No Rate Hike: U.S. Federal Reserve Addresses Inflation And Unemployment Challenges
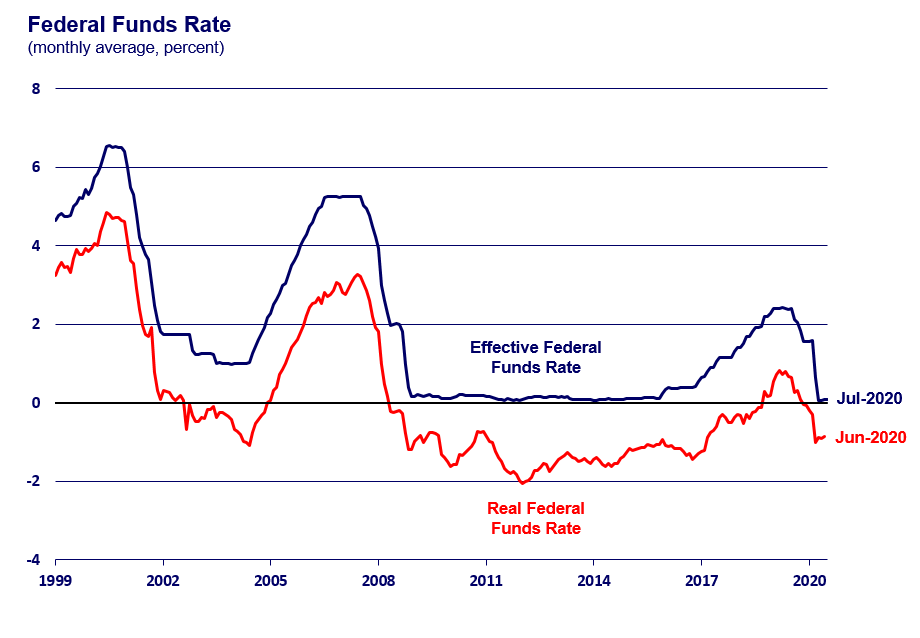
Table of Contents
The Federal Reserve's Rationale for No Rate Hike
The Federal Reserve's decision to maintain interest rates stemmed from a careful assessment of several key economic factors. The delicate balancing act between controlling inflation and fostering employment growth played a central role.
Inflationary Pressures
Current inflation rates remain stubbornly high. While showing signs of moderation, inflation still significantly surpasses the Federal Reserve's target of 2%. Several factors contribute to this persistent inflationary pressure:
- Supply chain disruptions: Ongoing global supply chain bottlenecks continue to impact the availability and prices of goods.
- Elevated energy prices: Fluctuations in global energy markets, particularly oil and natural gas, have significantly influenced inflation.
- Strong consumer demand: Robust consumer spending, fueled by pent-up demand and government stimulus, has put upward pressure on prices.
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) and the Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) index, key measures of inflation, remain above the Fed's target, though recent data suggests a potential slowing of the inflation rate. The Fed closely monitors these indexes to gauge the effectiveness of its monetary policy.
Unemployment Concerns
The current unemployment rate is relatively low, indicating a tight labor market. However, the Fed's dual mandate requires it to consider both price stability and maximum employment. While a low unemployment rate is generally positive, it can also contribute to upward pressure on wages and, consequently, inflation.
- Unemployment rate: [Insert current unemployment rate data from a reputable source].
- Labor market tightness: [Discuss current indicators of labor market tightness or looseness, e.g., job openings, labor force participation rate].
The Fed carefully weighs the risks of inflation against the potential benefits of a strong labor market when making its monetary policy decisions.
Economic Growth Assessment
The pace of economic growth is another critical factor influencing the Fed's decisions. While the economy has shown resilience, there are concerns about a potential slowdown.
- GDP growth: [Insert recent GDP growth data].
- Consumer spending: [Discuss trends in consumer spending and its impact on economic growth].
- Business investment: [Analyze business investment levels and their implications for future growth].
A slowing economy could necessitate a different monetary policy approach than one geared towards cooling an overheated economy.
Market Reactions to the No Rate Hike Decision
The Federal Reserve's decision to hold off on a rate hike sent ripples throughout the financial markets.
Stock Market Response
The stock market generally reacted positively to the news, with major indexes experiencing gains in the immediate aftermath of the announcement. However, the impact varied across sectors.
