Recent Study Shows Elevated ADHD Rates In Adults With Autism And Intellectual Disabilities
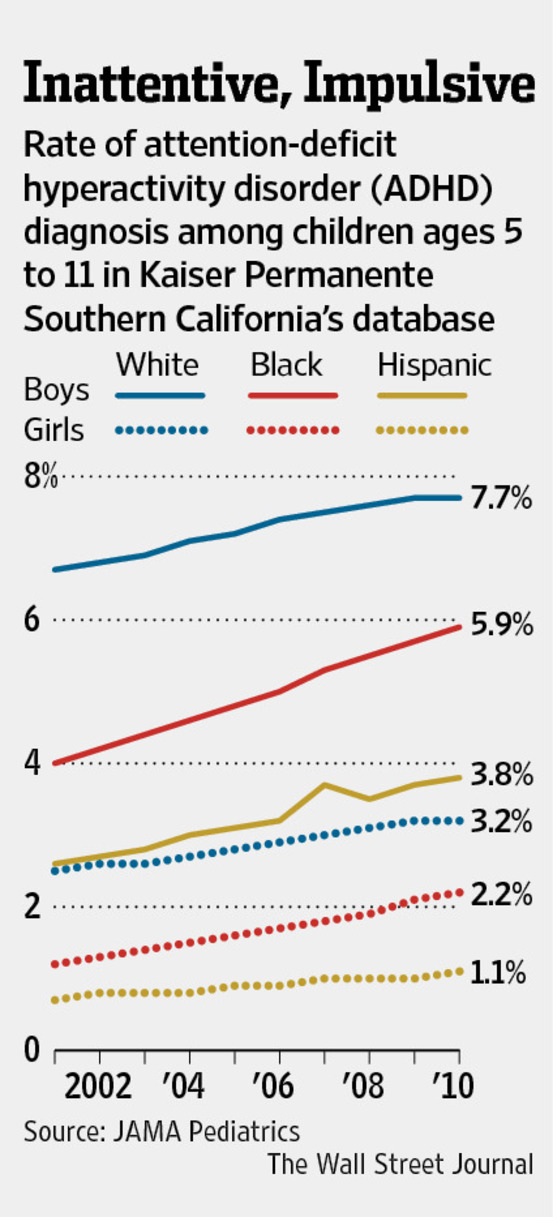
Table of Contents
The Study's Methodology and Findings
This pivotal research employed a robust methodology to investigate the prevalence of ADHD in adults with autism and intellectual disabilities. The study involved a substantial sample size of [Insert Sample Size Here] adults, ensuring statistically significant results. Participants were recruited from [Insert Recruitment Sources Here] and underwent comprehensive diagnostic assessments using a combination of standardized tools.
- Diagnostic Tools: The study utilized validated assessment instruments including the [List Specific Diagnostic Tools, e.g., Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale, Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule, Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale].
- Participant Demographics: The participants comprised a diverse group, with an age range of [Insert Age Range Here], and a gender distribution of [Insert Gender Distribution Here]. The study specifically focused on adults to address the often-overlooked prevalence of ADHD in this age group.
- Key Findings: The research produced compelling evidence of a significantly elevated prevalence of ADHD in adults with autism and intellectual disabilities. Specifically, [Insert Percentage or Ratio Here] of participants diagnosed with autism and intellectual disabilities also met the criteria for ADHD. This finding was statistically significant (p < 0.05).
- Study Limitations: While the study provides valuable insights, it's important to acknowledge limitations such as [Insert Limitations, e.g., potential sampling bias, reliance on self-report measures]. Further research with larger, more diverse samples is needed to generalize these findings.
Understanding the Co-occurrence of ADHD, Autism, and Intellectual Disabilities
The high comorbidity of ADHD, autism, and intellectual disabilities suggests a complex interplay of genetic, neurological, and environmental factors. Many symptoms overlap, making accurate diagnosis challenging.
- Overlapping Symptoms: Inattention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity—core symptoms of ADHD—can also manifest in autism and intellectual disabilities, creating diagnostic ambiguity. For example, difficulties with executive function, common in all three conditions, can lead to challenges with organization, planning, and task completion.
- Neurobiological Links: Research suggests potential shared genetic vulnerabilities or neurological pathways contributing to the co-occurrence of these conditions. Further investigation into the underlying neurobiological mechanisms is needed to clarify these relationships.
