Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF: Factors Affecting Net Asset Value (NAV)
Table of Contents
Market Performance of the Dow Jones Industrial Average
The Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF's NAV is intrinsically linked to the performance of its underlying index: the Dow Jones Industrial Average. This means the ETF's value directly reflects the collective performance of the 30 large, publicly-owned companies that constitute the index. Individual company stock price movements significantly influence the overall index value and, consequently, the ETF's NAV.
Factors impacting the Dow Jones Industrial Average, and thus the ETF's NAV, include:
- Economic Indicators: Strong economic data, like positive GDP growth or low unemployment rates, typically boosts investor confidence and pushes the Dow (and the ETF's NAV) higher. Conversely, negative economic news can lead to declines.
- Geopolitical Events: Global events, such as political instability, international conflicts, or trade wars, can create market uncertainty, influencing the Dow and impacting the ETF's NAV.
- Industry Trends: Positive developments within specific sectors represented in the Dow can drive up the index and the ETF's NAV, while negative trends can have the opposite effect.
Bullet Points:
- Positive market trends: Generally lead to an increase in the ETF's NAV, reflecting higher stock prices within the Dow Jones Industrial Average.
- Negative market trends: Typically result in a decrease in the ETF's NAV, mirroring declines in the underlying index's constituent stocks.
- Examples: The COVID-19 pandemic initially caused a sharp drop in the Dow and the ETF's NAV, while subsequent economic recovery led to a rebound. Similarly, unexpected geopolitical events can trigger significant, short-term fluctuations. A strong correlation exists between Dow performance and the Amundi ETF's NAV.
Currency Fluctuations and their Impact on NAV
For internationally invested ETFs, currency fluctuations can significantly impact the NAV. The Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF, while focused on US companies, may still be subject to currency effects depending on its base currency and the currencies in which its underlying assets are held.
- Currency Appreciation/Depreciation: If the ETF's base currency appreciates against the US dollar, the NAV (calculated in the base currency) may increase, even if the Dow remains unchanged. Conversely, depreciation of the base currency can reduce the NAV.
- Hedging Strategies: The ETF provider may employ currency hedging strategies to mitigate currency risk. This involves using financial instruments to offset potential losses from exchange rate movements. However, hedging isn't always perfect and may incur costs that slightly affect the NAV.
Bullet Points:
- Impact on NAV calculation: Currency movements are factored into the daily NAV calculation, influencing the final value presented to investors.
- Hedging strategies: While aiming to minimize currency risk, these strategies aren't foolproof and can introduce complexities in NAV calculation.
- Examples: A strengthening Euro against the US dollar would potentially boost the NAV of a Euro-denominated Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF, assuming all other factors remain constant.
ETF Expenses and their Effect on NAV
The Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF, like any other ETF, incurs operational costs. These expenses, including management fees, administrative expenses, and other operational costs, are deducted from the fund's assets and therefore affect the NAV.
Bullet Points:
- Detailed breakdown of expenses: The ETF's prospectus clearly outlines all expenses, providing investors with transparency regarding cost structure.
- Expense ratios: The expense ratio, typically expressed as a percentage of the ETF's assets under management, directly impacts the overall return to investors by reducing the NAV growth.
- Comparison with similar ETFs: Investors should compare the expense ratios of the Amundi ETF with similar Dow Jones Industrial Average ETFs to assess their competitiveness.
Dividend Distributions and their Influence on NAV
Dividend payments from the underlying companies within the Dow Jones Industrial Average affect the ETF's NAV.
Bullet Points:
- Impact on NAV on the ex-dividend date: On the ex-dividend date (the date on or after which a buyer of the stock does not receive the next dividend payment), the NAV is typically reduced by the amount of the dividend per share, reflecting the distribution to shareholders.
- Timing and calculation: Dividends are usually paid out quarterly or annually, and their amount is calculated based on the underlying companies' dividend policies.
- Impact of dividend reinvestment: If the dividend is reinvested into purchasing additional ETF shares, it can contribute to overall NAV growth over time.
Supply and Demand Dynamics in the ETF Market
The market price of the Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF shares, traded on the secondary market, can temporarily deviate from its NAV due to supply and demand dynamics.
Bullet Points:
- High trading volume: High trading volume can cause short-term price fluctuations, creating a temporary premium or discount to the NAV.
- Difference between market price and NAV: While the NAV represents the theoretical value of the ETF's assets, the market price reflects the actual trading price on the exchange. These can differ due to supply and demand imbalances.
- Factors affecting discrepancies: Market sentiment, investor behavior, and order flow can all contribute to short-term deviations of the market price from the NAV.
Conclusion: Investing Wisely with the Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF
Understanding the factors influencing the Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF's NAV is crucial for successful investment. This article highlighted the significant roles played by the Dow Jones Industrial Average's performance, currency fluctuations, ETF expenses, dividend distributions, and supply and demand dynamics. Remember that while the NAV provides a crucial indicator of the ETF's underlying value, the market price can fluctuate independently in the short term. Thorough research and a careful consideration of your personal risk tolerance are paramount before investing in any ETF, including the Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF. Learn more about the Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF and its NAV performance by visiting [link to relevant resource]. Consider adding the Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF to your diversified investment portfolio for exposure to the Dow Jones Industrial Average.

