China's Nuclear Power Expansion: 10 New Reactors Approved
Table of Contents
The 10 New Reactor Approvals: Location, Type, and Capacity
The approval of these ten new reactors represents a substantial leap forward in China's nuclear energy capacity. The geographical distribution of these new plants reflects a strategic approach to ensuring widespread access to clean energy across the country. The reactor types selected also indicate a focus on proven technologies and potential for future innovation. Key features of the approved reactors include:
- Shandong Province: 2 x HPR1000 reactors, 1200 MW each. These reactors utilize advanced pressurized water reactor (PWR) technology, known for its safety and efficiency. This location is strategically chosen due to its proximity to industrial centers.
- Guangdong Province: 2 x CAP1400 reactors, 1400 MW each. CAP1400 reactors represent a domestically developed, third-generation PWR technology, showcasing China's advancements in nuclear technology. This province has a history of successful nuclear power plant operation.
- Fujian Province: 2 x Hualong One reactors, 1100 MW each. Hualong One is another domestically developed reactor design, furthering China's goal of technological self-reliance in the nuclear sector. Coastal locations like Fujian are well-suited for nuclear power plants.
- Liaoning Province: 2 x ACP1000 reactors, 1000 MW each. This represents another type of advanced pressurized water reactor technology, contributing to the diversification of reactor types within the China nuclear power plants location strategy.
- Jiangsu Province: 2 x CPR1000 reactors, 1000 MW each. Further demonstrating commitment to domestic technology development, this province benefits from established infrastructure for nuclear power operations.
This diverse portfolio of reactor types and locations highlights China's commitment to enhancing its nuclear reactor capacity and its strategy for geographic distribution across the nation. The strategic placement of these new plants, combined with diverse reactor technologies, contributes significantly to China's energy security and strengthens its position in the global nuclear power market.
Driving Forces Behind China's Nuclear Power Push
China's aggressive pursuit of nuclear power is driven by several key factors. Foremost among these is energy security and the need to reduce reliance on fossil fuels. China's rapidly expanding economy demands ever-increasing energy production, and nuclear power offers a stable, reliable, and relatively low-carbon alternative to coal and oil.
- Energy Security: Reducing reliance on volatile global fossil fuel markets is crucial for economic stability.
- Meeting Growing Energy Demands: Nuclear power provides a substantial and consistent source of electricity to power China's industrial growth and burgeoning population.
- Government Policy and Financial Incentives: Significant government investment and supportive policies have fueled the rapid expansion of the nuclear power sector.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Reducing carbon emissions is a crucial element of China's broader environmental goals. Nuclear power significantly contributes to this effort by providing a low-carbon alternative to fossil fuel-based electricity generation.
Economic Implications of the Expansion
The expansion of China's nuclear power sector has far-reaching economic implications. The construction and operation of these new plants will create numerous jobs across a range of industries, from engineering and construction to manufacturing and maintenance. Furthermore, the development and deployment of domestically designed reactors foster technological innovation and create export opportunities for China.
- Job Creation: Thousands of jobs will be created in the construction, operation, and maintenance of these new plants, stimulating economic activity across multiple sectors.
- Technological Advancements: Investment in nuclear technology leads to innovations that can be applied across other industrial sectors.
- Export Opportunities: China's development of advanced reactor technologies creates potential for exporting these technologies to other countries.
- Long-Term Economic Growth: A reliable and affordable energy supply is essential for sustained economic growth, and nuclear power plays a crucial role in ensuring this.
Environmental Considerations and Safety Concerns
While nuclear power offers a low-carbon alternative to fossil fuels, it also presents environmental challenges, notably nuclear waste disposal and potential safety risks. Addressing these concerns is crucial for maintaining public trust and ensuring the responsible development of nuclear energy.
- Nuclear Waste Disposal: China is actively developing solutions for safe and long-term storage of nuclear waste.
- Nuclear Safety: Stringent safety regulations and advanced safety technologies are being implemented to minimize the risks associated with nuclear power plants.
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Compared to coal-fired power plants, nuclear power plants generate significantly fewer greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to climate change mitigation.
