Understanding Stock Market Valuations: BofA's Investor Guidance
Table of Contents
Key Valuation Metrics Explained
Understanding stock market valuations hinges on several key metrics. Let's explore some of the most commonly used, and how BofA might incorporate them into its analysis.
Price-to-Earnings Ratio (P/E)
The Price-to-Earnings Ratio is a fundamental valuation metric calculated by dividing a company's stock price by its earnings per share (EPS). A high P/E ratio suggests investors are willing to pay a premium for each dollar of earnings, often indicating high growth expectations. Conversely, a low P/E ratio might suggest undervaluation or lower growth potential.
- Examples: A high P/E stock might be a rapidly growing tech company with substantial future earnings potential, while a low P/E stock could be a mature, established company with slower growth.
- BofA's Approach: BofA likely uses both trailing P/E (based on past earnings) and forward P/E (based on projected future earnings) ratios in its analysis, providing a more comprehensive view of a company's valuation. The forward P/E is particularly useful for companies experiencing rapid growth.
Price-to-Book Ratio (P/B)
The Price-to-Book Ratio compares a company's market capitalization to its book value (assets minus liabilities). It's particularly relevant in sectors with substantial tangible assets, like banking or manufacturing. A P/B ratio below 1 could suggest undervaluation, while a high ratio may indicate overvaluation.
- BofA's Utilization: BofA might utilize P/B ratios to assess the net asset value of a company, especially when analyzing companies with significant tangible assets. It helps identify potential undervaluation or situations where the market is not fully appreciating the company's underlying assets.
- Limitations: The P/B ratio has limitations; book value can be affected by accounting practices and may not accurately reflect a company's true market value, especially for companies with significant intangible assets like intellectual property.
Price-to-Sales Ratio (P/S)
The Price-to-Sales Ratio compares a company's market capitalization to its revenue. It's particularly useful for valuing early-stage companies or those currently operating at a loss, where P/E ratios are not applicable.
- BofA's Incorporation: BofA could incorporate P/S ratios, particularly in its analysis of high-growth technology companies that may not yet be profitable. This metric provides a relative valuation even in the absence of earnings.
- Benefits and Drawbacks: The advantage is its applicability across various company stages. However, it doesn't consider profitability or expenses, providing only a snapshot of revenue generation.
Understanding BofA's Valuation Approach
BofA's valuation approach is multifaceted and sophisticated. They employ a combination of quantitative and qualitative factors to arrive at their assessments.
BofA's Investment Philosophy and Methodologies
BofA's investment philosophy likely emphasizes a blend of fundamental analysis (examining financial statements) and quantitative analysis (using statistical models). They may employ proprietary valuation models to assess intrinsic value and compare it to market prices.
- Research Examples: BofA publishes numerous research reports and analyses covering individual stocks and broader market sectors, readily available to clients and sometimes publicly.
- Proprietary Models: While the specifics of BofA's proprietary models are often confidential, their use allows for a more nuanced and possibly more accurate valuation than relying solely on standard metrics.
Macroeconomic Factors
BofA considers macroeconomic factors, such as interest rates, inflation, and GDP growth, in their valuation process. These factors significantly influence market sentiment and company performance.
- Impact of Indicators: Rising interest rates can negatively impact growth stocks, while high inflation can compress profit margins. GDP growth influences consumer spending and corporate earnings.
Qualitative Factors
BofA also integrates qualitative factors into their valuation, such as management quality, competitive landscape, and regulatory changes. These factors can substantially impact a company's long-term prospects.
- Qualitative Impact: A strong management team can significantly improve a company's performance, while a highly competitive market can pressure profit margins.
Interpreting BofA's Recommendations
BofA's research typically includes "buy," "sell," and "hold" recommendations for various stocks. Understanding how to interpret these recommendations is crucial.
Understanding Recommendations
A "buy" recommendation suggests BofA believes the stock is undervalued and has significant upside potential. A "sell" recommendation indicates an overvaluation and potential downside risk. A "hold" recommendation means BofA sees little reason to buy or sell at the current price.