- Dow Jones Industrial Average: [Insert details about the Dow's reaction].
- S&P 500: [Insert details about the S&P 500's reaction].
- Nasdaq Composite: [Insert details about the Nasdaq's reaction].
Certain sectors, such as technology, often benefit from lower interest rates, while others may be more sensitive to inflation.
Bond Market Response
Bond yields, which move inversely to prices, experienced a [increase/decrease] following the announcement. This reflects the market's expectations regarding future interest rate adjustments.
- Yield curve analysis: [Discuss the shape of the yield curve and its implications].
- Short-term interest rates: [Explain the impact on short-term borrowing costs].
- Long-term interest rates: [Explain the impact on long-term borrowing costs].
Currency Market Response
The US dollar's value against other major currencies [strengthened/weakened] following the decision. This reflects the market's assessment of the relative attractiveness of US assets.
- Exchange rate fluctuations: [Provide specific examples of exchange rate changes].
- Impact on international trade: [Discuss potential consequences for US exports and imports].
Long-Term Implications of the No Rate Hike Policy
The decision to hold off on a rate hike has significant long-term implications for the US economy.
Potential for Future Rate Hikes
The possibility of future rate increases remains very real. The Fed's decision to hold rates steady doesn't signal an end to its fight against inflation. Several factors could trigger future rate hikes:
- Persistent high inflation: If inflation remains stubbornly high, the Fed is likely to act.
- Accelerated wage growth: Rapid wage growth can fuel inflationary pressures.
- Stronger-than-expected economic growth: If the economy overheats, the Fed may need to cool it down with rate hikes.
The Fed will continue to closely monitor economic data and adjust its policy as needed.
Impact on Consumer Spending and Borrowing
The "no rate hike" decision could encourage continued consumer spending and borrowing, potentially further fueling inflation if not managed carefully.
- Consumer debt: [Discuss potential implications for consumer debt levels].
- Mortgage rates: [Analyze the impact on mortgage rates and housing affordability].
- Business investment: [Discuss how the decision might influence business expansion and investment].
Overall Economic Outlook
The long-term economic outlook remains uncertain. The Fed's decision reflects a calculated risk, attempting to balance the need to control inflation with the desire to avoid triggering a recession.
- Economic growth forecast: [Provide a forecast for future economic growth].
- Inflation forecast: [Offer a prediction for future inflation rates].
- Unemployment forecast: [Predict future unemployment rates].
Conclusion: Understanding the Implications of the No Rate Hike Decision
The Federal Reserve's decision to hold off on a rate hike was a strategic move based on its assessment of inflation, unemployment, and economic growth. This decision carries significant implications for markets and the broader economy, impacting everything from stock prices and bond yields to consumer spending and business investment. While potentially offering a short-term boost to the economy, the long-term success hinges on the Fed's ability to navigate the delicate balance between controlling inflation and fostering sustainable economic growth. The path forward remains uncertain, and future adjustments are likely. Stay updated on future Federal Reserve decisions regarding rate hikes and their impact on inflation and unemployment by subscribing to our newsletter or following us on social media. Learn more about the implications of the Federal Reserve's no-rate-hike policy and its impact on the U.S. economy.

Featured Posts
-
 Exploring The He Morgan Brother 5 Theories About David In High Potential
May 10, 2025
Exploring The He Morgan Brother 5 Theories About David In High Potential
May 10, 2025 -
 Falling Reserves In Indonesia Analysis Of The Rupiahs Recent Weakness
May 10, 2025
Falling Reserves In Indonesia Analysis Of The Rupiahs Recent Weakness
May 10, 2025 -
 Behind The Scenes Of Celebrity Antiques Road Trip An Insiders Look
May 10, 2025
Behind The Scenes Of Celebrity Antiques Road Trip An Insiders Look
May 10, 2025 -
 Eu Must Do More To Counter Us Tariffs Says French Minister
May 10, 2025
Eu Must Do More To Counter Us Tariffs Says French Minister
May 10, 2025 -
 Ajaxs Brobbey A Physical Force To Reckon With In Upcoming Europa League Match
May 10, 2025
Ajaxs Brobbey A Physical Force To Reckon With In Upcoming Europa League Match
May 10, 2025
