The Economic Impact Of Trump's China Tariffs: Higher Costs And Scarcity
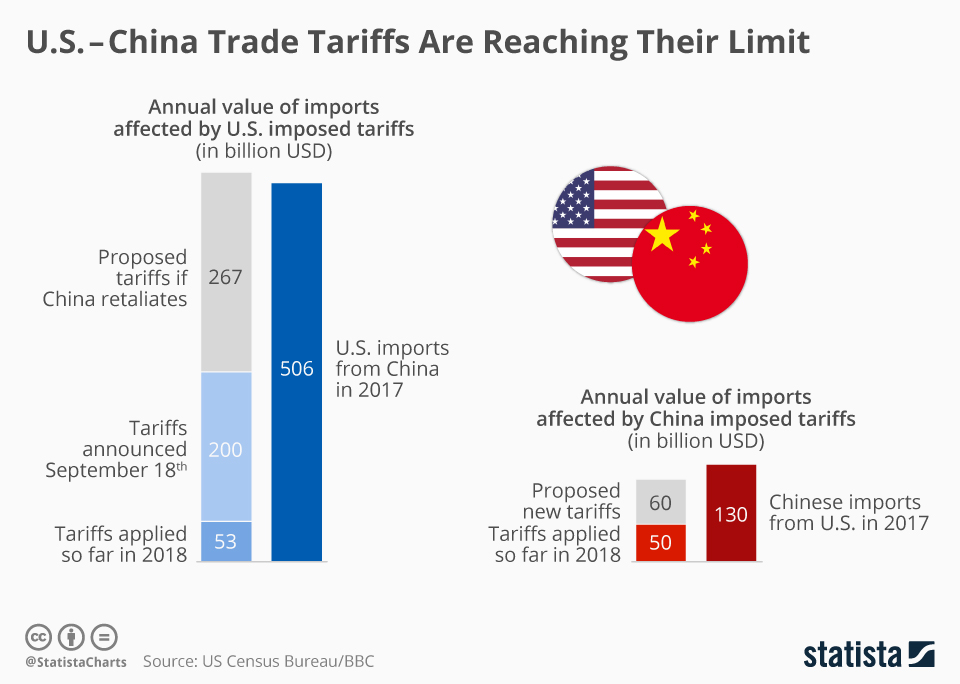
Table of Contents
Increased Prices for Consumers
The tariffs implemented by the Trump administration dramatically increased the cost of numerous goods imported from China, directly impacting American consumers' wallets.
Impact on Everyday Goods
The impact wasn't limited to niche products; everyday items felt the brunt of the tariff increases.
- Electronics: Smartphones, laptops, and televisions saw noticeable price hikes, with some estimates showing increases of 10-15%.
- Clothing and Footwear: The cost of apparel and shoes rose, impacting consumers' purchasing power, particularly for low-income households.
- Furniture: Consumers faced higher prices on furniture, impacting home furnishing and renovation projects.
These price increases are well documented. A study by the Peterson Institute for International Economics found a direct correlation between the tariffs and increased consumer prices, estimating that the average American household paid an extra $831 annually due to these tariffs. The disproportionate impact on low-income families is significant, as they allocate a larger percentage of their income to essential goods, making price increases particularly burdensome.
The Ripple Effect on Inflation
The increased import costs didn't just affect the price of imported goods; they had a ripple effect, contributing to broader inflation across the economy.
- Increased input costs for businesses: Manufacturers and retailers faced higher costs for raw materials and components, forcing them to raise prices for their finished products.
- Reduced consumer spending: Higher prices reduced consumer purchasing power, leading to decreased demand and potentially slowing economic growth.
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) showed a notable increase during the period of increased tariffs, further supporting the link between trade policies and inflation. This broader inflationary pressure impacted various sectors and exacerbated existing economic challenges.
Reduced Availability and Supply Chain Disruptions
Beyond price increases, the tariffs also led to significant disruptions in the availability of goods and exacerbated existing supply chain challenges.
Scarcity of Goods
The reduced imports due to tariffs resulted in shortages of specific goods.
- Certain electronic components: Manufacturers faced delays and shortages of crucial parts, impacting production schedules.
- Specialized machinery: Businesses reliant on specific machinery imported from China experienced disruptions.
- Specific consumer goods: The availability of certain clothing items, furniture, and other goods decreased.
This scarcity not only frustrated consumers but also significantly impacted businesses relying on a steady supply of imported goods for production or resale.
Supply Chain Bottlenecks
The tariffs further complicated already strained supply chains, leading to significant delays and increased transportation costs.
- Increased port congestion: Tariffs led to a surge in imports at the beginning of the implementation before slowing drastically, further complicating logistics.
