Investigating The Effects Of A Toxic Algae Bloom On California's Coast
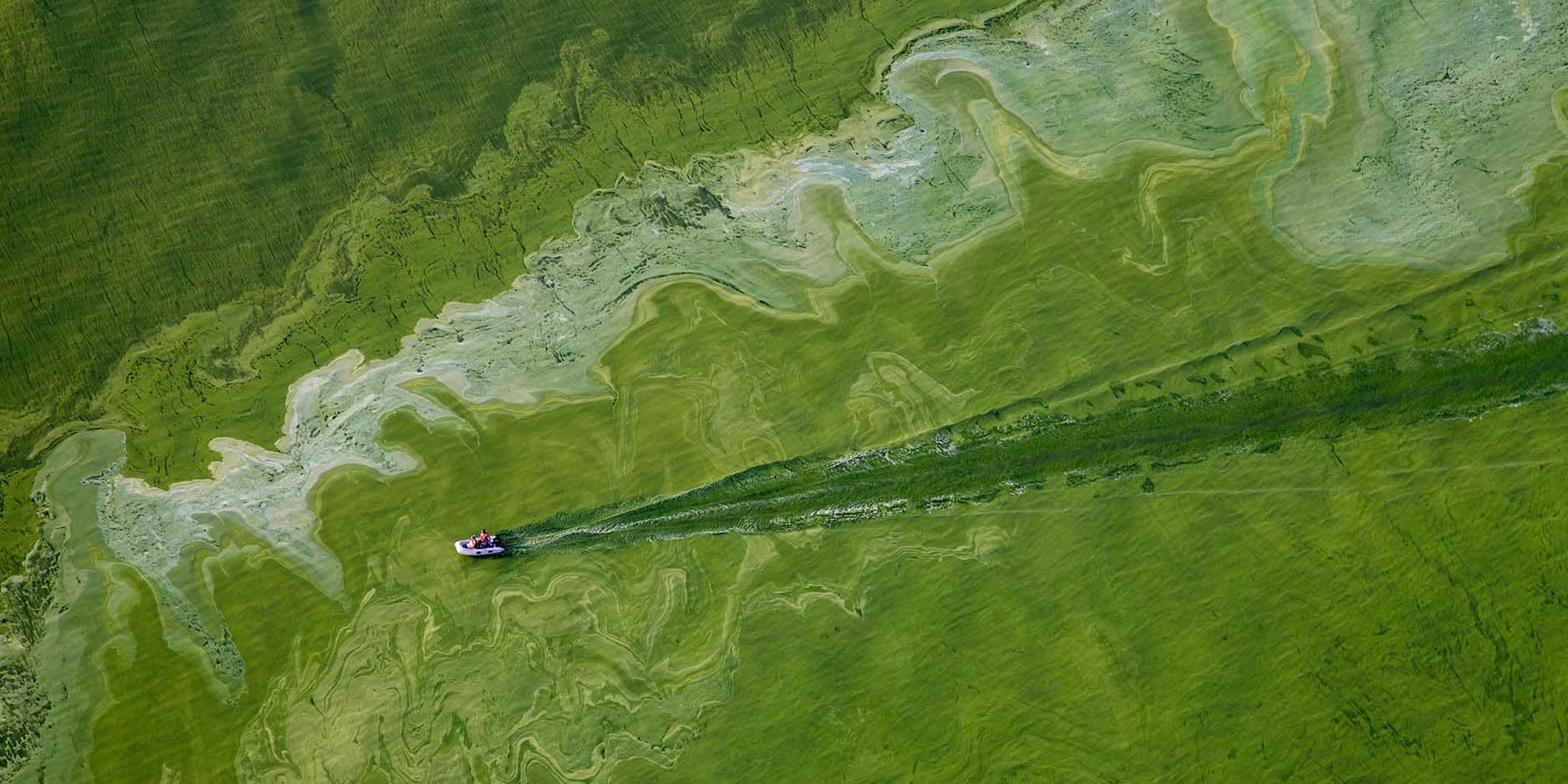

Table of Contents
Causes of Toxic Algae Blooms in California
Several factors contribute to the proliferation of toxic algae blooms along California's coast. These blooms are not a new phenomenon, but their intensity and frequency are increasing, largely due to human activity and climate change.
Nutrient Pollution
Excessive nutrients in coastal waters fuel the explosive growth of algae. This process, known as eutrophication, is primarily driven by:
- Agricultural runoff: Fertilizers containing nitrogen and phosphorus from farms wash into rivers and streams, eventually reaching the ocean.
- Sewage discharge: Untreated or inadequately treated sewage releases high levels of nutrients into the water.
- Stormwater: Urban runoff carries fertilizers, pet waste, and other pollutants from streets and yards into waterways.
These nutrient inputs create a "fertilizer effect" for algae, leading to rapid and often harmful blooms. Specific examples in California include agricultural runoff from the Central Valley impacting the Sacramento-San Joaquin River Delta and coastal areas, and sewage discharge from various coastal cities.
Climate Change Impacts
Climate change exacerbates the problem of toxic algae blooms in several ways:
- Warmer waters: Rising ocean temperatures accelerate algal growth rates, creating ideal conditions for blooms.
- Altered water circulation: Changes in ocean currents can concentrate algae in specific areas, leading to larger and more intense blooms.
- Increased rainfall and runoff: More frequent and intense rainfall events increase nutrient runoff into coastal waters.
These interconnected effects of climate change create a perfect storm for the development and expansion of harmful algal blooms.
Ocean Acidification
Ocean acidification, a direct consequence of increased atmospheric CO2, further complicates the situation. While the exact impact on all algae species is still being researched, it's known that:
- Shell-forming organisms are affected: Ocean acidification hinders the ability of shellfish and other organisms to build and maintain their shells, impacting the entire food web.
