Tracking The Spread: A New COVID-19 Variant And Its Effect On Infection Rates
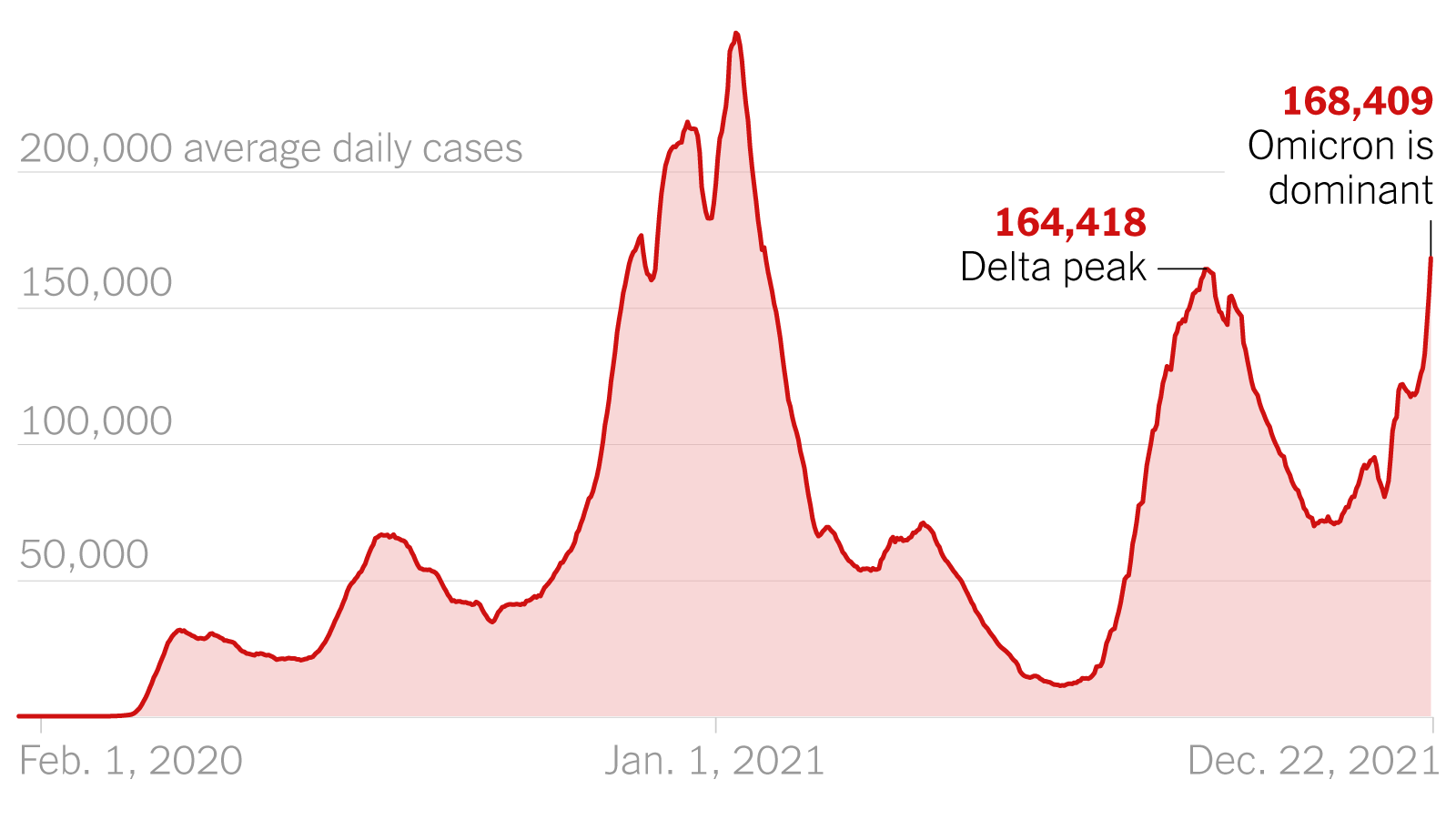
Table of Contents
Understanding the New COVID-19 Variant
Origin and Characteristics
This hypothetical new COVID-19 variant, tentatively named "Variant X," is believed to have originated in [Hypothetical Location]. Its genetic makeup reveals several key mutations, particularly in the [Hypothetical Spike Protein Location] region of the spike protein. These mutations are of significant concern due to their potential impact on several crucial factors:
- Increased Transmissibility: Preliminary data suggests Variant X exhibits higher transmissibility than previous variants like Delta and Omicron, potentially due to the mutations affecting its ability to bind to human cells. This could lead to a faster spread of the new COVID strain.