- Impact on Daily Functioning: The combined effects of ADHD, autism, and intellectual disabilities can significantly impact daily functioning, leading to difficulties in academic, occupational, and social spheres. This emphasizes the importance of comprehensive assessment and tailored support.
Challenges in Diagnosis and Treatment
Accurately diagnosing ADHD in individuals with autism and intellectual disabilities presents unique challenges due to the overlap of symptoms. A multidisciplinary approach is essential for effective assessment and treatment planning.
- Comprehensive Assessments: Behavioral observations, alongside clinical interviews and standardized assessments, are crucial for differentiating ADHD symptoms from those associated with autism and intellectual disabilities. This process often requires the expertise of multiple professionals.
- Role of Specialists: A collaborative team, including psychologists, psychiatrists, neurologists, and occupational therapists, is often necessary for a comprehensive evaluation and individualized treatment plan. Each specialist brings a unique perspective and expertise to address the multifaceted needs of these individuals.
- Effective Treatment Strategies: Treatment approaches may involve a combination of medication, therapy (such as cognitive behavioral therapy or behavioral interventions), and educational support. Medication management requires careful monitoring due to potential side effects and interactions with other medications.
Implications for Support Services and Future Research
The findings underscore the critical need for improved training and resources for professionals working with adults who have ADHD, autism, and intellectual disabilities. Tailored support services are essential to address their unique needs and improve their quality of life.
- Improving Diagnostic Practices: Increased training on differential diagnosis, utilizing validated assessment tools, and employing multidisciplinary approaches are essential steps towards improving diagnostic accuracy.
- Specialized Support Programs: Development of specialized support programs addressing the unique challenges faced by individuals with co-occurring conditions is crucial. These programs should incorporate individualized educational plans, vocational training, and social skills development.
- Future Research Directions: Further research is needed to explore the underlying genetic and neurological mechanisms contributing to the co-occurrence of these conditions. Longitudinal studies tracking long-term outcomes and the effectiveness of different interventions are also vital. Investigating the efficacy of specific therapeutic interventions tailored to this population is also a critical area for future research.
Conclusion
