Planning A Reactor Power Uprate? Navigating The NRC Process
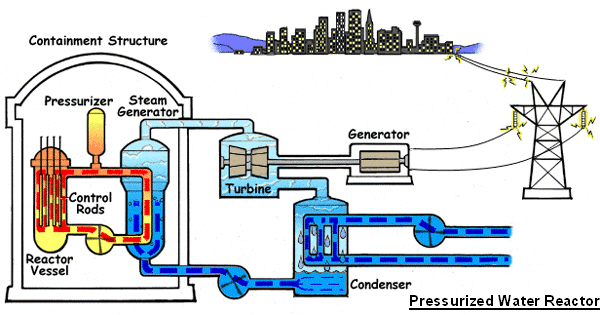
Table of Contents
Understanding the NRC's Role in Reactor Power Uprates
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) holds ultimate authority over all aspects of nuclear power plant operations in the United States, and reactor power uprates are no exception. Their oversight ensures the safety and security of the public and the environment. The NRC's role extends to every stage of the project, from initial application to final approval and ongoing monitoring.
To legally proceed with a reactor power uprate, you'll need several crucial licenses and permits. This typically involves amendments to your existing operating license, requiring a rigorous demonstration of continued compliance with all relevant safety regulations. The application process is demanding and involves extensive documentation.
- Detailed safety analysis requirements: The NRC mandates comprehensive safety analyses demonstrating that the uprated power level won't compromise plant safety or increase the risk of accidents. This includes thorough evaluations of thermal-hydraulic limits, emergency core cooling systems, and other critical safety functions.
- Environmental impact assessments: A detailed environmental impact statement (EIS) is usually required, assessing the potential environmental consequences of the increased power output. This might include analyses of water usage, thermal discharges, and potential impacts on local ecosystems.
- Compliance with existing regulations and standards: Adherence to all existing NRC regulations, industry standards (e.g., ASME codes), and best practices is paramount throughout the entire process. Any deviation requires thorough justification and NRC approval.
- Public engagement and notification processes: The NRC requires proactive public engagement and notification, ensuring transparency and addressing any public concerns regarding the reactor power uprate project. This often involves public meetings, information dissemination, and opportunities for public comment.
Pre-Application Planning for a Successful Reactor Power Uprate
Thorough preparation before submitting your application is paramount to a successful reactor power uprate. Jumping into the application process without a solid plan will likely lead to delays, increased costs, and potential project failure. A well-defined pre-application phase is crucial.
Conducting preliminary feasibility studies is the first critical step. This involves a comprehensive assessment of your plant's capabilities and limitations, identifying potential technical challenges and assessing the economic viability of the project.
- Assessment of plant capabilities and limitations: Evaluate the existing infrastructure, equipment, and systems to determine their capacity to handle the increased power output. This includes analyzing the capabilities of the reactor core, turbine generator, and all associated systems.
- Identification of potential technical challenges: Proactively identify and address potential technical hurdles, such as limitations in cooling systems, instrumentation, or control systems. Early identification allows for proactive planning and mitigation.
- Development of a detailed project schedule and budget: Create a comprehensive project schedule outlining all key milestones and deadlines. A realistic budget, encompassing all anticipated costs, including engineering, licensing, construction, and testing, is equally crucial.
- Assembling a qualified team of engineers and consultants: Recruit experienced professionals with expertise in nuclear engineering, regulatory compliance, and project management to ensure the project's success. Their specialized knowledge is invaluable during all stages.
- Early engagement with the NRC: Initiate early discussions with the NRC to establish a clear understanding of their expectations and to gain preliminary feedback on your plans. This fosters a collaborative relationship and minimizes future surprises.
Technical Aspects of Reactor Power Uprates
The technical considerations for a reactor power uprate are extensive and demand meticulous attention to detail. A successful uprate necessitates a thorough understanding of the complex interactions within the nuclear power plant.
- Thermal-hydraulic analysis: This crucial analysis evaluates the plant's thermal and hydraulic performance at the increased power level, ensuring the integrity of the reactor core and other critical components.
- Safety system upgrades: Existing safety systems may require upgrades or modifications to maintain adequate safety margins at the higher power level. This often involves enhancing capacity and redundancy.