- Longer shipping times: Businesses experienced longer lead times for receiving goods, impacting inventory management and production schedules.
- Increased transportation costs: The added complexity and delays resulted in higher freight and logistics costs, adding to the overall price increases.
These supply chain bottlenecks significantly impacted businesses' ability to meet consumer demand, leading to decreased productivity and potentially lost revenue.
Impact on Specific Industries
The effects of the tariffs weren't uniform across all industries; some were hit harder than others.
Manufacturing Sector
US manufacturers faced a double whammy. Some relied on imported components from China, driving up their production costs. Others faced increased competition from foreign producers who could offer lower prices due to not being subject to the same tariffs.
- Automotive industry: Car manufacturers experienced increased costs for parts sourced from China.
- Electronics manufacturing: Companies faced higher costs for components and potentially lost market share to competitors in other countries.
- Textile and apparel manufacturing: US manufacturers faced stiffer competition from producers in countries not subject to tariffs.
These challenges led to job losses in some sectors and reduced investment in others.
Retail Sector
Retailers were forced to either absorb the increased costs, reducing profit margins, or pass them on to consumers, potentially impacting sales.
- Reduced profit margins: Retailers saw a decrease in profitability as they struggled to absorb higher costs.
- Decreased consumer spending: Higher prices led to decreased consumer spending, affecting retailers' sales.
- Shift in consumer behavior: Consumers sought alternatives, like buying from cheaper sources (even if quality suffered), and adjusted their spending habits to account for price increases.
The retail sector bore a significant brunt of the economic consequences, grappling with decreased profitability and adapting to changing consumer behavior.
Counterarguments and Alternative Perspectives
It's important to acknowledge that some argued that the tariffs were necessary to protect domestic industries and promote economic growth. Proponents believed that the tariffs would encourage domestic production, reduce reliance on foreign imports, and create American jobs. However, the evidence suggests that these benefits, if any, were outweighed by the negative consequences detailed above. The complexity of the issue lies in the trade-offs between short-term economic pain and potentially long-term gains from protecting certain industries. Analyzing data on domestic industry growth during and after the tariff implementation is necessary to obtain a comprehensive understanding.
Conclusion: Understanding the Long-Term Economic Effects of Trump's China Tariffs
In conclusion, the Trump administration's tariffs on Chinese imports had significant and largely negative economic consequences. Higher prices for consumers, reduced availability of goods, and widespread supply chain disruptions were the key takeaways. These effects disproportionately impacted low-income households and strained businesses across multiple sectors. While arguments exist in favor of such tariffs, the evidence points to a substantial negative impact on the overall American economy. Learn more about the lasting impact of the Trump administration's China tariffs and analyze the broader effects of trade wars and their influence on economic stability by researching keywords like "economic impact of tariffs," "China trade war," and "supply chain disruptions."

Featured Posts
-
 Akeso Stock Drops After Cancer Drug Trial Fails To Meet Expectations
Apr 29, 2025
Akeso Stock Drops After Cancer Drug Trial Fails To Meet Expectations
Apr 29, 2025 -
 10 New Nuclear Reactors Approved In China A Major Expansion
Apr 29, 2025
10 New Nuclear Reactors Approved In China A Major Expansion
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Technical Issue Forces Blue Origin To Postpone Rocket Launch
Apr 29, 2025
Technical Issue Forces Blue Origin To Postpone Rocket Launch
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Lynas Texas Refinery Seeking Us Government Support To Combat Rising Costs
Apr 29, 2025
Lynas Texas Refinery Seeking Us Government Support To Combat Rising Costs
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Trumps China Tariffs Higher Prices And Empty Shelves In The Us
Apr 29, 2025
Trumps China Tariffs Higher Prices And Empty Shelves In The Us
Apr 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Exclusive Ivy League Universities Create Coalition To Oppose Trump
Apr 29, 2025
Exclusive Ivy League Universities Create Coalition To Oppose Trump
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Top Universities Unite Against Trump Administration An Exclusive Look
Apr 29, 2025
Top Universities Unite Against Trump Administration An Exclusive Look
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Elite Universities Form Private Group To Counter Trump Administration Policies
Apr 29, 2025
Elite Universities Form Private Group To Counter Trump Administration Policies
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Beyond Quinoa Discover The Next Generation Of Healthy Grains
Apr 29, 2025
Beyond Quinoa Discover The Next Generation Of Healthy Grains
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Is This The New Quinoa A Look At The Latest Superfood Trend
Apr 29, 2025
Is This The New Quinoa A Look At The Latest Superfood Trend
Apr 29, 2025
