Investigating Whidbey Clams: Citizen Scientists Lead The Way
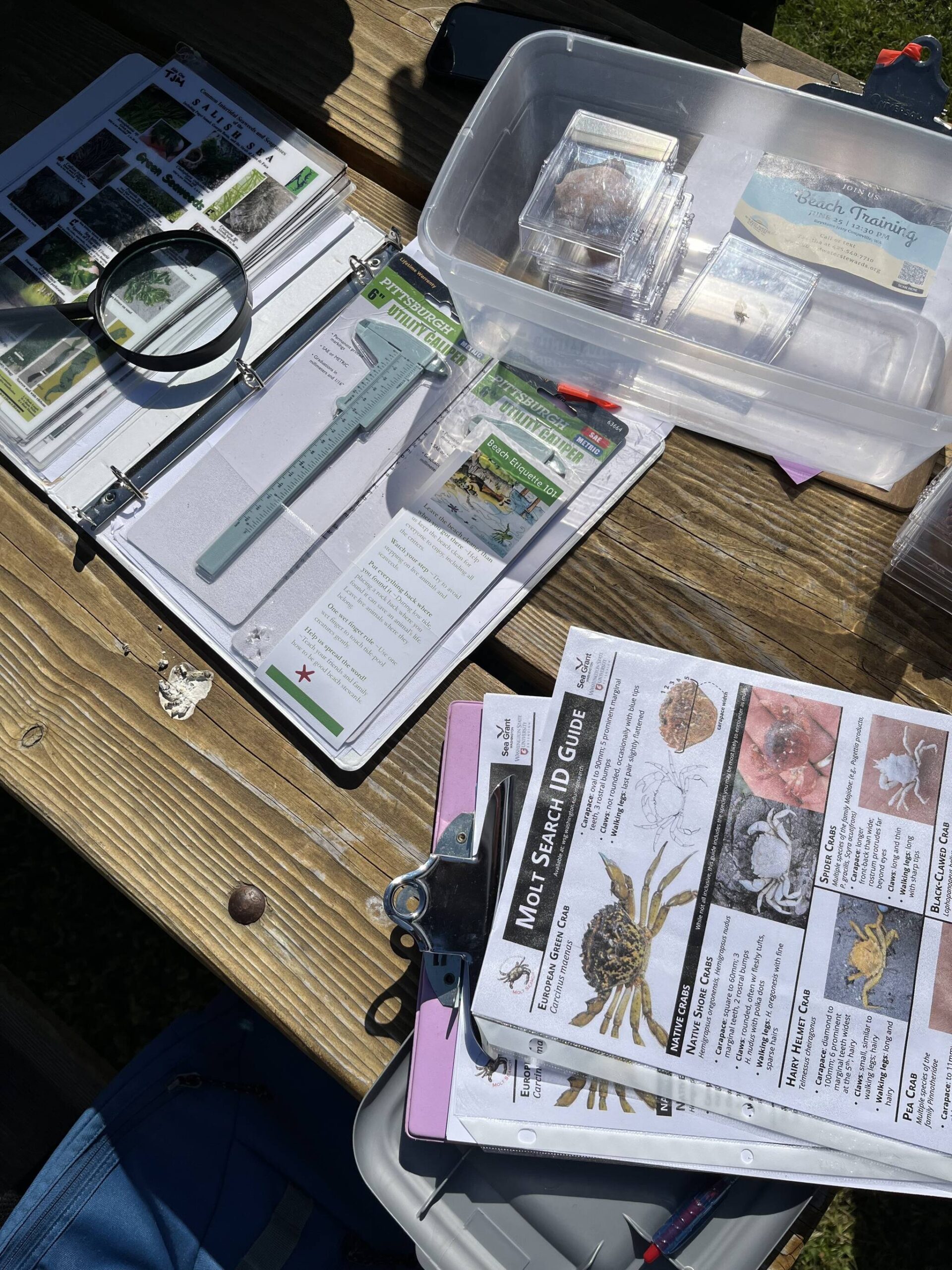

Table of Contents
The Importance of Whidbey Clam Monitoring
Whidbey clams, a key component of the Whidbey Island ecosystem, play a vital role in maintaining its health. Their importance stems from several key factors:
-
Ecological Role: As filter feeders, Whidbey clams play a crucial role in water purification. They filter out algae, plankton, and other particles, improving water clarity and quality. This contributes to the overall health of the intertidal zone and supports other marine life. They are also a significant part of the local food web, serving as a food source for various birds, fish, and other invertebrates. Understanding their numbers directly informs us about the health of the entire ecosystem.
