Toxic Chemical Contamination: The Ohio Derailment's Lingering Impact On Buildings
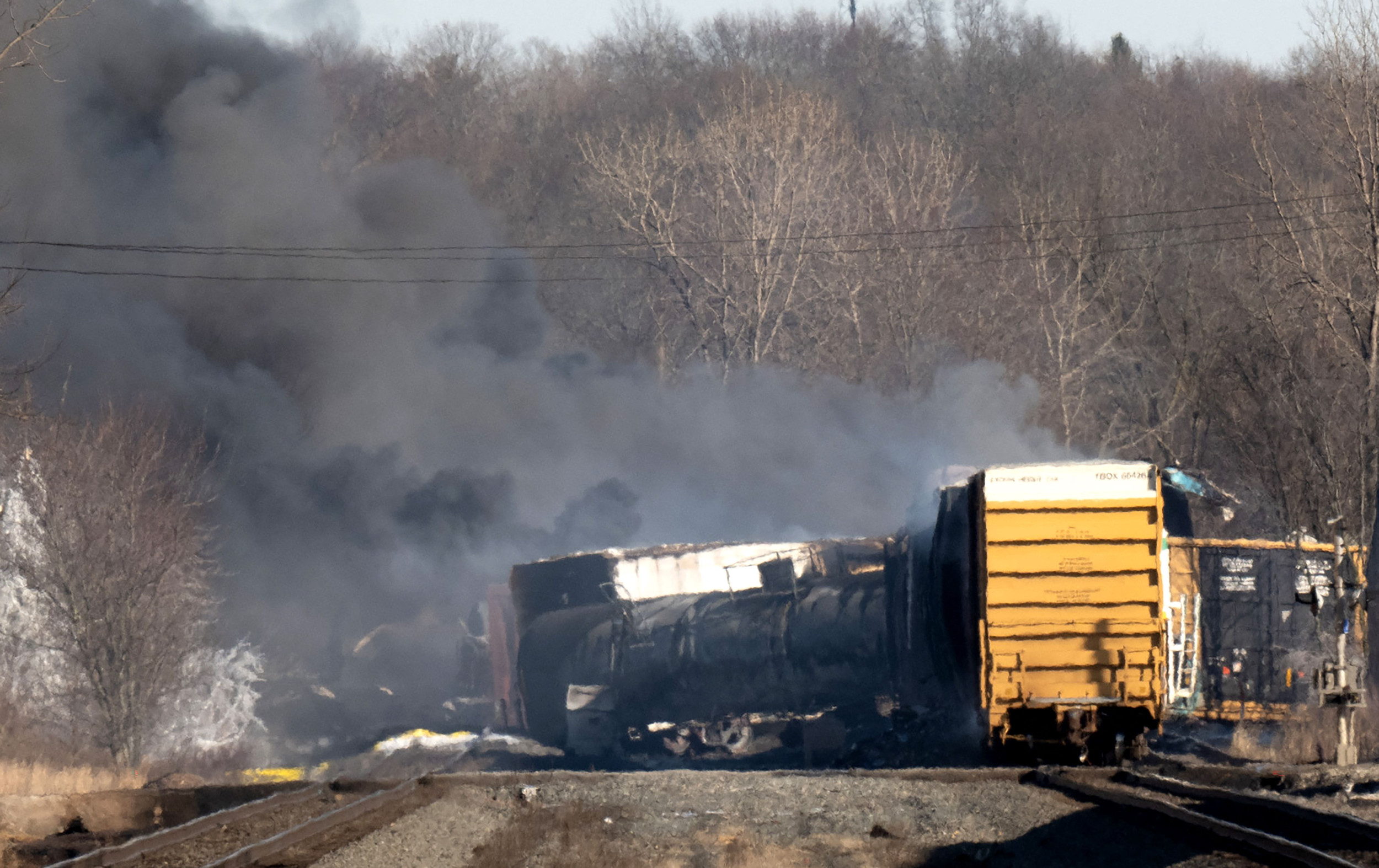

Table of Contents
Assessing the Immediate Damage from Toxic Chemical Contamination
The immediate aftermath of the derailment revealed significant damage caused by the released chemicals. Assessing this damage requires a multi-faceted approach, examining the structural integrity of buildings, indoor air quality, and the extent of contamination within building materials.
Structural Damage
Exposure to vinyl chloride and other toxic chemicals can severely compromise building materials. The potential consequences are far-reaching and can lead to significant structural instability.
- Corrosion: Metal components, like support beams and roofing, are susceptible to accelerated corrosion.
- Weakening: Certain building materials, such as wood, may experience significant weakening and degradation due to chemical exposure.
- Discoloration: Visible discoloration of building materials can be an indicator of chemical penetration and damage.
- Long-Term Instability: The initial damage might not be immediately apparent, leading to potentially catastrophic structural failures down the line. Specialized inspections are crucial to identify these vulnerabilities.
Indoor Air Quality Degradation
The release of toxic chemicals has severely compromised indoor air quality in affected buildings. This poses a significant health hazard for occupants.
- Health Risks: Vinyl chloride is a known carcinogen, while butyl acrylate can cause respiratory irritation and other health problems. Long-term exposure to these chemicals can lead to a variety of serious health issues.
- Air Quality Testing: Comprehensive air quality testing is essential to determine the levels of toxic chemicals present within buildings.