- Public Perception: Open communication and transparency are crucial for addressing public concerns and fostering trust in the safety and efficacy of nuclear power.
Global Implications of China's Nuclear Power Growth
China's rapid expansion of its nuclear power sector has significant global implications. It will increase the demand for nuclear technology, equipment, and services, impacting the global nuclear energy market. It also holds the potential for increased international collaboration and technology transfer.
- Global Energy Market: China's increased demand for nuclear technology and fuel will affect global prices and supply chains.
- International Cooperation: China's experience in nuclear power development can be shared with other countries, promoting international cooperation in clean energy.
- Nuclear Technology Transfer: The transfer of technology and expertise from China to other countries could accelerate global adoption of nuclear power.
- Climate Change Mitigation: China's efforts to expand its nuclear energy capacity contribute significantly to global efforts to mitigate climate change.
Conclusion: The Future of China's Nuclear Power Expansion
The approval of ten new nuclear reactors underscores the scale and ambition of China's nuclear power expansion. This expansion is driven by the need for energy security, economic growth, and climate change mitigation. While environmental considerations and safety concerns must be carefully addressed, the long-term benefits of this endeavor are significant. China's Nuclear Power Expansion is poised to reshape the global energy landscape, influencing international collaboration and technological innovation within the nuclear industry. Stay informed about the ongoing developments in China's nuclear power expansion by following our updates and exploring further resources on this rapidly evolving field.

Featured Posts
-
 Anchor Brewing Companys Closure A Legacy Concludes After 127 Years
Apr 29, 2025
Anchor Brewing Companys Closure A Legacy Concludes After 127 Years
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Us Attorney General Demands Minnesota Enforce Transgender Athlete Ban
Apr 29, 2025
Us Attorney General Demands Minnesota Enforce Transgender Athlete Ban
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Nba Fines Anthony Edwards 50 000 For Vulgar Comment To Fan
Apr 29, 2025
Nba Fines Anthony Edwards 50 000 For Vulgar Comment To Fan
Apr 29, 2025 -
 50 000 Fine For Anthony Edwards Nba Disciplinary Action Explained
Apr 29, 2025
