California's Coastal Crisis: Toxic Algae Bloom Impact On Marine Ecosystems
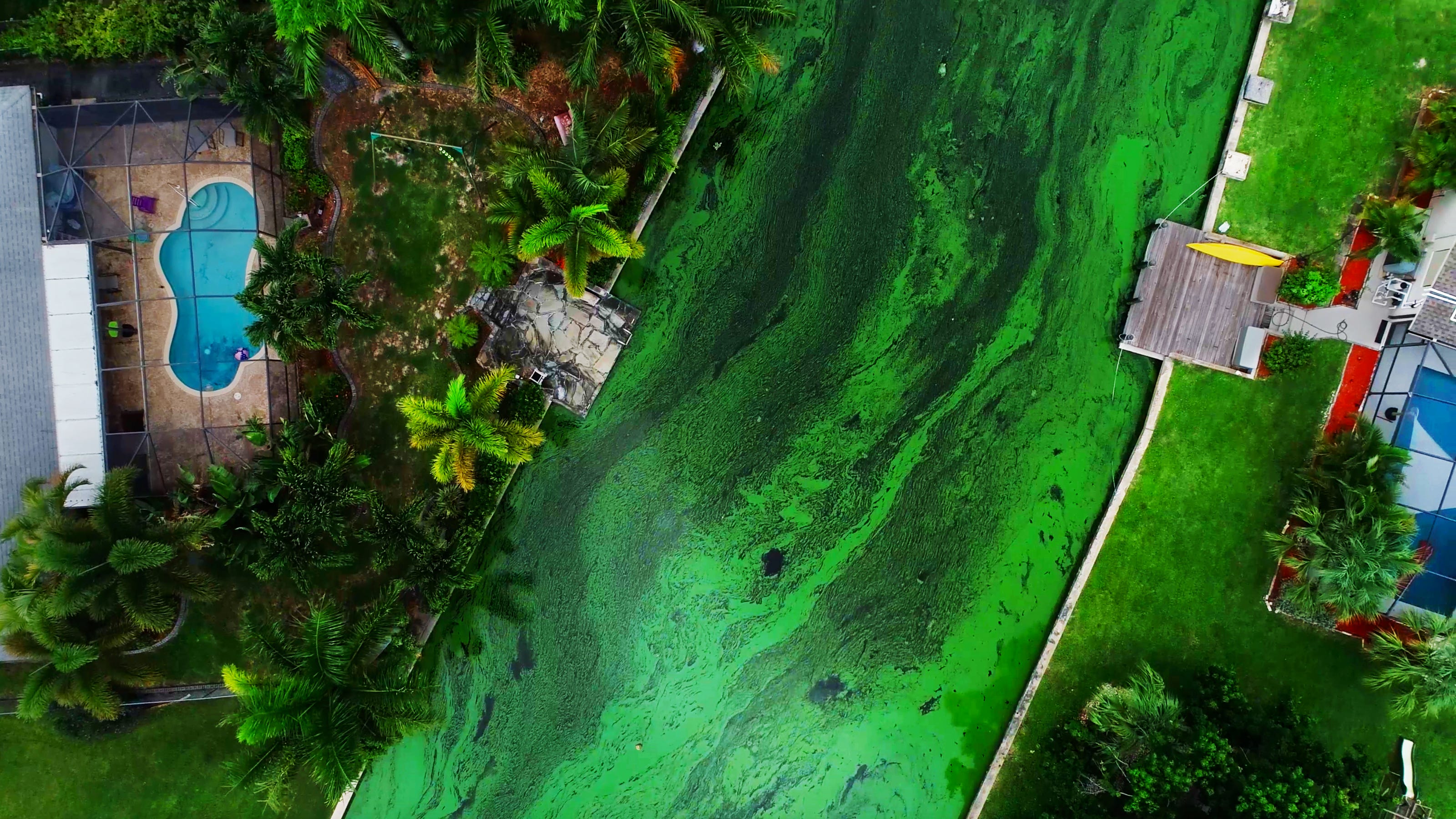

Table of Contents
The Science Behind Toxic Algae Blooms in California
What are Harmful Algal Blooms (HABs)?