-
Threats to Whidbey Clams: Unfortunately, Whidbey clams face numerous threats, impacting their populations and long-term survival. These threats include:
- Pollution: Runoff from agricultural lands and urban areas introduces pollutants into the water, harming clam health and reproduction.
- Climate Change: Rising sea levels, ocean acidification, and altered temperature patterns negatively impact clam habitats and survival rates.
- Habitat Loss: Coastal development and shoreline alteration destroy crucial clam habitats, reducing suitable areas for them to thrive.
- Predation: Various predators, including shorebirds and crabs, prey on Whidbey clams, impacting population numbers.
-
The Essential Role of Citizen Science: Professional monitoring of Whidbey clam populations is resource-intensive. Citizen science initiatives offer a powerful solution by expanding monitoring efforts significantly. This increased participation provides:
- Wider Geographic Coverage: Citizen scientists can monitor clams across a much broader area than professional researchers alone.
- More Frequent Data Collection: Volunteers can contribute data more frequently, allowing for better tracking of population fluctuations and responses to environmental changes.
- Enhanced Public Awareness: Citizen science initiatives raise public awareness about the importance of Whidbey clams and their conservation.
- Cost-Effective Data Gathering: Utilizing volunteers drastically reduces the financial burden of comprehensive monitoring programs.
Methods Used by Citizen Scientists in Whidbey Clam Research
Citizen scientists employ a variety of methods to investigate Whidbey clam populations. These methods are carefully designed to ensure data accuracy and consistency:
-
Specific Techniques: Volunteers participate in various activities including:
- Transect Surveys: Systematic walks along designated lines to count and measure clams within specific areas.
- Clam Counts and Size Measurements: Recording the number of clams found and their size to assess population density and growth rates.
- Habitat Assessments: Evaluating the quality and characteristics of clam habitats, identifying factors that may influence clam populations.
-
Training and Support: To ensure data quality and consistency, citizen scientists receive thorough training. This includes:
- Workshops: Hands-on training sessions covering identification, data collection techniques, and safety procedures.
- Online Resources: Access to online guides, manuals, and tutorials to support data collection and identification.
- Mentorship Programs: Experienced researchers and volunteers mentor new participants to provide guidance and support.
-
Data Collection Tools and Technologies: Modern technology enhances data collection and analysis efficiency:
- Mobile Apps: User-friendly apps simplify data entry and GPS location recording.
- GPS Devices: Accurate location data is crucial for mapping clam populations and habitat characteristics.
- Underwater Cameras: Cameras can be used to visualize clam beds and assess habitat conditions.
Impact and Results of Citizen Science on Whidbey Clam Conservation
The contributions of citizen scientists have already yielded significant results for Whidbey clam conservation:
-
Data Use and Analysis: Data gathered by citizen scientists has provided valuable insights into:
- Population Trends: Identifying fluctuations in clam populations over time, highlighting areas of concern.
- Identifying Areas of Concern: Pinpointing locations with low clam densities or degraded habitats.
- Informing Conservation Strategies: Data informs the development of targeted conservation and restoration efforts.
-
Success Stories: Citizen science has led to several successes, including:
- Improved Understanding of Clam Distribution: Mapping of clam populations has revealed previously unknown locations and patterns.
- Identification of Pollution Sources: Data has helped pinpoint sources of pollution impacting clam populations, leading to remediation efforts.
- Implementation of Habitat Restoration Projects: Citizen science data has supported the development and implementation of successful habitat restoration initiatives.
-
Collaboration and Partnerships: Citizen science initiatives foster collaboration between various stakeholders:
- Washington Department of Fish and Wildlife: Collaboration with government agencies ensures data integration into broader conservation strategies.
- Local Environmental Groups: Partnerships with local groups increase community engagement and support for clam conservation.
Conclusion:
The involvement of citizen scientists in investigating Whidbey clams is proving invaluable for understanding and protecting this vital species. Through rigorous data collection and collaborative efforts, these dedicated volunteers are making significant contributions to conservation efforts and fostering a deeper understanding of the delicate balance of Whidbey Island's ecosystems. To learn more about participating in Whidbey clam research and becoming a citizen scientist, contact your local environmental organizations, such as [insert local organization name and website here], or visit relevant government websites. Get involved and help protect our precious Whidbey clams and their vital habitat!

