Analyzing Japan's Steep Bond Curve: Risks And Opportunities
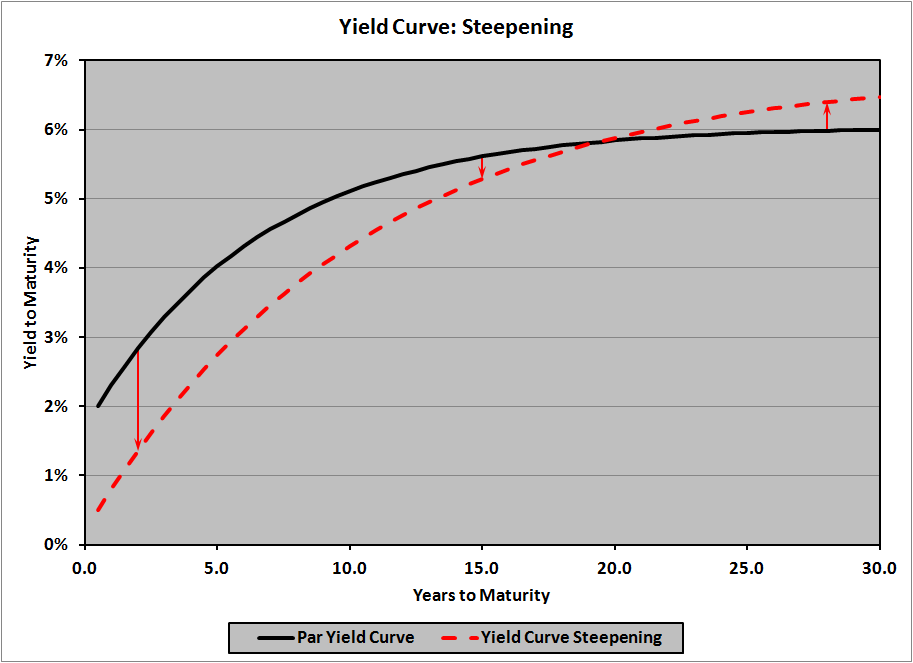
Table of Contents
Understanding Japan's Steep Bond Curve
The Mechanics of the Yield Curve
A yield curve graphically represents the relationship between the interest rates (yields) and the time to maturity of debt instruments of the same credit quality. In essence, it shows what returns investors can expect for lending money to a borrower for different lengths of time. A steep yield curve, like the one currently observed in Japan's bond market, signifies a substantial difference between short-term and long-term yields.
- Definition of yield curve: A line graph plotting the yields of bonds with different maturities.
- Factors influencing yield curve shape: Inflation expectations (higher expected inflation leads to higher long-term yields), monetary policy (central bank actions influence short-term rates), economic growth (strong growth often leads to a steeper curve), and risk aversion.
- Visual representation: [Insert a graph showing a typical steep yield curve here. Ideally, this would be an interactive graph showing historical JGB yields.]
Current State of Japan's Bond Market
Japan's JGB yield curve currently exhibits a significant steepness, a departure from historical norms and a stark contrast to the flatter curves seen in many other developed economies. This steepness reflects a widening gap between short-term and long-term yields.
- Specific yield data points: [Insert current yield data for various JGB maturities, e.g., 2-year, 5-year, 10-year, 30-year JGB yields. Source the data appropriately.]
- Comparison with other major economies: [Compare Japanese JGB yields with equivalent maturity bonds from the US, Germany, or UK. Highlight the difference in steepness.]
- Visual representation of the current yield curve: [Insert a graph showing the current JGB yield curve, clearly labeling axes and data sources.]
Factors Contributing to the Steepness
Several interconnected economic and policy factors contribute to the steepness of Japan's bond curve:
- Bank of Japan's monetary policy (yield curve control): The BOJ's yield curve control (YCC) policy, aimed at keeping short-term interest rates low, has played a major role. However, the effectiveness of YCC in controlling the long end of the curve has been debated.
- Inflation expectations in Japan: While inflation has recently risen in Japan, expectations about its persistence and the BOJ's response remain crucial drivers of long-term JGB yields.
- Government debt levels: Japan has one of the highest levels of government debt relative to GDP globally. This large debt supply influences long-term bond yields.
- Global economic uncertainty: Global factors, such as geopolitical risks and the potential for global recession, can affect investor demand for safe-haven assets like JGBs, impacting long-term yields.
Risks Associated with Japan's Steep Bond Curve
Interest Rate Risk
The steepness of the yield curve amplifies interest rate risk for investors holding long-term JGBs.
- Impact of interest rate hikes on bond prices: Rising interest rates lead to falling bond prices, particularly for longer-maturity bonds.
- Duration risk: Longer-maturity bonds have higher duration, making them more sensitive to interest rate changes.
