These harmful algae blooms outcompete native species, disrupting delicate ecosystems and causing significant ecological damage. Understanding these "killer seaweed" species is the first step in combating their spread.
-
Caulerpa taxifolia (Killer Algae): This species, notorious for its rapid growth and resilience, has caused widespread damage along the Australian coastline. Its dense mats smother native seagrass beds and coral reefs, destroying habitats and reducing biodiversity. Images of its dense, bright green growth are easily identifiable online.
-
Undaria pinnatifida (Wakame): While used as a food source in some cultures, this invasive seaweed is highly competitive, quickly outgrowing and displacing native kelp forests and other valuable marine plants. Its spread is particularly concerning in cooler, temperate waters.
-
Other Significant Invasive Seaweed Species: Other invasive seaweed species, such as Asparagopsis taxiformis and various species of Sargassum, are also causing concern in different regions of Australia, each with unique ecological impacts. The geographic distribution of these harmful algae blooms varies widely, requiring region-specific management strategies.
[Insert high-quality images of Caulerpa taxifolia and Undaria pinnatifida here]
Keywords: Invasive seaweed species, Australia, Caulerpa taxifolia, Undaria pinnatifida, harmful algae, killer algae, seaweed infestation
The Devastating Impact of Invasive Seaweed on Marine Ecosystems
The ecological consequences of killer seaweed infestations are far-reaching and devastating. These invasive species disrupt the delicate balance of marine ecosystems, leading to significant biodiversity loss and habitat destruction.
-
Displacement of Native Species and Biodiversity Loss: Killer seaweed aggressively outcompetes native species for resources like sunlight and nutrients, leading to a decline in native flora and fauna populations. This results in a significant loss of biodiversity, impacting the overall health and resilience of the ecosystem.
-
Habitat Destruction and Changes to Ecosystem Structure: The dense mats formed by invasive seaweed can smother and destroy vital habitats like seagrass beds and coral reefs, altering the physical structure of the ecosystem. This habitat loss has cascading effects on the entire food web.
-
Impacts on Fisheries and Aquaculture: The proliferation of killer seaweed can negatively affect fisheries and aquaculture industries by reducing the abundance and quality of commercially important species. It can also impact water quality affecting shellfish harvesting.
-
Effects on Water Quality and Oxygen Levels: Large blooms of seaweed can deplete oxygen levels in the water, creating "dead zones" where marine life cannot survive. They can also release toxins, further degrading water quality.
Studies have shown significant declines in fish populations and shellfish yields in areas heavily infested with killer seaweed. The economic consequences are substantial, impacting livelihoods and local economies that depend on healthy marine ecosystems.
Keywords: Biodiversity loss, ecosystem disruption, marine habitat, water quality, fisheries, aquaculture, harmful algae blooms
Current Mitigation and Control Strategies for Killer Seaweed
Controlling the spread of invasive seaweed requires a multi-pronged approach, employing a variety of methods, each with its own advantages and limitations.
-
Manual Removal: This method involves physically removing the seaweed from affected areas. While effective on a small scale, manual removal is labor-intensive, costly, and impractical for large-scale infestations.
-
Chemical Control: Chemical herbicides can be used to kill invasive seaweed, but their use is strictly regulated due to potential environmental impacts on non-target species and broader ecosystem health. Further research into selective herbicides with minimal environmental impact is crucial.
-
Biological Control: This promising approach involves introducing natural predators or competitors of the invasive seaweed to control its population. Research is ongoing to identify suitable biological control agents with minimal risk of unintended ecological consequences.
-
Integrated Pest Management (IPM): IPM strategies combine different methods to provide the most effective and environmentally responsible approach to managing killer seaweed. This often involves a combination of manual removal, targeted chemical treatments, and ongoing monitoring.
Ongoing research is crucial in developing new and improved control techniques, including exploring the use of innovative technologies and genetically modified organisms.
Keywords: Seaweed control, invasive species management, biological control, chemical control, integrated pest management, seaweed removal
Protecting Our Shores: Community Involvement and Government Initiatives
Combating killer seaweed requires a collaborative effort involving communities, researchers, and government agencies.
-
Community Involvement: Citizen scientists play a vital role in monitoring and reporting seaweed infestations. Early detection is crucial for effective management. Local groups and community-based monitoring programs are crucial to this process.
-
Government Initiatives: The Australian government, along with state and local authorities, has implemented various policies, regulations, and funding programs aimed at controlling invasive seaweed and protecting marine biodiversity. These initiatives often involve research funding, management plans, and public awareness campaigns.
-
Public Awareness Campaigns: Education and awareness are critical. Public awareness campaigns aim to inform the public about the impacts of invasive seaweed and encourage responsible behavior, such as cleaning boat hulls to prevent the spread of invasive species.
