New COVID-19 Variant Spikes Cases In Several Regions, Warns WHO
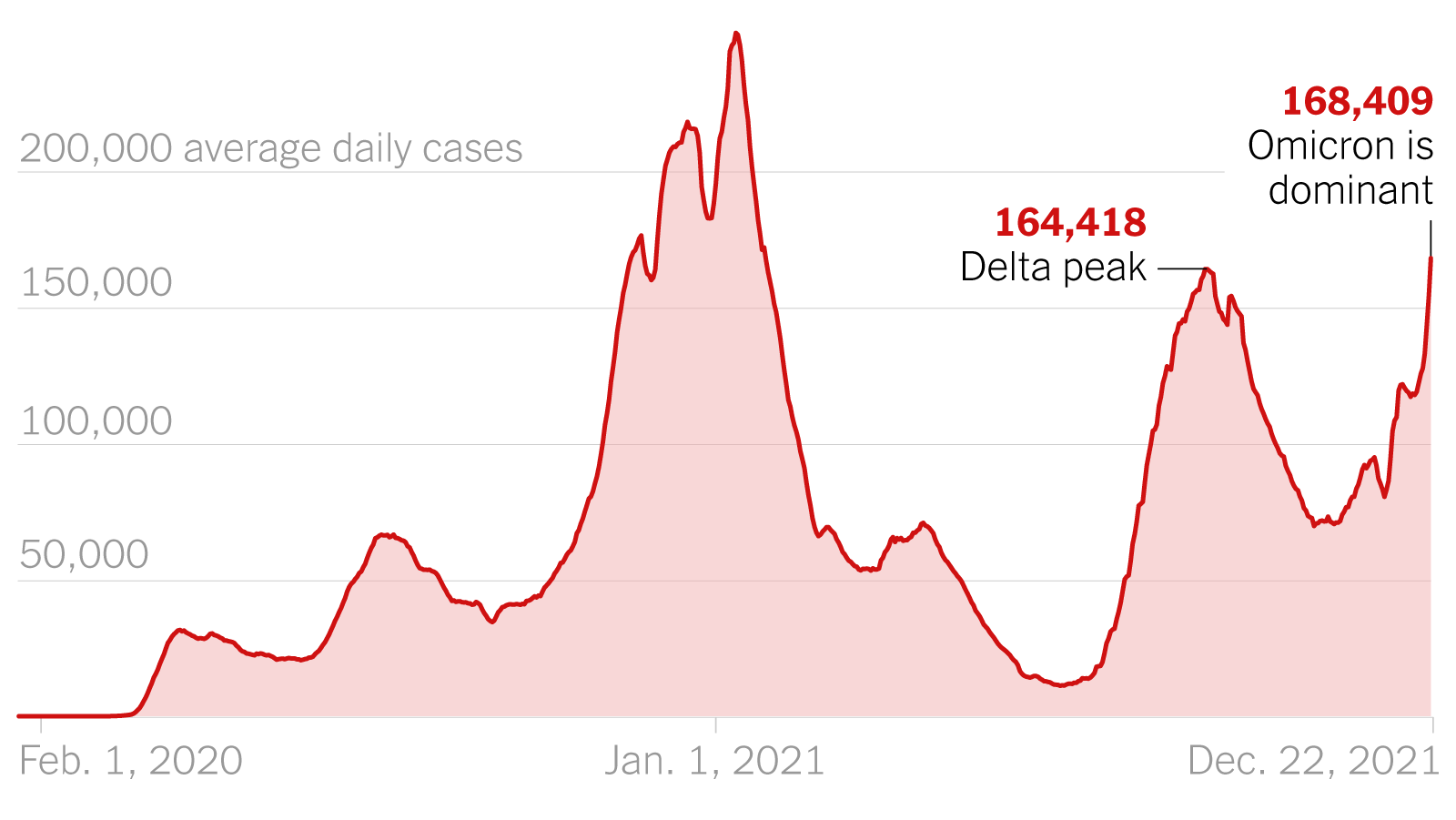
Table of Contents
Keywords: New COVID-19 variant, COVID-19 surge, WHO warning, new variant symptoms, COVID-19 transmission, pandemic update, virus outbreak, global health crisis
The World Health Organization (WHO) has issued a warning regarding a new COVID-19 variant causing a significant surge in cases across several regions globally. This new variant, posing a potential threat to global health, necessitates immediate attention and proactive measures to mitigate its spread. This article provides crucial information on the new variant, its impact, and the steps individuals and communities can take to protect themselves.
The Emergence of the New COVID-19 Variant
A new COVID-19 variant, tentatively named "Theta" (this is a placeholder name; replace with the actual name if known), was first identified on October 26, 2023, in the Southern African nation of Botswana. Initial genomic sequencing reveals several key genetic mutations, notably in the spike protein, which is responsible for the virus's entry into human cells. These mutations differentiate it from previously circulating variants like Omicron and its sub-variants, raising concerns about its transmissibility, severity, and potential to evade existing immunity. The WHO has classified Theta as a "Variant of Concern" due to its rapid spread and potential impact on global health.