- Contributing Factors: These recommendations are based on their valuation analysis, considering both quantitative and qualitative factors, macroeconomic conditions, and their outlook for the company's future performance.
Risk Tolerance
It's essential to remember that BofA's recommendations are not financial advice. Always consider your own risk tolerance and investment goals before making any investment decisions.
- Responsible Investing: Diversify your portfolio, conduct thorough due diligence, and consult with a financial advisor before acting on any investment recommendation.
Accessing BofA's Resources
BofA's research and investor resources are primarily available to their clients. However, some publicly available information can be found on their website.
- Finding Resources: Check BofA's official website for research reports, market commentary, and investor education materials.
Conclusion: Mastering Stock Market Valuations with BofA's Guidance
Understanding stock market valuations is fundamental to successful investing. We've explored key metrics like P/E, P/B, and P/S ratios, and examined how BofA incorporates these metrics, alongside macroeconomic and qualitative factors, into its valuation approach. Remember that interpreting BofA's recommendations requires careful consideration of your own risk tolerance and investment goals. By leveraging BofA's expert guidance and understanding these valuation tools, you can enhance your investment strategy. Learn more about stock market valuations and leverage BofA's expert guidance to enhance your investment strategy. Start exploring BofA's research today!

Featured Posts
-
 Big Oils Resistance Impact On Global Oil Prices Before Opec Decision
May 05, 2025
Big Oils Resistance Impact On Global Oil Prices Before Opec Decision
May 05, 2025 -
 Hate Crime Attack Man Receives 53 Year Prison Sentence
May 05, 2025
Hate Crime Attack Man Receives 53 Year Prison Sentence
May 05, 2025 -
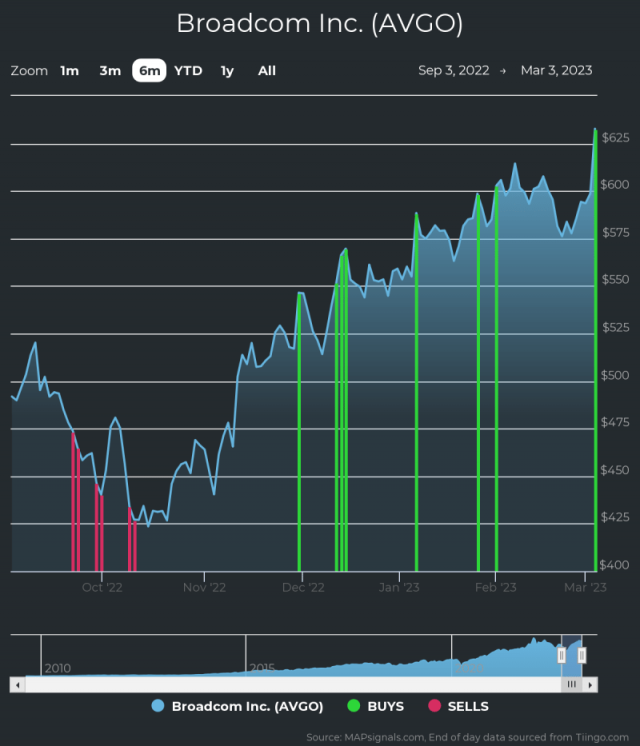 At And T Exposes Extreme Cost Increase In Broadcoms V Mware Deal
May 05, 2025
At And T Exposes Extreme Cost Increase In Broadcoms V Mware Deal
May 05, 2025 -
 Broadcoms V Mware Deal An Extreme Price Hike For At And T And Others
May 05, 2025
Broadcoms V Mware Deal An Extreme Price Hike For At And T And Others
May 05, 2025 -
 Office365 Security Failure Hackers Multi Million Dollar Scheme Exposed
May 05, 2025
Office365 Security Failure Hackers Multi Million Dollar Scheme Exposed
May 05, 2025
Latest Posts
-
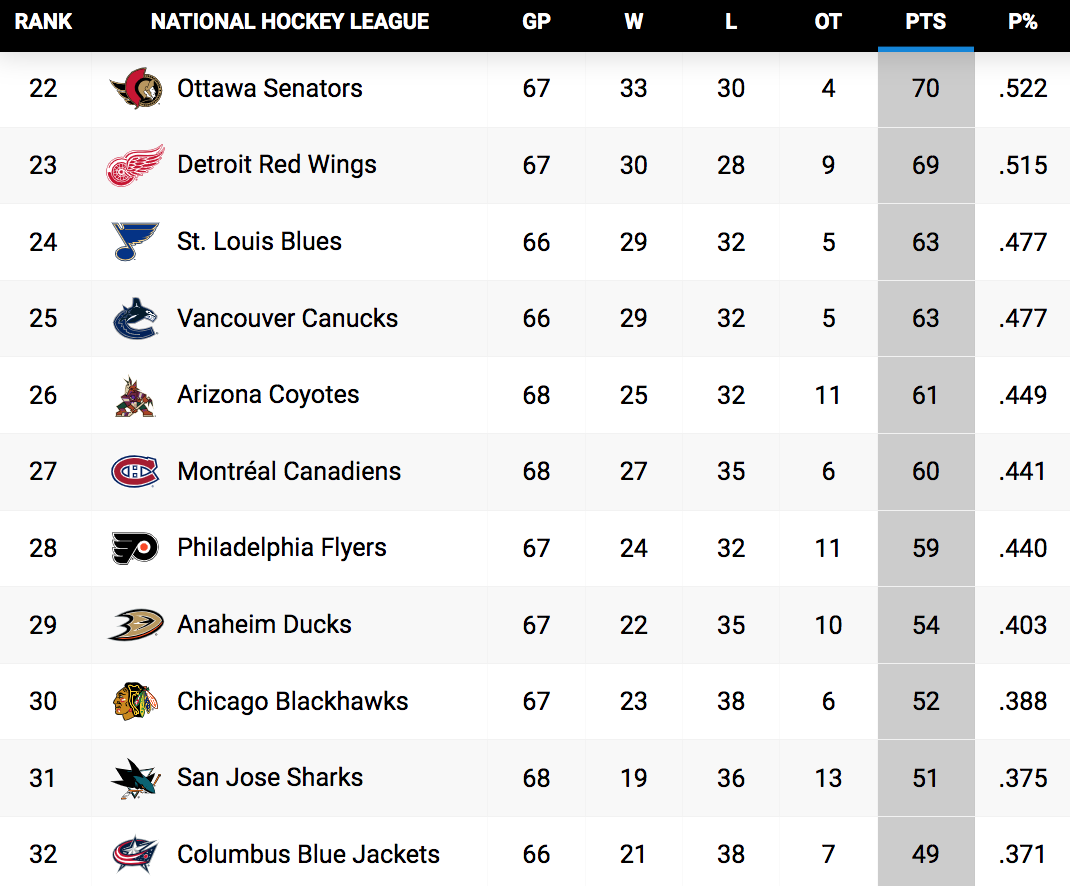 Nhl Standings Update Key Games To Watch On Showdown Saturday
May 05, 2025
Nhl Standings Update Key Games To Watch On Showdown Saturday
May 05, 2025 -
 Navigating The First Round Of The Nhl Playoffs
May 05, 2025
Navigating The First Round Of The Nhl Playoffs
May 05, 2025 -
 Nhl News Florida Panthers Stage Comeback Win Avalanche Suffer Heavy Loss
May 05, 2025
Nhl News Florida Panthers Stage Comeback Win Avalanche Suffer Heavy Loss
May 05, 2025 -
 Nhl Playoff Race Heats Up Showdown Saturdays Key Matchups And Standings Implications
May 05, 2025
Nhl Playoff Race Heats Up Showdown Saturdays Key Matchups And Standings Implications
May 05, 2025 -
 Nhl Stanley Cup Playoffs A Look At The First Round
May 05, 2025
Nhl Stanley Cup Playoffs A Look At The First Round
May 05, 2025