- Increased toxicity is possible: Some studies suggest that certain algae species may produce more toxins under acidic conditions.
Impacts of Toxic Algae Blooms on California's Coast
The consequences of toxic algae blooms in California are far-reaching and impact numerous aspects of the coastal environment and human society.
Impacts on Marine Life
HABs cause significant harm to marine life:
- Mortality: Many fish, shellfish, marine mammals, and other organisms die from exposure to toxins or oxygen depletion caused by the blooms. For example, sea lions and other marine mammals can suffer neurological damage from domoic acid, a toxin produced by certain algae.
- Bioaccumulation of toxins: Toxins accumulate in the tissues of marine organisms, leading to biomagnification up the food chain. This means that larger predators consuming smaller, contaminated prey accumulate higher levels of toxins.
- Economic impact on fisheries: Shellfish harvesting closures due to HABs result in significant economic losses for the fishing industry.
Impacts on Human Health
Humans are also vulnerable to the effects of toxic algae blooms:
- Neurotoxic shellfish poisoning (NSP): Consumption of contaminated shellfish can cause neurological symptoms, including memory loss and seizures.
- Beach closures: High concentrations of toxins necessitate beach closures, impacting tourism and recreational activities.
- Economic impact on tourism: HABs reduce tourism revenue due to beach closures, impacting businesses and local economies. Airborne toxins can also cause respiratory irritation.
Economic Impacts
The economic consequences of HABs are substantial:
- Fisheries losses: Closures of shellfish beds and reduced fish catches lead to significant financial losses for fishermen and related businesses.
- Tourism losses: Beach closures and health concerns deter tourists, affecting hotels, restaurants, and other businesses.
- Monitoring and mitigation costs: The expense of monitoring HABs and implementing mitigation measures places a burden on government agencies and taxpayers.
Monitoring and Mitigation Strategies for Toxic Algae Blooms in California
Addressing the challenge of toxic algae blooms requires a multifaceted approach that combines monitoring, prevention, and mitigation.
Early Warning Systems
Effective monitoring is critical for early detection and prediction of HABs:
- Satellite imagery: Remote sensing technologies allow for large-scale monitoring of algal blooms.
- Water sampling: Regular water sampling provides data on toxin levels and algal species present.
- Predictive modeling: Advanced models can forecast the development and movement of blooms.
These tools provide crucial information for timely warnings and management decisions.
Mitigation and Management Techniques
Various strategies can help reduce the frequency and intensity of HABs:
- Improved wastewater treatment: Upgrading wastewater treatment plants to remove more nutrients before discharge into the environment.
- Nutrient management in agriculture: Implementing best management practices in agriculture to reduce fertilizer runoff.
- Bioremediation: Exploring the potential of using microorganisms to break down algal toxins or reduce algal growth.
- Policy and regulation: Strong policies and regulations are needed to control nutrient pollution and promote sustainable land and water management practices.
Conclusion
Toxic algae blooms in California present a significant and complex challenge. Their devastating impacts on marine ecosystems, human health, and the economy demand urgent attention. By integrating advanced monitoring techniques, implementing effective mitigation strategies, and addressing the underlying drivers like nutrient pollution and climate change, we can work towards a more resilient coastal environment. Continued research, collaborative efforts, and strong policy interventions are vital to protecting California's coastline and safeguarding this valuable resource for future generations. Learn more about ongoing efforts to combat toxic algae blooms in California and how you can contribute to solutions.

Featured Posts
-
 Analiza Rozmow Telefonicznych Miedzy Donaldem Trumpem A Wolodymyrem Zelenskim
May 30, 2025
Analiza Rozmow Telefonicznych Miedzy Donaldem Trumpem A Wolodymyrem Zelenskim
May 30, 2025 -
 Harga Kawasaki Ninja 500 Dan 500 Se 2025 Lebih Dari Rp100 Juta
May 30, 2025
Harga Kawasaki Ninja 500 Dan 500 Se 2025 Lebih Dari Rp100 Juta
May 30, 2025 -
 Imunisasi Anak Di Gorontalo Terancam Lonjakan Kasus Suspek Campak Di Pohuwato
May 30, 2025
Imunisasi Anak Di Gorontalo Terancam Lonjakan Kasus Suspek Campak Di Pohuwato
May 30, 2025 -
 2025 Bts Comeback Hybe Addresses Fan Concerns And Explains Extended Hiatus
May 30, 2025
2025 Bts Comeback Hybe Addresses Fan Concerns And Explains Extended Hiatus
May 30, 2025 -
 Finding Your Place In Line Ticketmasters Taylor Swift Update
May 30, 2025
Finding Your Place In Line Ticketmasters Taylor Swift Update
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Best Spring Hotel Deals Up To 30 Discount
May 31, 2025
Best Spring Hotel Deals Up To 30 Discount
May 31, 2025 -
 Responsible Ai Acknowledging The Limits Of Current Ai Learning Capabilities
May 31, 2025
Responsible Ai Acknowledging The Limits Of Current Ai Learning Capabilities
May 31, 2025 -
 Ai And The Illusion Of Learning A Call For Responsible Ai Use
May 31, 2025
Ai And The Illusion Of Learning A Call For Responsible Ai Use
May 31, 2025 -
 The Reality Of Ai Learning Addressing Misconceptions And Promoting Responsible Use
May 31, 2025
The Reality Of Ai Learning Addressing Misconceptions And Promoting Responsible Use
May 31, 2025 -
 The Reality Of Ai Learning Promoting Responsible Ai Practices
May 31, 2025
The Reality Of Ai Learning Promoting Responsible Ai Practices
May 31, 2025