Featured Posts
-
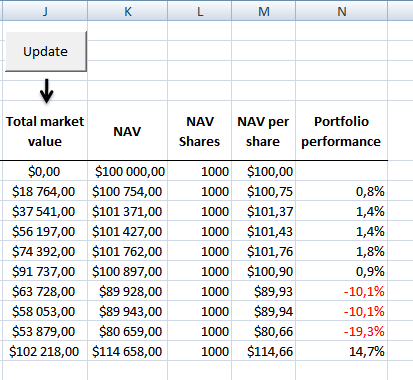 How To Track The Net Asset Value Nav Of The Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average Ucits Etf
May 24, 2025
How To Track The Net Asset Value Nav Of The Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average Ucits Etf
May 24, 2025 -
 M62 Westbound Resurfacing Project Causes Manchester To Warrington Closure
May 24, 2025
M62 Westbound Resurfacing Project Causes Manchester To Warrington Closure
May 24, 2025 -
 Dreyfus Affair Lawmakers Propose Posthumous Honor To Right A Historical Wrong
May 24, 2025
Dreyfus Affair Lawmakers Propose Posthumous Honor To Right A Historical Wrong
May 24, 2025 -
 Investing In The Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average Ucits Etf Nav Analysis
May 24, 2025
Investing In The Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average Ucits Etf Nav Analysis
May 24, 2025 -
 Escape To The Country Budgeting For Your Rural Relocation
May 24, 2025
Escape To The Country Budgeting For Your Rural Relocation
May 24, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Heinekens Strong Revenue Growth Outlook Unchanged Despite Tariff Challenges
May 24, 2025
Heinekens Strong Revenue Growth Outlook Unchanged Despite Tariff Challenges
May 24, 2025 -
 Heineken Revenue Surpasses Projections Outlook Remains Strong Despite Trade Concerns
May 24, 2025
Heineken Revenue Surpasses Projections Outlook Remains Strong Despite Trade Concerns
May 24, 2025 -
 Significant Losses In Amsterdam Stock Market Falls 7 On Trade War Fears
May 24, 2025
Significant Losses In Amsterdam Stock Market Falls 7 On Trade War Fears
May 24, 2025 -
 Analisi Borsa Europa Prudente Italgas In Luce Banche In Difficolta
May 24, 2025
Analisi Borsa Europa Prudente Italgas In Luce Banche In Difficolta
May 24, 2025 -
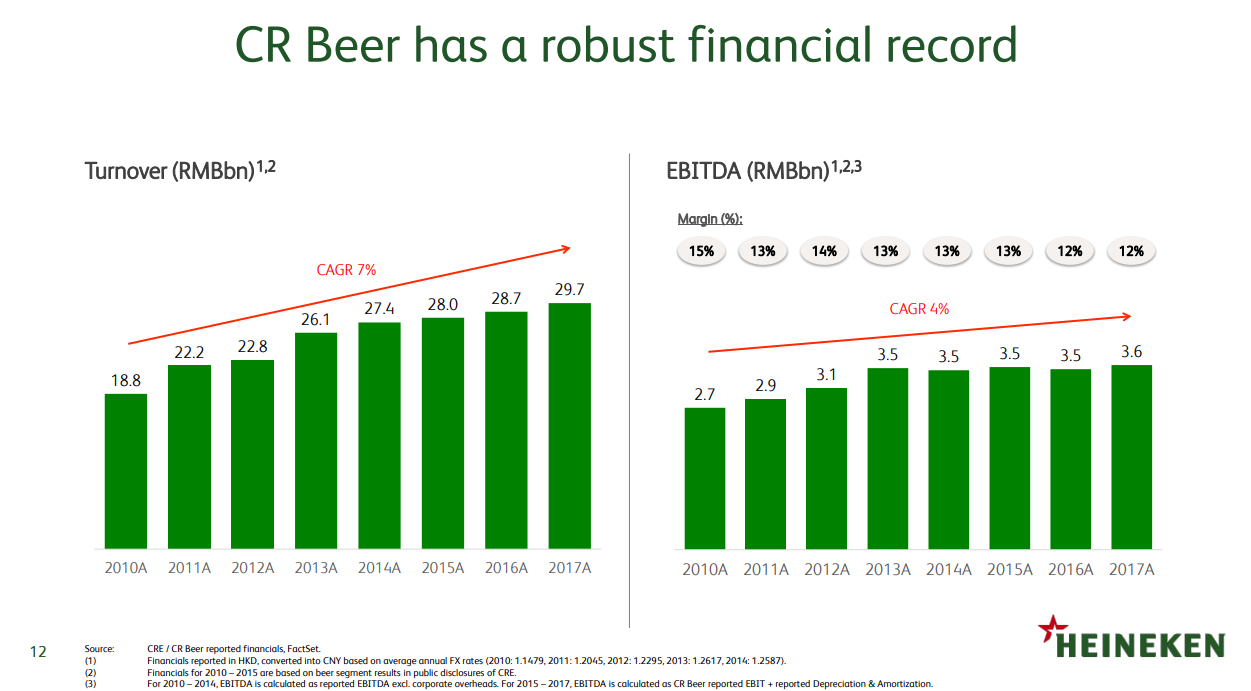 Heineken Exceeds Revenue Forecasts Maintains Positive Outlook Amid Tariffs
May 24, 2025
Heineken Exceeds Revenue Forecasts Maintains Positive Outlook Amid Tariffs
May 24, 2025