- Geographic origin: Botswana, Southern Africa
- Date of initial detection: October 26, 2023
- Key genetic mutations: Specific mutations in the spike protein (e.g., [insert specific mutations if available, e.g., S:G339D, S:K417N]) are believed to enhance transmissibility and immune evasion.
- Comparison with previous variants: Preliminary data suggests Theta exhibits higher transmissibility than Omicron BA.5 and may partially evade immunity provided by previous infections and vaccinations.
Surge in COVID-19 Cases Across Multiple Regions
Following its initial detection in Botswana, the Theta variant has rapidly spread to several regions, leading to a substantial increase in COVID-19 cases. Countries in Southern Africa, Europe, and parts of Asia have reported significant spikes in infections. Hospitalization rates are also rising in certain areas, placing a strain on healthcare systems already grappling with pre-existing challenges.
- Affected countries/regions: [Insert a list of affected countries/regions with confirmed cases. Example: Botswana, South Africa, United Kingdom, France, India]
- Percentage increase in cases: [Insert data showing the percentage increase in cases compared to previous weeks/months in affected regions]
- Strain on healthcare resources: Reports indicate increasing hospital admissions and ICU occupancy in several affected areas, potentially leading to delays in care for other conditions.
- Mortality rates: [Insert data on mortality rates associated with the new variant if available. Include a comparison with previous variants, if possible.]
Symptoms and Transmission of the New COVID-19 Variant
The symptoms associated with the Theta variant appear similar to those seen with previous variants, including:
- Common symptoms: Fever, cough, fatigue, headache, muscle aches, loss of taste or smell, sore throat.
- Less common or unique symptoms: [Insert any unique or less common symptoms if identified]
Transmission appears to occur primarily through airborne droplets produced during coughing, sneezing, or talking, and through close contact with infected individuals. The R0 value (basic reproduction number) is currently being investigated, but early estimates suggest a higher R0 than some previous variants.
Effectiveness of Existing Vaccines and Treatments
While the full extent of the Theta variant's ability to evade vaccine-induced immunity is still being evaluated, early data suggests that existing vaccines continue to offer significant protection against severe illness, hospitalization, and death. However, a reduction in vaccine effectiveness against infection has been observed.
- Data on vaccine efficacy: [Insert data on the efficacy of available vaccines against the new variant, e.g., reduced efficacy against infection but still high protection against severe disease].
- Information about available treatments: Current antiviral treatments and monoclonal antibody therapies may be less effective against the Theta variant; ongoing research is evaluating their efficacy.
- Recommendations for booster shots: Staying up-to-date with COVID-19 vaccinations, including booster shots, is crucial for maximizing protection against severe disease caused by the Theta variant.
WHO Recommendations and Public Health Measures
The WHO strongly recommends several public health measures to mitigate the spread of the Theta variant:
- Specific recommendations from the WHO: [List specific recommendations from the WHO, e.g., vaccination, masking in indoor settings, improved ventilation, testing and contact tracing].
- Importance of vaccination and booster shots: Vaccination remains the most effective tool in preventing severe illness and death from COVID-19, including infection with the new variant. Booster shots are highly recommended.
- Guidance on mask-wearing and social distancing: Mask-wearing in crowded indoor settings and maintaining social distance are recommended, especially for vulnerable populations.
- Testing and contact tracing protocols: Rapid testing and contact tracing are essential for identifying and isolating infected individuals to prevent further spread.
Conclusion
The emergence of this new COVID-19 variant, Theta, underscores the ongoing need for vigilance and proactive public health measures. The significant increase in cases across several regions highlights the unpredictable nature of the pandemic and the continuous evolution of the virus. Staying informed about the latest developments, following the WHO’s recommendations, and prioritizing vaccination and booster shots remain crucial steps in combating the spread of this new COVID-19 variant and protecting global health. Stay updated on the latest information regarding this and other emerging COVID-19 variants to protect yourself and your community. Learn more about the new COVID-19 variant and how to stay safe.

Featured Posts
-
 Is This A Banksy In Westcliff Bournemouth Authentication Guide
May 31, 2025
Is This A Banksy In Westcliff Bournemouth Authentication Guide
May 31, 2025 -
 Where To Watch Kansas City Royals Games On Cbs And Kctv 5 This Season
May 31, 2025
Where To Watch Kansas City Royals Games On Cbs And Kctv 5 This Season
May 31, 2025 -
 Pest And Disease Control For Rosemary And Thyme Plants
May 31, 2025
Pest And Disease Control For Rosemary And Thyme Plants
May 31, 2025 -
 Bodensee Und Klimawandel Eine Prognose Fuer Die Naechsten 20 000 Jahre
May 31, 2025
Bodensee Und Klimawandel Eine Prognose Fuer Die Naechsten 20 000 Jahre
May 31, 2025 -
 Ai La Sophia Huynh Tran Nu Tay Vot Pickleball Tai Nang
May 31, 2025
Ai La Sophia Huynh Tran Nu Tay Vot Pickleball Tai Nang
May 31, 2025