Harmful algal blooms are rapid increases in the population of algae in water, often exhibiting discoloration (hence the "red tide" moniker, though blooms can be other colors). These blooms aren't all harmful; however, certain species produce potent toxins that can have devastating consequences. These toxins accumulate in the food web, impacting marine life and ultimately, humans. Several factors contribute to HAB formation, including:
- Nutrient runoff: Excess nutrients, primarily nitrogen and phosphorus from agricultural fertilizers, sewage, and urban runoff, act as potent fertilizers for algae, fueling their explosive growth.
- Warmer water temperatures: Climate change is contributing to rising ocean temperatures, creating more favorable conditions for certain harmful algae species to thrive.
- Ocean currents: Currents can transport algae blooms over vast distances, spreading their impact across large areas of the coastline.
Several toxic algae species are prevalent in California waters, including:
- Pseudo-nitzschia: This diatom produces domoic acid, a neurotoxin that accumulates in shellfish and can cause amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP) in humans.
- Alexandrium: This dinoflagellate produces saxitoxin, a potent neurotoxin responsible for paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP).
Geographic Distribution and Seasonal Patterns of HABs in California
HABs occur along the entire California coast, but certain areas are particularly susceptible. A map showing the frequency and intensity of blooms would highlight hotspots along the central and southern coasts. Bloom occurrences are often seasonal, typically peaking during warmer months when water temperatures and nutrient levels are highest. However, climate change is disrupting these patterns, leading to more frequent and intense blooms outside of typical seasons. Specific regions experiencing frequent or severe toxic algae blooms include:
- Monterey Bay
- Southern California Bight
- San Francisco Bay
The Devastating Ecological Impacts of Toxic Algae Blooms
Effects on Marine Wildlife
The toxins produced by HABs have devastating effects on a wide range of marine organisms. Fish populations experience significant mortality, impacting reproductive success and overall abundance. Marine mammals, such as seals, sea lions, and whales, suffer from toxin ingestion, leading to neurological damage, seizures, and death. Seabirds and other marine invertebrates are also affected, disrupting the delicate balance of the marine ecosystem. Examples of species severely impacted by past HAB events include:
- Various fish species (e.g., anchovies, sardines)
- Sea otters
- Brown pelicans
Impacts on the Food Web and Ecosystem Services
Widespread mortality caused by HABs disrupts the marine food web, with cascading effects throughout the ecosystem. Shellfish closures due to toxin contamination cause significant economic losses to the fishing industry and related businesses. The loss of biodiversity reduces the overall resilience of the ecosystem, making it more vulnerable to future disturbances. Economic consequences include:
- Loss of revenue from shellfish harvesting
- Decline in tourism due to beach closures
- Increased costs for monitoring and mitigation efforts
Human Health Risks Associated with California's Toxic Algae Blooms
Direct and Indirect Exposure to Toxins
Humans can be exposed to HAB toxins through several pathways:
- Consuming contaminated seafood: Shellfish are particularly vulnerable to accumulating toxins, posing a significant risk to human health if consumed during a bloom.
- Respiratory problems: During intense blooms, airborne toxins can cause respiratory irritation and other health problems in people near the coast.
- Skin irritation: Direct contact with affected waters can cause skin irritation in some individuals.
Symptoms of domoic acid and saxitoxin poisoning can range from mild gastrointestinal distress to severe neurological symptoms, including seizures and memory loss. Safe seafood consumption guidelines during bloom events are essential.
