The Impact Of China's Rate Cuts On Bank Lending And The Economy
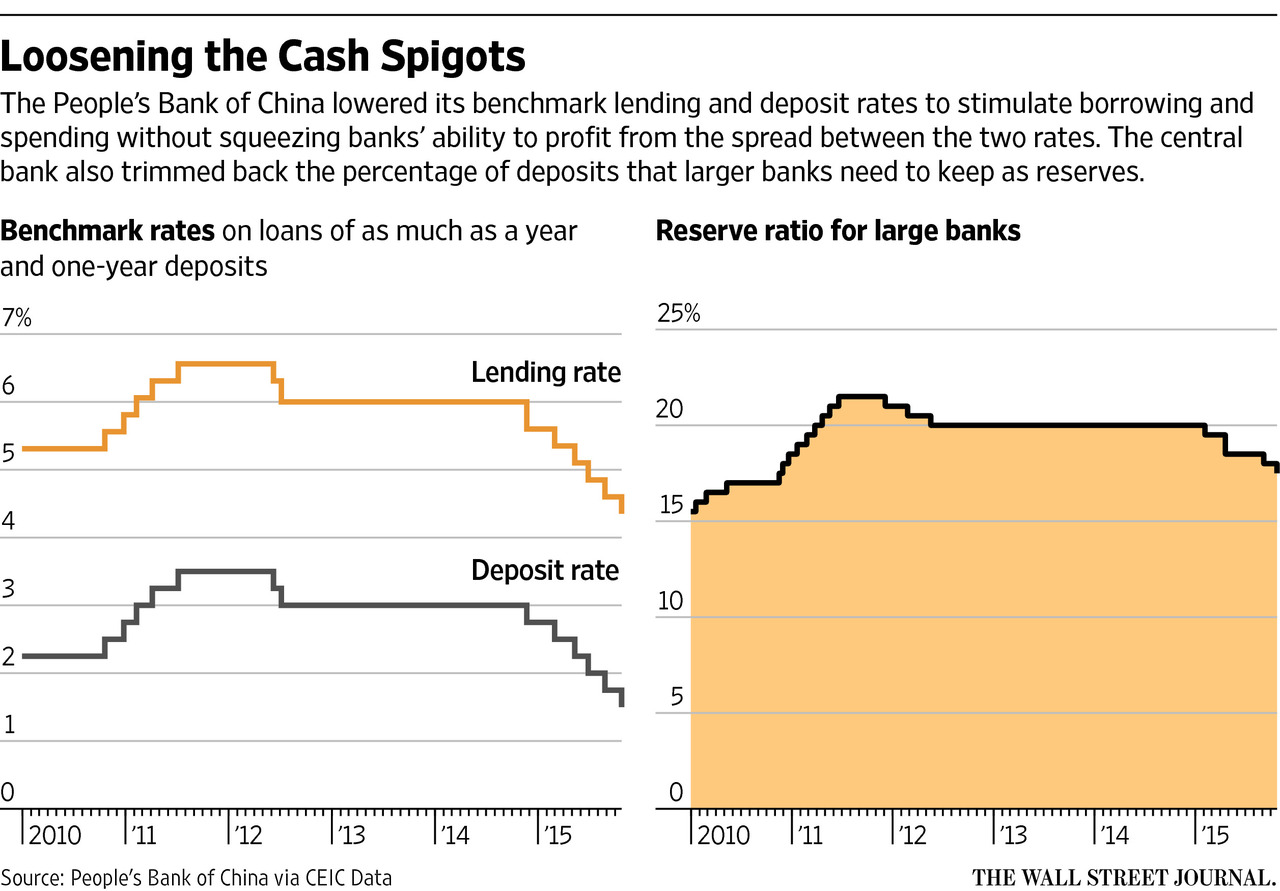
Table of Contents
China's recent rate cuts have sent ripples throughout its financial system and broader economy. These monetary policy adjustments are a significant development, impacting bank lending practices, investment behavior, and overall economic growth. This article will delve into the multifaceted consequences of these policy decisions, examining both the intended outcomes and potential unintended side effects. We will explore how China's rate cuts influence everything from stimulating bank lending to impacting the global financial landscape.
<h2>Stimulating Bank Lending: The Intended Effect of China's Rate Cuts</h2>
The primary goal of China's rate cuts is to invigorate bank lending and thereby boost economic activity. This involves a complex interplay of factors.
<h3>Lower Interest Rates and Increased Borrowing</h3>
Lower interest rates directly incentivize banks to lend more. Reduced borrowing costs make loans more attractive to businesses and consumers, leading to increased demand for credit. The People's Bank of China (PBOC) has implemented several rate cuts in recent months, including reductions in the benchmark lending rate (LPR) and the medium-term lending facility (MLF) rate. For example, the 1-year LPR was lowered by X basis points in [Month, Year] and by Y basis points in [Month, Year], resulting in a notable decrease in overall lending rates. This directly translates to lower monthly payments for borrowers, freeing up capital for investment and consumption.
- Mechanism: Lower interest rates decrease the cost of funds for banks, making it cheaper for them to lend.
- Data: [Insert data comparing lending rates before and after the rate cuts. Source the data appropriately.]
- Impact: Increased access to credit stimulates business expansion and consumer spending.
