Significant Drop In Indonesia's Reserves: A Consequence Of Rupiah Pressure
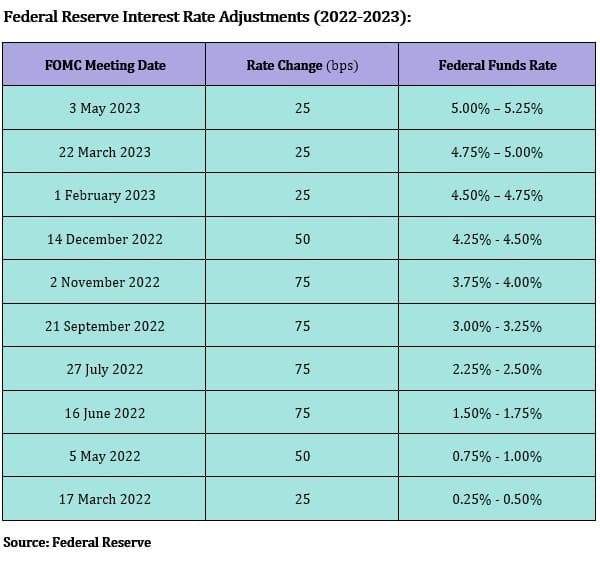
Table of Contents
The Weakening Rupiah: A Primary Driver
The weakening Rupiah is undeniably a primary driver of the decline in Indonesia's foreign exchange reserves. Understanding the factors contributing to the Rupiah's volatility is crucial to grasping the current crisis.
Understanding the Rupiah's Volatility
Several factors influence the Rupiah's exchange rate, creating a complex and volatile environment. These include:
-
Global Economic Uncertainty: Global recessionary fears and geopolitical instability significantly impact investor confidence, leading to capital flight and a weakening Rupiah. For example, the ongoing war in Ukraine and rising interest rates in developed economies have created significant uncertainty, impacting emerging markets like Indonesia.
-
Interest Rate Differentials: Interest rate hikes in developed countries, like the US, attract foreign investment, leading to capital outflow from Indonesia and putting downward pressure on the Rupiah. Conversely, lower interest rates in Indonesia compared to other countries can also contribute to the weakening of the currency.
-
Commodity Prices: Indonesia's economy is heavily reliant on commodity exports, particularly oil and palm oil. Fluctuations in global commodity prices directly affect the Rupiah's value. A decline in global commodity prices can negatively impact export revenues and weaken the Rupiah.
The Impact of Capital Outflows
A weakening Rupiah incentivizes capital flight as foreign investors seek higher returns elsewhere, reducing foreign direct investment (FDI) and further depleting Indonesia's foreign exchange reserves.
-
Mechanics of Capital Outflows: When the Rupiah weakens, foreign investors holding Rupiah-denominated assets may convert their holdings into stronger currencies, leading to a net outflow of capital. This puts downward pressure on the Rupiah and reduces the supply of foreign currency available to the central bank.
-
Statistics Illustrating Capital Outflow Trends: [Insert relevant statistics and data on capital outflows from credible sources, e.g., Bank Indonesia reports, IMF data]. These statistics should clearly show the correlation between the weakening Rupiah and the outflow of capital.
-
Examples of Investors Pulling Out: [Cite specific examples of investors reducing their exposure to Indonesian assets due to Rupiah weakness. Include links to news articles or official statements if possible].
The Role of Import Dependence
Indonesia's reliance on imports exacerbates the impact of a weaker Rupiah on its foreign exchange reserves.
Indonesia's Reliance on Imports
Indonesia's import-heavy economy, characterized by a significant reliance on imported goods, makes it highly vulnerable to currency fluctuations.
-
Key Imported Goods and Cost in Rupiah: [Provide examples of key imported goods such as fuel, machinery, and consumer goods, illustrating their cost in Rupiah and how this cost increases with a weaker Rupiah].
-
Impact of a Weaker Rupiah on Import Costs: A weaker Rupiah increases the Rupiah cost of imports, placing pressure on the current account balance and further depleting foreign exchange reserves. This also affects the overall cost of living in Indonesia.
-
Statistics Illustrating Import Dependence: [Insert relevant statistics on Indonesia's import dependence from credible sources. This should highlight the significant proportion of imports to GDP].
The Impact on Inflation
Increased import costs, due to the weaker Rupiah, inevitably lead to inflationary pressures in Indonesia.
-
Inflationary Pressures of Higher Import Prices: Higher import costs translate to higher consumer prices, impacting the purchasing power of Indonesian citizens. This can lead to social unrest and economic instability.
-
Potential Government Responses to Rising Inflation: The Indonesian government might respond by implementing measures such as interest rate hikes to curb inflation, potentially further weakening economic growth.
Government Interventions and Policy Responses
The Indonesian government, through Bank Indonesia (BI) and fiscal policy adjustments, has been actively trying to mitigate the impact of the weakening Rupiah.
Bank Indonesia's Actions
Bank Indonesia (BI) has employed several measures to stabilize the Rupiah and manage foreign exchange reserves.
-
Examples of BI Interventions: These include adjusting interest rates to attract foreign investment and intervening in the foreign exchange market to manage the Rupiah's value. Specific examples of interest rate adjustments and forex interventions should be included here.
-
Assessment of the Effectiveness of BI's Policies: [Provide an assessment of the effectiveness of BI's interventions, citing any economic reports or analyses].
Fiscal Policy Adjustments
The Indonesian government has also implemented fiscal policy changes to address the situation.
-
Examples of Fiscal Policy Adjustments: These may include budget cuts, tax adjustments, or other measures aimed at reducing the current account deficit and bolstering the Rupiah.
-
Assessment of the Effectiveness of Fiscal Policy Measures: [Provide an assessment of the effectiveness of fiscal policy measures implemented by the Indonesian government, referencing credible sources].
Conclusion
The significant drop in Indonesia's foreign exchange reserves is largely attributable to the weakening Rupiah, exacerbated by import dependence and capital outflows. The Indonesian government's responses, through Bank Indonesia's monetary policy interventions and fiscal adjustments, are crucial in navigating this challenging economic environment. The outlook for Indonesia's foreign exchange reserves remains uncertain, heavily dependent on global economic conditions and the success of these policy interventions.
To better understand the evolving situation, it's vital to monitor the fluctuations of the Rupiah and Indonesia's foreign exchange reserves. Stay updated on the impact of Rupiah pressure on Indonesia's economic stability by following reputable economic news sources and reports from Bank Indonesia and the Indonesian government. Closely observing these factors will be crucial in assessing the future trajectory of the Indonesian economy and its capacity to maintain financial stability.

Featured Posts
-
 108 000 Funding Injection For Madeleine Mc Cann Case
May 09, 2025
108 000 Funding Injection For Madeleine Mc Cann Case
May 09, 2025 -
 Bayern Munich Stunned By Inter Milan In Champions League Quarterfinal
May 09, 2025
Bayern Munich Stunned By Inter Milan In Champions League Quarterfinal
May 09, 2025 -
 F1 News Alpine Team Principals Strong Statement To Doohan
May 09, 2025
F1 News Alpine Team Principals Strong Statement To Doohan
May 09, 2025 -
 Sporedba Dali Neko Mu Parira Na Bekam
May 09, 2025
Sporedba Dali Neko Mu Parira Na Bekam
May 09, 2025 -
 Elon Musks Net Worth How Us Policy Impacts Teslas Ceo Fortune
May 09, 2025
Elon Musks Net Worth How Us Policy Impacts Teslas Ceo Fortune
May 09, 2025