Public Health Response and Monitoring Efforts
State and federal agencies, such as the California Department of Public Health (CDPH) and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), play a crucial role in monitoring HABs, issuing public health advisories, and closing beaches when necessary. Research efforts are focused on improving HAB prediction and mitigation strategies. Organizations responsible for monitoring HABs in California include:
- CDPH
- NOAA
- Various University research programs
Mitigation and Management Strategies for California's Toxic Algae Blooms
Reducing Nutrient Runoff
Reducing nutrient pollution is a key strategy for mitigating HABs. This involves:
- Implementing sustainable agricultural practices to reduce fertilizer use.
- Upgrading wastewater treatment plants to remove excess nutrients.
- Establishing buffer zones along waterways to filter pollutants before they reach the ocean.
Specific policy recommendations might include stricter regulations on fertilizer application, investments in advanced wastewater treatment technologies, and incentives for farmers to adopt sustainable practices.
Enhancing Monitoring and Early Warning Systems
Improved monitoring and early warning systems are crucial for minimizing the impacts of HABs. This includes:
- Utilizing satellite imagery and advanced data analysis to predict bloom development and spread.
- Developing sophisticated early warning systems to alert coastal communities and relevant stakeholders.
- Increasing public awareness and education campaigns to inform the public about the risks of HABs.
Technologies such as satellite remote sensing, advanced modeling techniques, and real-time monitoring buoys are crucial for effective HAB monitoring and prediction.
Conclusion
California's coastal crisis, characterized by increasingly frequent and intense toxic algae blooms, presents a serious threat to both marine ecosystems and human health. Understanding the science behind HABs, their far-reaching ecological impacts, and the associated human health risks is paramount for implementing effective mitigation strategies. Addressing this complex issue necessitates a multi-pronged approach involving reduced nutrient pollution, enhanced monitoring and early warning systems, and continued investment in research. We must act collaboratively to safeguard California's invaluable coastal resources and mitigate the devastating effects of toxic algae blooms. Learn more about how you can contribute to protecting California's coast from future toxic algae blooms and support organizations dedicated to this crucial effort.

Featured Posts
-
 Ticketmaster Lanza Herramienta De Vista Previa De Asientos Virtual Venue
May 30, 2025
Ticketmaster Lanza Herramienta De Vista Previa De Asientos Virtual Venue
May 30, 2025 -
 Investigating The Death Bath A Serial Killers Six Victims And Their Fate
May 30, 2025
Investigating The Death Bath A Serial Killers Six Victims And Their Fate
May 30, 2025 -
 Ne Vykhodite Iz Doma Ekstrennoe Preduprezhdenie Politsii Izrailya
May 30, 2025
Ne Vykhodite Iz Doma Ekstrennoe Preduprezhdenie Politsii Izrailya
May 30, 2025 -
 Kunstnerisk Udforskning Kare Quists Han Taler Udenom Hos Ditte Okman
May 30, 2025
Kunstnerisk Udforskning Kare Quists Han Taler Udenom Hos Ditte Okman
May 30, 2025 -
 The Best Neighborhoods In Paris A Locals Perspective
May 30, 2025
The Best Neighborhoods In Paris A Locals Perspective
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Why Current Stock Market Prices Dont Signal A Crash Bof As View
May 31, 2025
Why Current Stock Market Prices Dont Signal A Crash Bof As View
May 31, 2025 -
 Understanding Elevated Stock Market Valuations A Bof A Perspective
May 31, 2025
Understanding Elevated Stock Market Valuations A Bof A Perspective
May 31, 2025 -
 High Stock Valuations And Investor Confidence A Bof A Analysis
May 31, 2025
High Stock Valuations And Investor Confidence A Bof A Analysis
May 31, 2025 -
 Addressing Investor Concerns Bof A On Elevated Stock Market Valuations
May 31, 2025
Addressing Investor Concerns Bof A On Elevated Stock Market Valuations
May 31, 2025 -
 Stock Market Valuations Bof As Argument For Why Investors Shouldnt Worry
May 31, 2025
Stock Market Valuations Bof As Argument For Why Investors Shouldnt Worry
May 31, 2025