<h3>Targeting Specific Sectors</h3>
The PBOC isn't applying a blanket approach. Rate cuts are strategically aimed at supporting specific sectors vital to China's economic growth. This targeted approach prioritizes:
- Infrastructure: Funding for large-scale infrastructure projects remains crucial. Lower rates make financing these projects more feasible.
- Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs): SMEs are the backbone of the Chinese economy, and access to credit is often a major bottleneck. Rate cuts are designed to ease access to capital for these businesses.
- Green Initiatives: China's commitment to environmental sustainability is driving investments in green technology. Preferential lending programs often support these projects.
Government initiatives complement these rate cuts. This includes:
- Tax incentives for businesses investing in specific sectors.
- Government guarantees on loans to reduce risks for banks.
- Special lending funds directed towards specific industries.
<h3>Transmission Mechanism Challenges</h3>
Despite the PBOC's intentions, several challenges hinder the effective transmission of lower rates to borrowers:
- Risk Aversion: Banks may remain cautious in lending, even with lower rates, due to concerns about credit risk.
- Credit Constraints: Some businesses may still face difficulty accessing credit due to credit history or other factors.
- Liquidity Trap: While not as prevalent in China as in some other economies, there is a possibility that excess liquidity may not fully translate into increased borrowing if businesses lack confidence in future prospects.
- Non-Bank Financial Institutions: The role of shadow banks and other non-bank financial institutions needs further investigation in relation to rate cut effectiveness. These institutions may not always respond to the same stimuli as traditional banks.
<h2>Impact on Economic Activity: Growth and Investment</h2>
The ultimate aim of China's rate cuts is to boost economic activity.
<h3>Increased Investment and Economic Growth</h3>
Increased lending is expected to fuel investment and subsequently drive economic growth. This manifests as:
- Higher GDP Growth: Increased investment and consumption should translate to higher Gross Domestic Product (GDP) figures.
- Job Creation: Increased economic activity typically leads to more job opportunities.
- Fixed Asset Investment: Lower rates can stimulate investment in infrastructure, manufacturing, and other sectors.
[Insert data or forecasts on projected economic growth following the rate cuts. Source the data appropriately.]
<h3>Risks of Increased Inflation</h3>
Increased lending, fueled by lower interest rates, expands the money supply. This poses a risk of increased inflation. The PBOC needs to carefully balance stimulating growth with controlling inflation.
- Inflationary Pressures: Excess money supply without a corresponding increase in goods and services can lead to higher prices.
- PBOC Strategies: The PBOC utilizes various tools to manage inflation, such as reserve requirement ratios and open market operations.
- Current Inflation Rate: [Insert data on current inflation rate in China. Source the data appropriately.]
<h3>Impact on Real Estate Market</h3>
The real estate sector is particularly sensitive to interest rate changes. Lower rates can fuel further growth, but also carry the risk of speculative bubbles.
- Housing Market: Lower mortgage rates can increase demand for housing, potentially driving up prices.
- Government Regulations: The Chinese government actively manages the real estate market through various regulations to control property prices and speculative investments.
- Property Developers: Access to credit for property developers is significantly impacted by these rate adjustments, affecting the supply of new housing units.
<h2>International Implications of China's Rate Cuts</h2>
China's economic actions rarely remain isolated. The rate cuts have global implications.
<h3>Global Capital Flows</h3>
China's rate cuts influence global capital flows:
- Capital Outflows: Lower interest rates can make investing in China less attractive compared to other countries with higher yields.
- Yuan Value: The value of the Chinese Yuan (CNY) can be affected by these policy shifts. A weaker Yuan can boost exports but also increases the cost of imports.
- Emerging Market Economies: China's rate cuts can have spillover effects on other emerging market economies, impacting capital flows and exchange rates.
<h3>Geopolitical Considerations</h3>
China's domestic economic policies are intricately linked with its geopolitical strategy. The rate cuts are not just a monetary policy decision but are also part of a broader economic and geopolitical strategy.
<h2>Conclusion</h2>
China's rate cuts are a powerful tool with wide-ranging implications. While aimed at stimulating bank lending and boosting the economy, careful consideration must be given to potential downsides such as inflation and asset bubbles. The ultimate effectiveness of these cuts hinges on successful transmission to borrowers and proactive management of potential risks. Continuous monitoring of China's rate cuts and their impact is vital to fully understanding the long-term consequences of this significant policy decision. Stay informed on the latest developments concerning China's rate cuts and their influence on the global economy.

Featured Posts
-
 2025 Ptt Is Basvurulari Tarihler Sartlar Ve Basvuru Kilavuzu
May 08, 2025
2025 Ptt Is Basvurulari Tarihler Sartlar Ve Basvuru Kilavuzu
May 08, 2025 -
 Este Betis Historia Del Real Betis Balompie
May 08, 2025
Este Betis Historia Del Real Betis Balompie
May 08, 2025 -
 Todays Weather Partly Cloudy With Temperature Range
May 08, 2025
Todays Weather Partly Cloudy With Temperature Range
May 08, 2025 -
 Chinas Growing Presence In Greenland A Threat To Us Interests
May 08, 2025
Chinas Growing Presence In Greenland A Threat To Us Interests
May 08, 2025 -
 Analysis Trump Medias Partnership With Crypto Com And Its Effect On Cro
May 08, 2025
Analysis Trump Medias Partnership With Crypto Com And Its Effect On Cro
May 08, 2025