[Insert links to relevant government websites and resources here]
Keywords: Community involvement, government initiatives, public awareness, environmental regulations, funding, marine conservation, invasive seaweed prevention
Conclusion
Killer seaweed poses a significant threat to Australia's unique marine biodiversity. The ecological and economic consequences of these harmful algae blooms are substantial, demanding urgent and sustained action. The strategies discussed – manual removal, chemical control, biological control, and integrated pest management – offer avenues for mitigating the impacts of killer seaweed. However, success depends on a collaborative effort involving communities, researchers, and government agencies.
To protect Australia’s precious marine ecosystems, we must all play a part. Learn more about invasive seaweed species, participate in monitoring efforts, support initiatives aimed at combating this ecological threat, and practice responsible boating and fishing to minimize the spread of invasive species. Contact your local authorities or environmental organizations to discover how you can contribute to the fight against killer seaweed and help protect Australia's marine biodiversity.
Keywords: Killer seaweed prevention, invasive seaweed removal, marine conservation Australia, protect marine biodiversity, harmful algae control

Featured Posts
-
 Bts Reunion New Teaser Fuels Comeback Anticipation
May 30, 2025
Bts Reunion New Teaser Fuels Comeback Anticipation
May 30, 2025 -
 Mentzen I Wybory Prezydenckie 2025 Niezwykla Kampania
May 30, 2025
Mentzen I Wybory Prezydenckie 2025 Niezwykla Kampania
May 30, 2025 -
 Test Drive Carjacking Prevention Protecting Yourself From Theft
May 30, 2025
Test Drive Carjacking Prevention Protecting Yourself From Theft
May 30, 2025 -
 Charleston Open Pegula Upsets Collins In Thrilling Match
May 30, 2025
Charleston Open Pegula Upsets Collins In Thrilling Match
May 30, 2025 -
 Manila Bay A Vibrant Ecosystem How Long Will It Last
May 30, 2025
Manila Bay A Vibrant Ecosystem How Long Will It Last
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
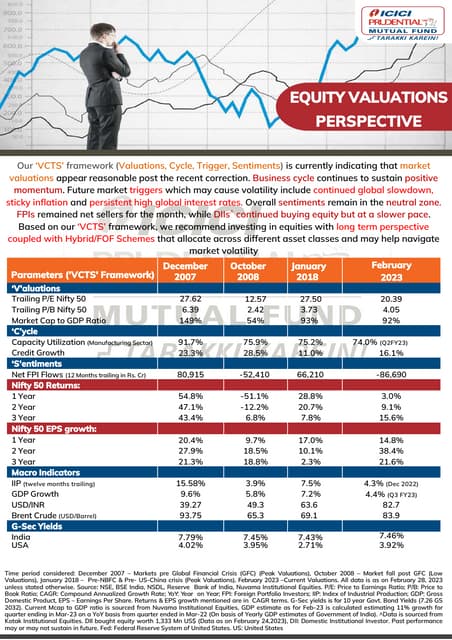 Understanding Elevated Stock Market Valuations A Bof A Perspective
May 31, 2025
Understanding Elevated Stock Market Valuations A Bof A Perspective
May 31, 2025 -
 High Stock Valuations And Investor Confidence A Bof A Analysis
May 31, 2025
High Stock Valuations And Investor Confidence A Bof A Analysis
May 31, 2025 -
 Addressing Investor Concerns Bof A On Elevated Stock Market Valuations
May 31, 2025
Addressing Investor Concerns Bof A On Elevated Stock Market Valuations
May 31, 2025 -
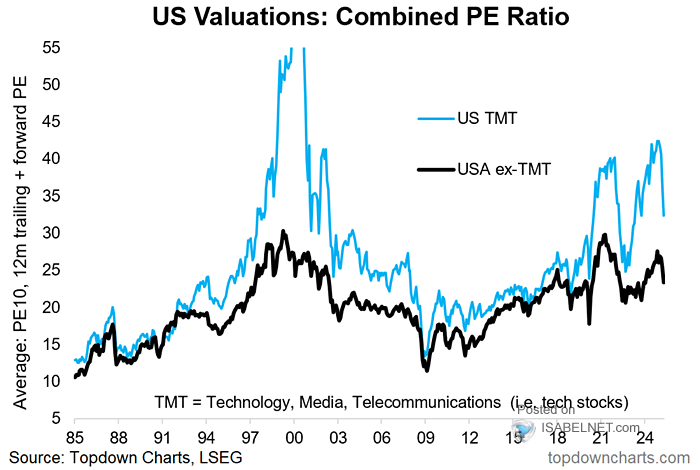 Stock Market Valuations Bof As Argument For Why Investors Shouldnt Worry
May 31, 2025
Stock Market Valuations Bof As Argument For Why Investors Shouldnt Worry
May 31, 2025 -
 Successfully Applying For Private Credit Jobs A 5 Point Guide
May 31, 2025
Successfully Applying For Private Credit Jobs A 5 Point Guide
May 31, 2025