- Remediation: Effective remediation strategies are necessary to mitigate the health risks associated with poor indoor air quality. This may involve air filtration systems, chemical neutralization, and complete air exchange.
- Long-Term Health Implications: The long-term health implications of exposure to these chemicals require ongoing monitoring and medical attention for affected residents.
Contamination of Building Materials
The pervasive nature of the released chemicals poses a significant challenge in remediation efforts. The chemicals may have permeated various building materials, requiring extensive decontamination or even demolition.
- Affected Materials: Drywall, insulation, flooring, and other porous materials can absorb and retain these toxic chemicals.
- Decontamination Challenges: Removing or neutralizing these chemicals from building materials can be incredibly complex and expensive.
- Demolition and Rebuilding: In severely affected cases, complete demolition and rebuilding may be the only viable solution to ensure the safety and habitability of the building.
Long-Term Effects of Toxic Chemical Contamination on Buildings
The impact of the toxic chemical contamination extends far beyond the initial damage. Long-term effects can manifest in unexpected ways, compounding the challenges for property owners.
Hidden Damage and Delayed Effects
The full extent of the damage may not be immediately evident. Latent damage can emerge over time, presenting new challenges and risks.
- Delayed Structural Failures: Weakened building materials might fail unexpectedly, leading to structural instability and potential collapse.
- Ongoing VOC Release: Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) can continue to be released from contaminated materials, leading to persistent indoor air quality issues.
- Delayed Health Problems: Health problems related to chemical exposure might not manifest until months or years after the initial incident.
The Role of Environmental Factors
Weather conditions can significantly influence the long-term impact of the contamination.
- Chemical Leaching: Rain and snow can leach chemicals from contaminated materials, potentially spreading the contamination to surrounding areas.
- Chemical Degradation and Release: Sunlight can accelerate the degradation of some chemicals, leading to the release of harmful byproducts.
- Secondary Contamination: Runoff from contaminated areas can lead to secondary contamination of previously unaffected buildings and land.
Economic Implications for Property Owners
The financial burden on homeowners and businesses affected by the contamination is substantial.
- Testing Costs: Professional assessment and testing are crucial, but can be expensive.
- Remediation Costs: Cleaning and remediating contaminated buildings can involve significant expenses.
- Repair Costs: Structural repairs and replacements can add further financial strain.
- Property Value Loss: The stigma of contamination can drastically reduce property values.
- Insurance Claims: Navigating insurance claims for damage related to the derailment can be a complex and lengthy process.
Remediation and Mitigation Strategies for Toxic Chemical Contamination
Effective remediation and mitigation strategies are crucial to address the long-term effects of toxic chemical contamination.
Professional Assessment and Testing
Professional assessments are the first critical step in determining the extent of contamination.
- Air Quality Testing: Measuring the levels of toxic chemicals in the air.
- Material Sampling: Analyzing building materials to assess the level of chemical penetration.
- Expert Assessment: Experienced professionals are needed to accurately assess the damage and recommend appropriate remediation strategies.
- Regulatory Compliance: Remediation efforts must adhere to all relevant environmental regulations and safety standards.
Remediation Techniques
Various techniques are available to clean up contaminated buildings, depending on the severity of the contamination.
- Chemical Treatment: Using specialized chemicals to neutralize or remove toxic substances.
- Material Removal: Removing and disposing of contaminated materials, such as drywall, insulation, or flooring.
- Demolition and Reconstruction: In severe cases, complete demolition and rebuilding may be necessary.
- Specialized Cleaning Protocols: Following rigorous cleaning protocols to minimize the spread of contamination.
Ongoing Monitoring and Maintenance
Long-term monitoring is crucial to prevent future problems and ensure the long-term safety of the buildings.
- Regular Air Quality Checks: Periodic testing to ensure indoor air quality remains safe.
- Structural Inspections: Regular inspections to detect any signs of further deterioration or structural damage.
- Ongoing Maintenance: Proactive maintenance to prevent further deterioration and ensure building integrity.
Conclusion
The Ohio train derailment serves as a stark reminder of the devastating and long-lasting impact of toxic chemical contamination on buildings. The consequences, including structural damage, compromised indoor air quality, and substantial economic burdens, highlight the urgency of thorough assessments, appropriate remediation, and ongoing monitoring. If you suspect your building has been affected by toxic chemical contamination, seek professional help immediately. Contact your local environmental agency for guidance and information on toxic chemical contamination assessment, toxic chemical remediation, and building decontamination. Don't wait; protect your health and property.

Featured Posts
-
 Rcn And Vet Nursing Collaboration A Plastic Glove Project Case Study
May 31, 2025
Rcn And Vet Nursing Collaboration A Plastic Glove Project Case Study
May 31, 2025 -
 March 26th The Day Prince Died Fentanyl Toxicology Report
May 31, 2025
March 26th The Day Prince Died Fentanyl Toxicology Report
May 31, 2025 -
 La Valorisation De Sanofi Comparaison Avec Les Laboratoires Pharmaceutiques Europeens
May 31, 2025
La Valorisation De Sanofi Comparaison Avec Les Laboratoires Pharmaceutiques Europeens
May 31, 2025 -
 Duncan Bannatynes Support For Moroccan Childrens Charity
May 31, 2025
Duncan Bannatynes Support For Moroccan Childrens Charity
May 31, 2025 -
 Princes Death Fentanyl Levels Revealed On March 26th
May 31, 2025
Princes Death Fentanyl Levels Revealed On March 26th
May 31, 2025