50 000 Fine For Anthony Edwards Nba Disciplinary Action Explained
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Open Ai And The Ftc Understanding The Ongoing Investigation Into Chat Gpt
Apr 29, 2025
Open Ai And The Ftc Understanding The Ongoing Investigation Into Chat Gpt
Apr 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
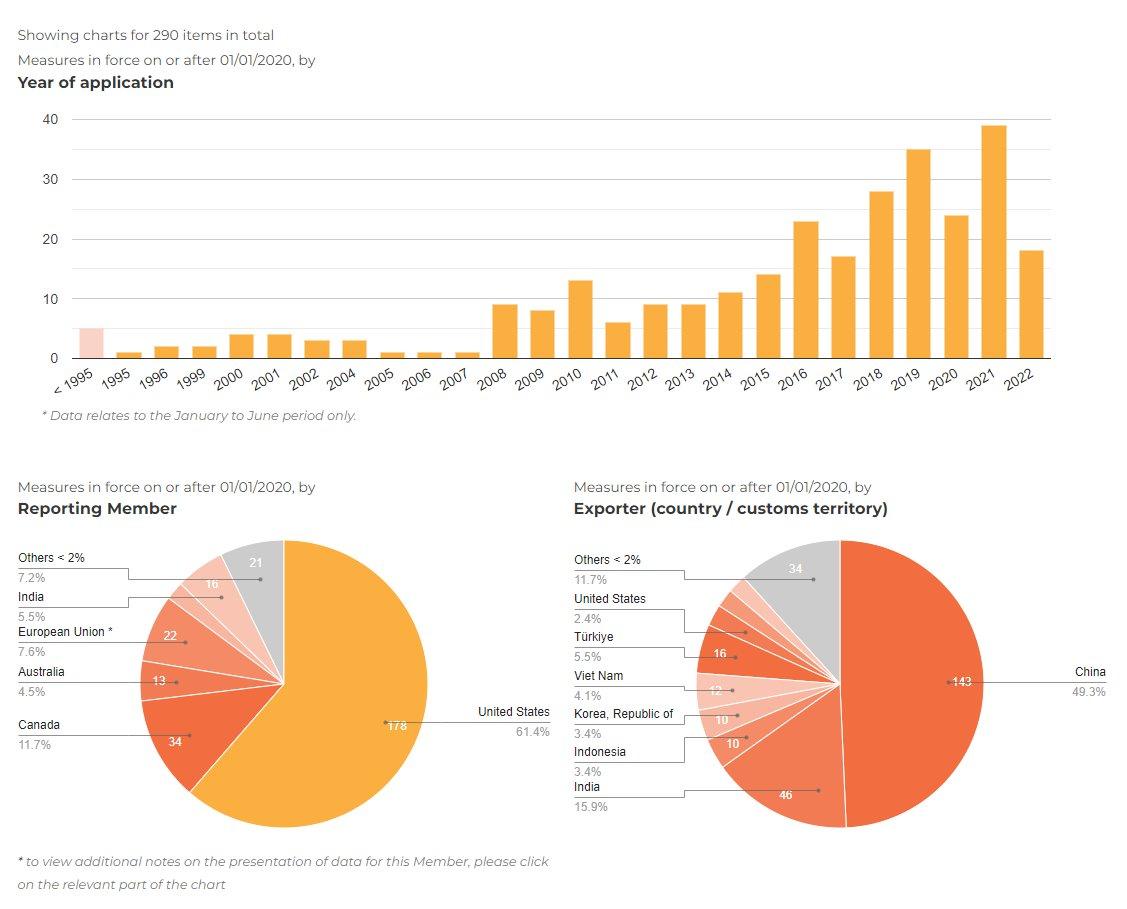 How U S Companies Are Responding To Tariff Uncertainty Through Cost Reduction
Apr 29, 2025
How U S Companies Are Responding To Tariff Uncertainty Through Cost Reduction
Apr 29, 2025 -
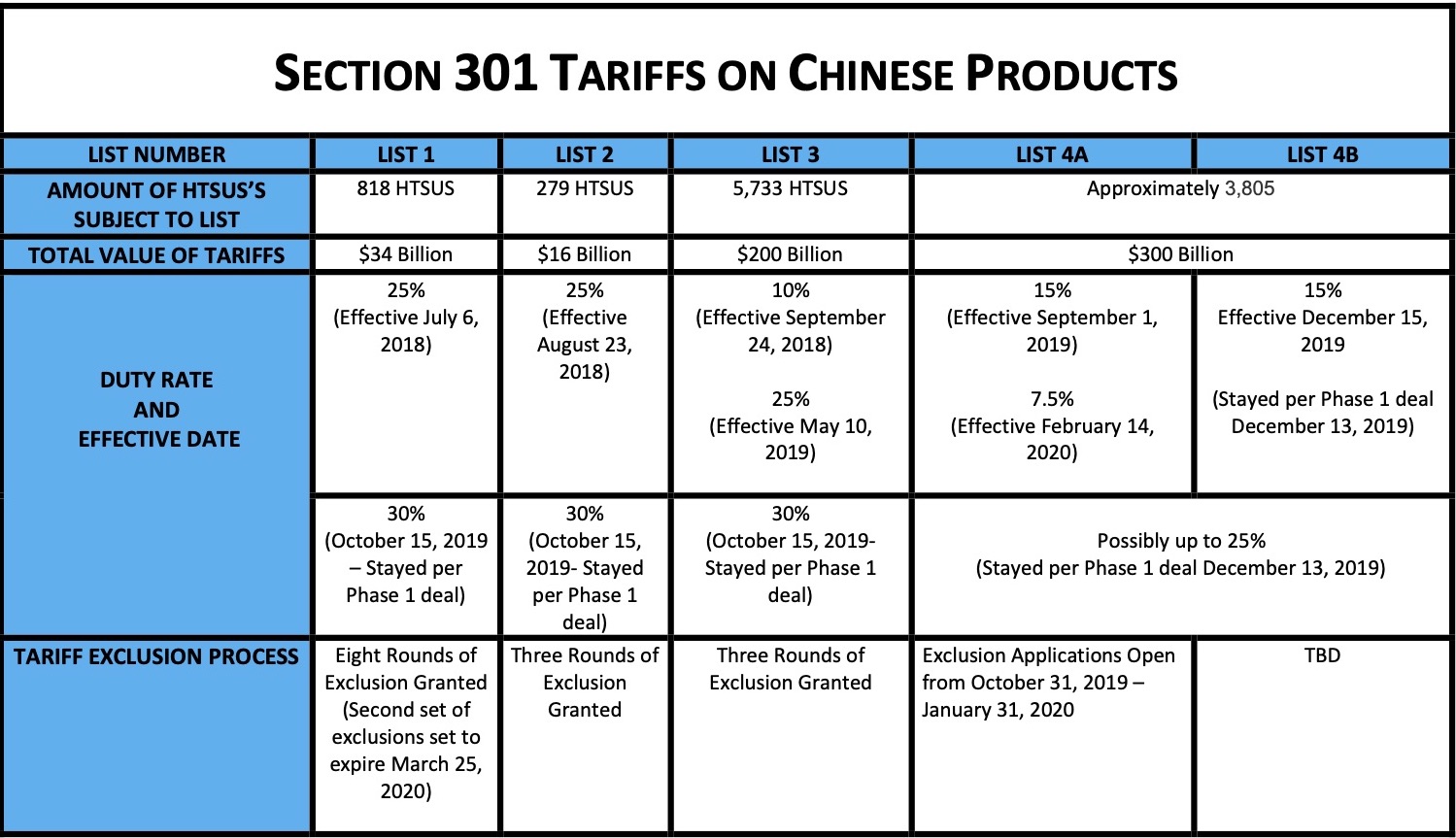 U S Businesses Implement Cost Cutting Strategies In Response To Tariffs
Apr 29, 2025
U S Businesses Implement Cost Cutting Strategies In Response To Tariffs
Apr 29, 2025 -
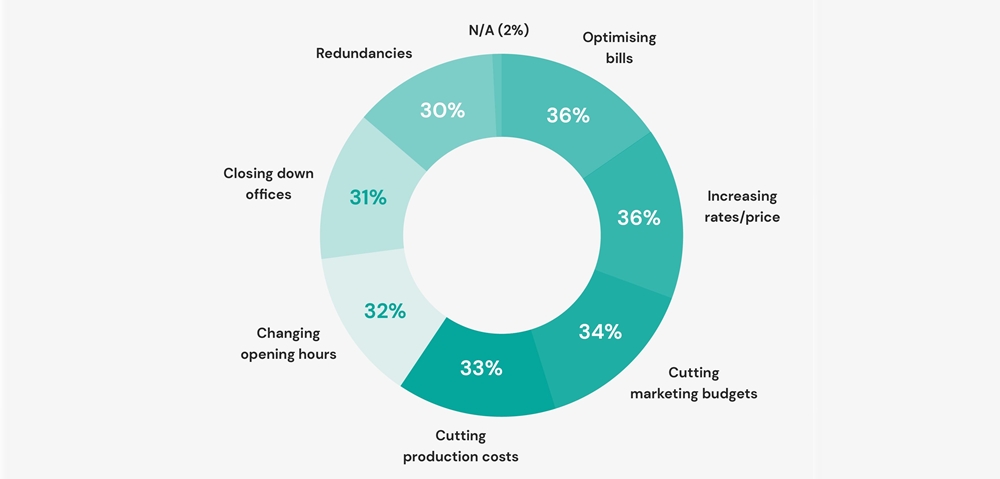 Cost Cutting Measures Rise As U S Companies Face Tariff Uncertainty
Apr 29, 2025
Cost Cutting Measures Rise As U S Companies Face Tariff Uncertainty
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Tariff Uncertainty Drives U S Businesses To Cut Costs
Apr 29, 2025
Tariff Uncertainty Drives U S Businesses To Cut Costs
Apr 29, 2025 -
 U S Companies Slash Costs Amid Tariff Uncertainty
Apr 29, 2025
U S Companies Slash Costs Amid Tariff Uncertainty
Apr 29, 2025