- Instrumentation and control modifications: Instrumentation and control systems may need adjustments or upgrades to accurately monitor and control the plant's operation at the higher power level.
- Fuel management strategies: Revised fuel management strategies may be necessary to optimize fuel utilization and ensure safe and efficient operation at the increased power level.
- Potential impact on plant life extension: Consider the impact of the uprate on the plant's overall lifespan. Proper planning can potentially extend the plant's operational life.
The NRC Application Process for Reactor Power Uprates
Submitting an application to the NRC is a complex, multi-stage process that requires meticulous attention to detail and precise adherence to NRC guidelines. The review process can be lengthy, and potential delays and challenges should be anticipated.
- Completing and submitting all necessary documentation: The application must include all required documentation, including safety analyses, environmental assessments, and detailed engineering plans. Omissions can cause significant delays.
- Responding to NRC requests for additional information: Expect the NRC to request additional information or clarification throughout the review process. Prompt and thorough responses are essential.
- Participating in NRC inspections and audits: The NRC conducts inspections and audits to verify compliance with safety regulations and the accuracy of the submitted information. Full cooperation is mandatory.
- Addressing any identified safety concerns: The NRC may identify safety concerns during the review process. Addressing these concerns promptly and effectively is crucial.
- Obtaining final NRC approval: Once all requirements are met and the NRC is satisfied with the safety and compliance aspects of the project, they will grant final approval for the reactor power uprate.
Managing Costs and Timelines in a Reactor Power Uprate
Careful budgeting and effective project management are paramount to ensure the financial viability and timely completion of a reactor power uprate. Unforeseen challenges can lead to cost overruns and schedule delays, impacting the project's overall success.
- Developing a realistic budget: Create a detailed budget that encompasses all anticipated expenses, including engineering, licensing, construction, testing, and contingency funds.
- Implementing effective project management techniques: Utilize proven project management methodologies to ensure efficient resource allocation, effective risk management, and timely completion of milestones.
- Monitoring progress and addressing potential problems proactively: Regularly monitor progress against the schedule and budget, proactively identifying and addressing potential problems before they escalate.
- Contingency planning for unforeseen challenges: Develop contingency plans to mitigate the impact of unforeseen events, such as equipment failures, regulatory delays, or unexpected cost increases.
- Understanding potential financial incentives and regulatory assistance: Explore potential financial incentives and regulatory assistance programs that may be available to support your reactor power uprate project.
Conclusion
Successfully completing a reactor power uprate requires meticulous planning, a profound understanding of the NRC's regulatory process, and a dedicated team of experienced professionals. From pre-application planning and technical assessments to navigating the application review and obtaining final approval, each stage demands scrupulous attention to detail and proactive engagement with the NRC. By meticulously following the steps outlined above and working closely with experienced professionals in nuclear engineering and regulatory compliance, you can significantly improve your chances of a successful reactor power uprate, maximizing the output and profitability of your nuclear power plant. Don't hesitate to consult experts for guidance on planning your reactor power uprate project. Remember, proper planning and a thorough understanding of the NRC process are the cornerstones of a successful reactor power uprate.