Featured Posts
-
 Los Angeles Wildfires And The Gambling Industry Ethical Concerns And The Current State Of Affairs
May 30, 2025
Los Angeles Wildfires And The Gambling Industry Ethical Concerns And The Current State Of Affairs
May 30, 2025 -
 Medine En Concert En Grand Est Subventions Et Polemique
May 30, 2025
Medine En Concert En Grand Est Subventions Et Polemique
May 30, 2025 -
 Analise Do Desempenho De Bruno Fernandes No Manchester United
May 30, 2025
Analise Do Desempenho De Bruno Fernandes No Manchester United
May 30, 2025 -
 Water Deficit Persists Despite March Rainfall
May 30, 2025
Water Deficit Persists Despite March Rainfall
May 30, 2025 -
 Talq Awstabynkw Mstmr Fy Mwsm Almlaeb Altrabyt
May 30, 2025
Talq Awstabynkw Mstmr Fy Mwsm Almlaeb Altrabyt
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Best Spring Hotel Deals Up To 30 Discount
May 31, 2025
Best Spring Hotel Deals Up To 30 Discount
May 31, 2025 -
 Responsible Ai Acknowledging The Limits Of Current Ai Learning Capabilities
May 31, 2025
Responsible Ai Acknowledging The Limits Of Current Ai Learning Capabilities
May 31, 2025 -
 Ai And The Illusion Of Learning A Call For Responsible Ai Use
May 31, 2025
Ai And The Illusion Of Learning A Call For Responsible Ai Use
May 31, 2025 -
 The Reality Of Ai Learning Addressing Misconceptions And Promoting Responsible Use
May 31, 2025
The Reality Of Ai Learning Addressing Misconceptions And Promoting Responsible Use
May 31, 2025 -
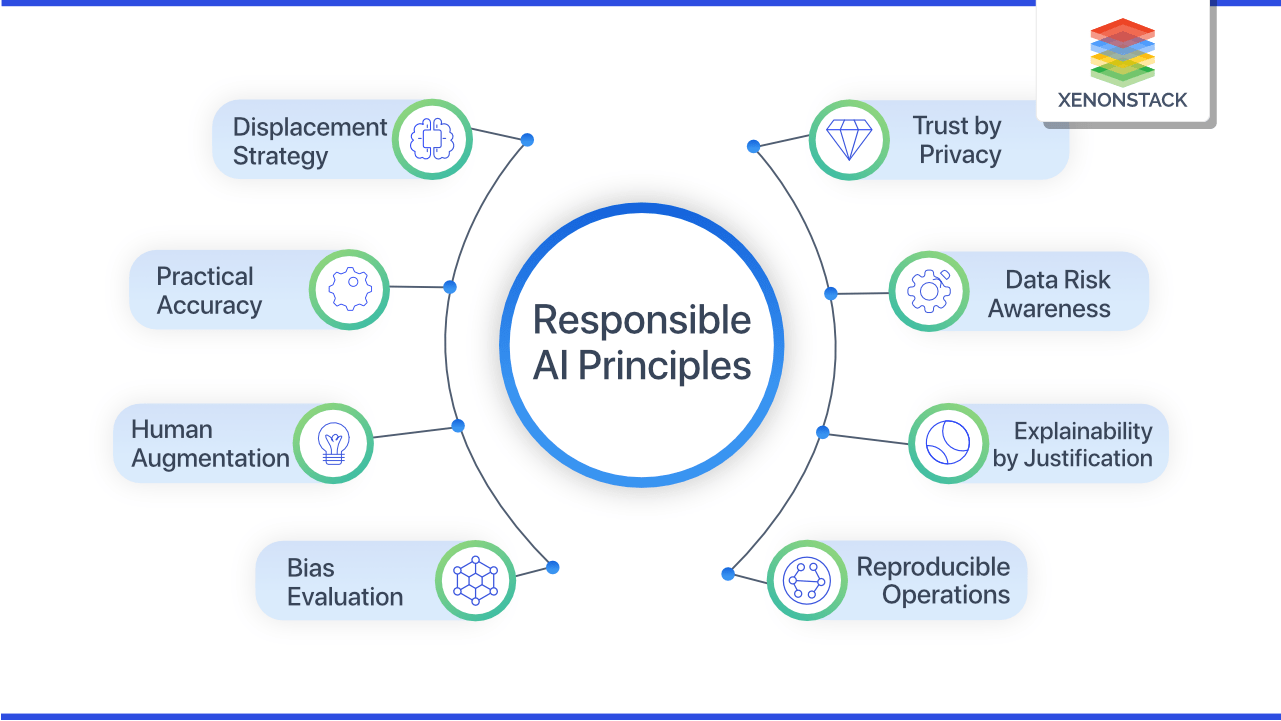 The Reality Of Ai Learning Promoting Responsible Ai Practices
May 31, 2025
The Reality Of Ai Learning Promoting Responsible Ai Practices
May 31, 2025