This study underscores the significantly elevated rates of ADHD in adults with autism and intellectual disabilities, highlighting the substantial challenges in diagnosis and treatment. The overlapping symptoms and complex interplay of these conditions necessitate a comprehensive, multidisciplinary approach involving skilled professionals. Improved training, tailored support services, and continued research are crucial for optimizing the lives of these individuals and their families. Learn more about the co-occurrence of ADHD, autism, and intellectual disabilities and share this article to raise awareness of ADHD in adults with Autism and Intellectual Disabilities. If you suspect that you or someone you know may be affected, seek professional help for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Early intervention and appropriate support are key to improving outcomes for individuals with these complex co-occurring conditions.

Featured Posts
-
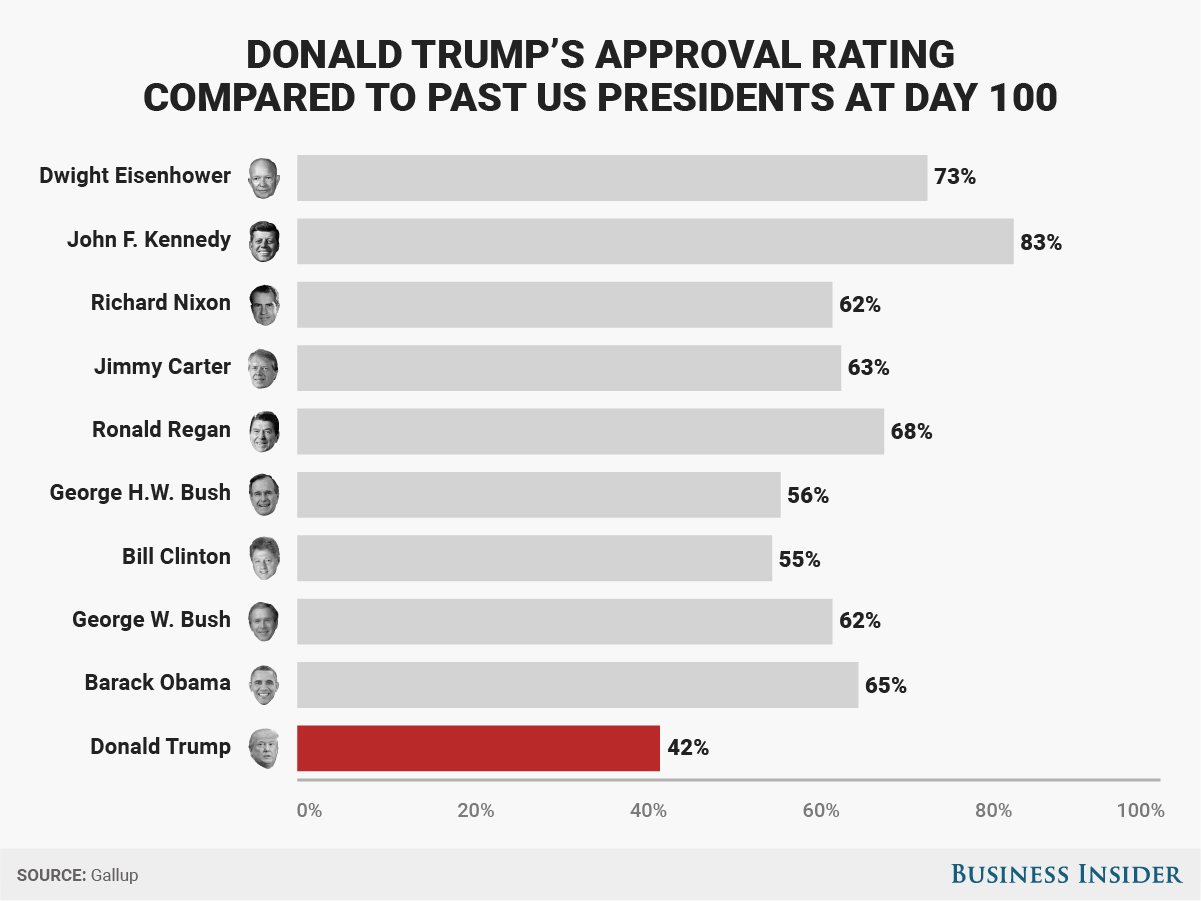 U S Dollars First 100 Days Under Scrutiny A Presidential Economic Comparison
Apr 29, 2025
U S Dollars First 100 Days Under Scrutiny A Presidential Economic Comparison
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Attorney General Targets Minnesota Over Transgender Athlete Ban Compliance Deadline Looms
Apr 29, 2025
Attorney General Targets Minnesota Over Transgender Athlete Ban Compliance Deadline Looms
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Louisville State Of Emergency Tornado Damage And Severe Flooding Forecast
Apr 29, 2025
Louisville State Of Emergency Tornado Damage And Severe Flooding Forecast
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Chinas Nuclear Power Push Approval For 10 New Reactors
Apr 29, 2025
Chinas Nuclear Power Push Approval For 10 New Reactors
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Cassidy Hutchinsons Memoir Key Jan 6 Witness To Detail Hearings In Upcoming Book
Apr 29, 2025
Cassidy Hutchinsons Memoir Key Jan 6 Witness To Detail Hearings In Upcoming Book
Apr 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Our Yorkshire Farm Family Reuben Owens News On His Brothers And Sisters
Apr 30, 2025
Our Yorkshire Farm Family Reuben Owens News On His Brothers And Sisters
Apr 30, 2025 -
 A Glimpse Into Chaos Amanda Owens Photos Of Her Nine Children
Apr 30, 2025
A Glimpse Into Chaos Amanda Owens Photos Of Her Nine Children
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Our Yorkshire Farms Amanda Owen Addresses Ongoing Disputes With Clive
Apr 30, 2025
Our Yorkshire Farms Amanda Owen Addresses Ongoing Disputes With Clive
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Amanda Owen Speaks Out Following Devastating Loss On Our Yorkshire Farm
Apr 30, 2025
Amanda Owen Speaks Out Following Devastating Loss On Our Yorkshire Farm
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Amanda Owen Shares Hilarious Photos Of Her 9 Childrens Chaos
Apr 30, 2025
Amanda Owen Shares Hilarious Photos Of Her 9 Childrens Chaos
Apr 30, 2025