Featured Posts
-
 Pakstan Myn Kshmyr Ke Ywm Ykjhty Ky Wsye Pymane Pr Tqrybat
May 01, 2025
Pakstan Myn Kshmyr Ke Ywm Ykjhty Ky Wsye Pymane Pr Tqrybat
May 01, 2025 -
 Los Angeles Wildfires And The Ethics Of Disaster Gambling
May 01, 2025
Los Angeles Wildfires And The Ethics Of Disaster Gambling
May 01, 2025 -
 Xrp Ripple Below 3 Investment Analysis And Risks
May 01, 2025
Xrp Ripple Below 3 Investment Analysis And Risks
May 01, 2025 -
 Meer Dan Duizend Limburgse Ondernemers Wachten Op Aansluiting Enexis
May 01, 2025
Meer Dan Duizend Limburgse Ondernemers Wachten Op Aansluiting Enexis
May 01, 2025 -
 Michael Sheen And Sharon Horgans British Drama A New Streaming Home
May 01, 2025
Michael Sheen And Sharon Horgans British Drama A New Streaming Home
May 01, 2025
Latest Posts
-
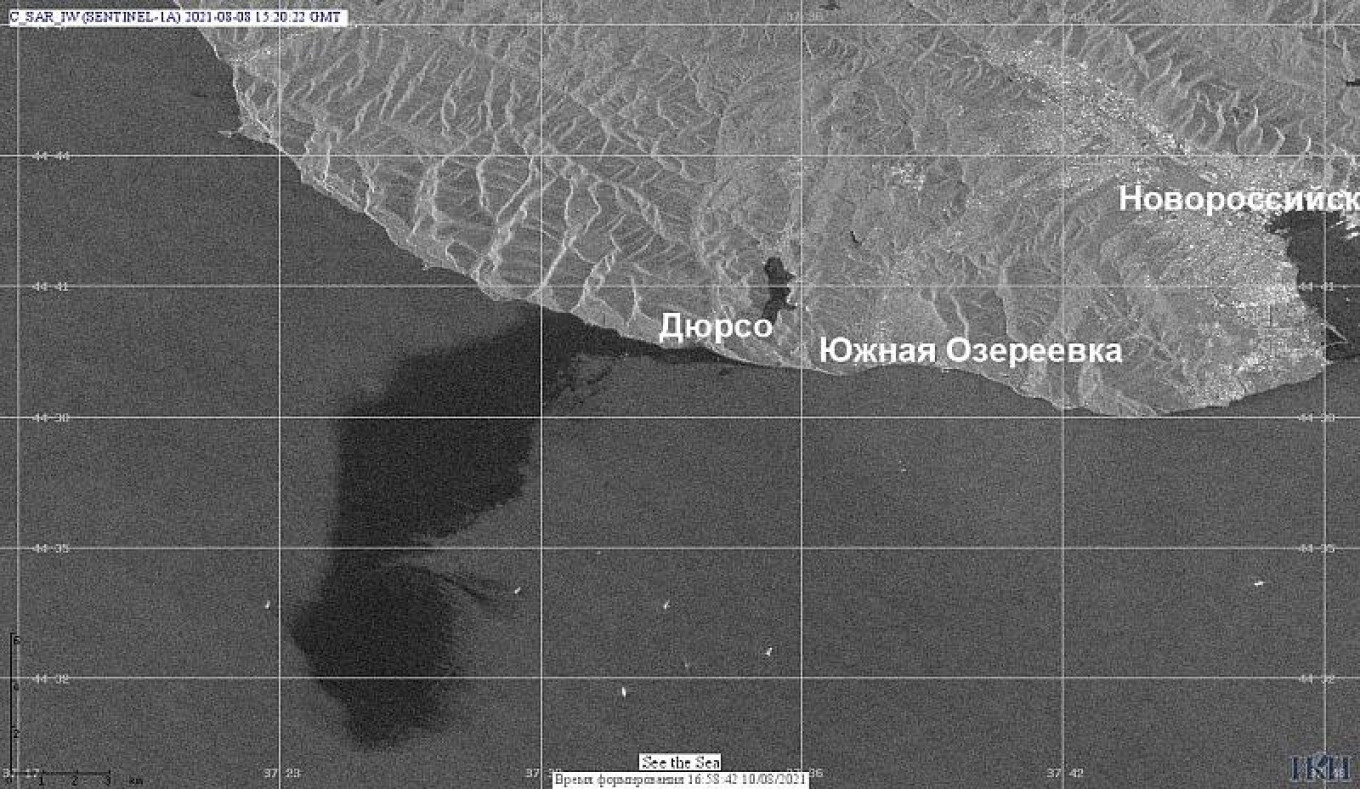 Major Oil Spill Forces Closure Of 62 Miles Of Russian Black Sea Beaches
May 01, 2025
Major Oil Spill Forces Closure Of 62 Miles Of Russian Black Sea Beaches
May 01, 2025 -
 39 Approval Trumps First 100 Days And The Impact Of Travel Restrictions
May 01, 2025
39 Approval Trumps First 100 Days And The Impact Of Travel Restrictions
May 01, 2025 -
 Black Sea Beaches Closed Russias Response To Major Oil Spill
May 01, 2025
Black Sea Beaches Closed Russias Response To Major Oil Spill
May 01, 2025 -
 Trump Approval Rating Drops To 39 Analysis Of The First 100 Days
May 01, 2025
Trump Approval Rating Drops To 39 Analysis Of The First 100 Days
May 01, 2025 -
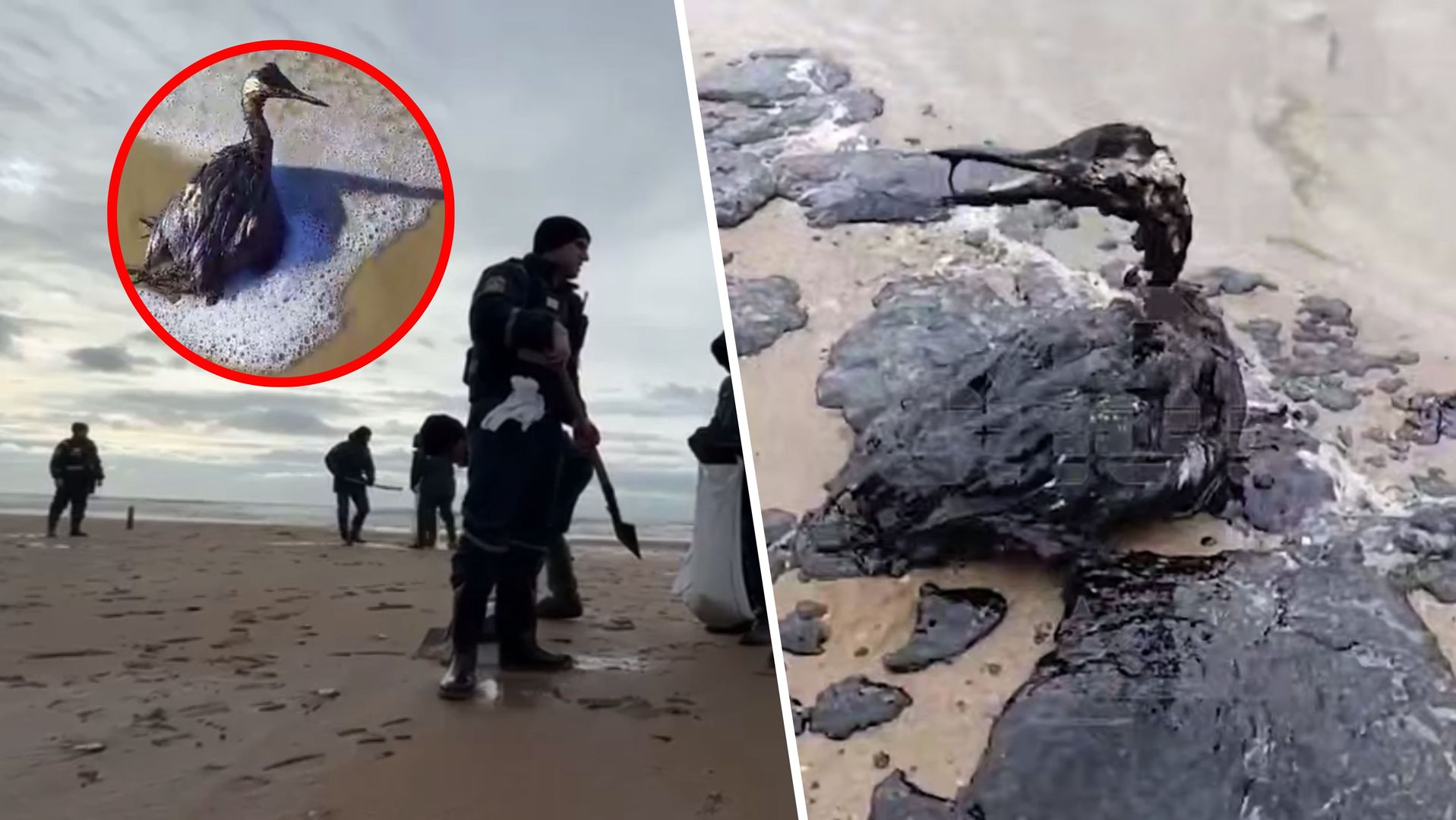 Russia Closes 62 Miles Of Black Sea Beaches Following Oil Spill
May 01, 2025
Russia Closes 62 Miles Of Black Sea Beaches Following Oil Spill
May 01, 2025