- Immune Evasion Potential: The mutations observed in Variant X raise concerns about its ability to evade the immune response generated by previous infections or vaccination. Further research is needed to determine the extent of its immune evasion capabilities.
- Severity of Symptoms: While early data suggests similar symptom profiles to previous variants, studies are ongoing to determine if Variant X causes more severe illness or different clinical presentations.
Spread and Transmission
The spread of Variant X is currently being monitored globally. Early reports indicate a rapid spread in [Hypothetical Geographic Regions]. The R0 value (basic reproduction number), a key indicator of transmissibility, is estimated to be [Hypothetical R0 Value], significantly higher than previous variants. This highlights the potential for rapid community spread. Specific demographic groups affected might be [Hypothetical Demographics], but further data is needed to confirm this. This rapid spread necessitates prompt and effective public health interventions.
Impact on Infection Rates
Increase in Cases
The emergence of Variant X has already led to a noticeable increase in COVID-19 cases in several regions. [Insert hypothetical data or graphs showcasing infection rate trends]. The sharp rise in cases is largely attributed to the variant's increased transmissibility and potential immune evasion capabilities. Hospitalization rates are also showing [Hypothetical Increase or Decrease], providing crucial data on the severity of the disease.
Severity of Illness
While the overall severity of illness associated with Variant X remains under investigation, early data suggests [Hypothetical Severity]. Mortality rates appear to be [Hypothetical Mortality Rate Comparison to previous variants]. The duration of hospital stays for patients infected with Variant X appears to be [Hypothetical Duration]. Further analysis is crucial to fully understand the long-term effects and clinical outcomes associated with this new COVID-19 variant.
Public Health Response and Mitigation Strategies
Vaccine Effectiveness
The effectiveness of existing COVID-19 vaccines against Variant X is a primary concern. Preliminary studies suggest that current vaccines may offer [Hypothetical Level] protection against severe illness and hospitalization. However, a decline in vaccine efficacy compared to previous variants is possible, potentially necessitating booster shots tailored to Variant X. Ongoing research is crucial for developing updated vaccines or booster formulations to maintain robust protection.
Public Health Measures
Several public health measures are essential to mitigate the spread of Variant X and limit the impact on infection rates. These include:
- Reinstatement of Mask Mandates: In areas experiencing high transmission rates, mask mandates may be necessary to slow down the spread.
- Enhanced Testing and Contact Tracing: Rapid and widespread testing, along with effective contact tracing, is critical for identifying and isolating infected individuals.
- Vaccination Campaigns: Continued efforts to increase vaccination coverage remain essential, particularly with booster shots to enhance protection against Variant X.
- Improved Ventilation: Improving ventilation in indoor spaces can significantly reduce the risk of transmission.
Conclusion
The emergence of a new COVID-19 variant, such as the hypothetical Variant X discussed here, underscores the continuous need for vigilance and preparedness. Understanding the variant's characteristics, its impact on infection rates, and the effectiveness of existing mitigation strategies is vital for an informed public health response. While vaccines remain crucial, continued monitoring, adaptation of public health measures, and ongoing research are crucial to managing the ongoing threat of new COVID-19 variants and controlling the spread of COVID-19. Stay updated on information regarding new COVID-19 variants and their impact on infection rates. Protect yourself and your community by following public health guidelines and getting vaccinated. Remember, responsible actions are key to mitigating the spread of this and future COVID-19 variants.

Featured Posts
-
 Dren Bios Myeloid Cell Engager A Key Acquisition For Sanofi
May 31, 2025
Dren Bios Myeloid Cell Engager A Key Acquisition For Sanofi
May 31, 2025 -
 Drought Forecast Uncanny Parallels Between Spring 1968 And Spring 2024
May 31, 2025
Drought Forecast Uncanny Parallels Between Spring 1968 And Spring 2024
May 31, 2025 -
 Solve The Nyt Mini Crossword May 13 2025 Answers And Guide
May 31, 2025
Solve The Nyt Mini Crossword May 13 2025 Answers And Guide
May 31, 2025 -
 The Reality Of Ai Learning Navigating The Challenges For Responsible Use
May 31, 2025
The Reality Of Ai Learning Navigating The Challenges For Responsible Use
May 31, 2025 -
 Nyt Mini Crossword Clues And Answers For Tuesday April 8th
May 31, 2025
Nyt Mini Crossword Clues And Answers For Tuesday April 8th
May 31, 2025