- Potential for capital losses: Investors could face significant capital losses if interest rates rise unexpectedly.
Inflation Risk
Unexpected inflation poses a significant threat to the real returns of JGBs.
- Inflation's impact on bond yields: Inflation erodes the purchasing power of future interest payments and the principal repayment at maturity.
- Potential for negative real returns: If inflation outpaces nominal yields, investors experience negative real returns.
- Hedging strategies against inflation: Investors can use inflation-linked bonds or other strategies to mitigate inflation risk.
Policy Uncertainty
Uncertainty surrounding future Bank of Japan policy adds another layer of risk.
- Potential changes to yield curve control: The BOJ's future actions regarding YCC remain uncertain, potentially leading to significant market volatility.
- Impact of policy changes on bond yields and market volatility: Any unexpected shifts in policy could trigger sharp movements in JGB yields.
- Potential for unexpected policy shifts: The abrupt abandonment of YCC would likely cause major disruptions in the JGB market.
Opportunities Presented by Japan's Steep Bond Curve
Potential for Higher Returns
Despite the risks, the steep yield curve offers the potential for higher returns on long-term JGBs compared to short-term bonds.
- Higher yields compared to short-term bonds: Long-term JGBs offer significantly higher yields than short-term bonds.
- Potential for capital appreciation if yields fall: If yields decline, the prices of long-term JGBs could appreciate.
- Strategies for managing risk: Investors can employ strategies like staggered maturities and hedging to mitigate risk.
Diversification Benefits
Incorporating JGBs into a global investment portfolio can offer diversification benefits.
- Low correlation with other asset classes: JGBs tend to have a low correlation with other asset classes like equities, offering portfolio diversification.
- Potential for hedging against global market downturns: JGBs can serve as a safe-haven asset during periods of global market uncertainty.
- Risk reduction through diversification: Adding JGBs can help reduce overall portfolio risk.
Carry Trade Strategies
The difference between short-term and long-term JGB yields creates opportunities for carry trade strategies.
- Borrowing at short-term rates and investing in long-term JGBs: Investors can borrow at low short-term rates and invest in higher-yielding long-term JGBs.
- Risk management considerations for carry trades: Carry trades are sensitive to interest rate changes and currency fluctuations.
Conclusion
Japan's steep bond curve presents a complex landscape of risks and opportunities. While the potential for higher returns from long-term JGBs is attractive, investors must carefully consider the significant interest rate and inflation risks. Understanding the factors contributing to the steep curve, including the Bank of Japan's monetary policy and the overall economic climate, is crucial for informed decision-making. By carefully assessing the risks and employing appropriate risk management strategies, investors can potentially capitalize on the opportunities presented by this unique market dynamic. Further research into Japan's economic outlook and the Bank of Japan's future policy decisions is vital for navigating the intricacies of Japan's steep bond curve effectively. Continue your exploration of Japan's steep bond curve and its implications to make well-informed investment choices.

Featured Posts
-
 Giants Vs Mariners Injury Report April 4 6 Series Preview
May 17, 2025
Giants Vs Mariners Injury Report April 4 6 Series Preview
May 17, 2025 -
 Japans Shrinking Economy A First Quarter Review
May 17, 2025
Japans Shrinking Economy A First Quarter Review
May 17, 2025 -
 Japans Rising Bond Yields Challenges And Outlook
May 17, 2025
Japans Rising Bond Yields Challenges And Outlook
May 17, 2025 -
 Exclusive Access Investigation Into Trumps Donor Events At Military Installations
May 17, 2025
Exclusive Access Investigation Into Trumps Donor Events At Military Installations
May 17, 2025 -
 Blue Origins Rocket Launch Abruptly Halted By Technical Glitch
May 17, 2025
Blue Origins Rocket Launch Abruptly Halted By Technical Glitch
May 17, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Track Roundup All Conference Honors Announced
May 17, 2025
Track Roundup All Conference Honors Announced
May 17, 2025 -
 Mariners Tigers Opening Series Injury Concerns And Predictions March 31 April 2
May 17, 2025
Mariners Tigers Opening Series Injury Concerns And Predictions March 31 April 2
May 17, 2025 -
 Josh Harts Wife On Jaylen Browns Crucial Game 5 Plays
May 17, 2025
Josh Harts Wife On Jaylen Browns Crucial Game 5 Plays
May 17, 2025 -
 Seattle Mariners Vs Detroit Tigers Key Injuries And Series Outlook March 31 April 2
May 17, 2025
Seattle Mariners Vs Detroit Tigers Key Injuries And Series Outlook March 31 April 2
May 17, 2025 -
 2024 25 High School Confidential Key Events Of Week 26
May 17, 2025
2024 25 High School Confidential Key Events Of Week 26
May 17, 2025
