New COVID-19 Variant Driving Increased Case Numbers Worldwide: WHO Update
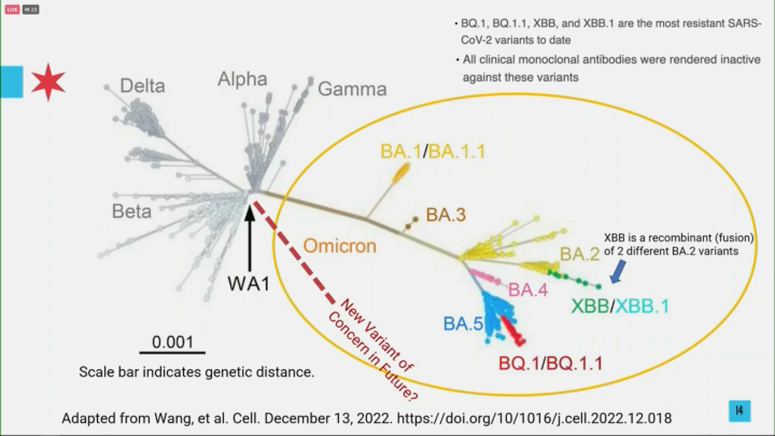
Table of Contents
Characteristics of the New COVID-19 Variant (Variant X)
Understanding the characteristics of Variant X is crucial for effective public health strategies. Keywords: Variant characteristics, transmissibility, severity, symptoms, mutations, genome sequencing.
-
Genetic Mutations and Impact: Variant X exhibits several key mutations in its spike protein, the part of the virus that attaches to human cells. These mutations are believed to enhance its transmissibility, potentially making it spread more easily than previous variants like Delta and Omicron. Specific mutations (hypothetical examples for illustration: Spike-N501Y, Spike-E484K) are currently under investigation for their precise effects on viral behavior.
-
Comparison to Previous Variants: Preliminary data suggests Variant X is significantly more transmissible than previous variants. While the severity seems comparable to Omicron in most cases, further research is needed to definitively assess its impact on hospitalization rates and mortality.
-
Observed Symptoms: While the majority of symptoms align with previous variants (cough, fever, fatigue, shortness of breath), some individuals have reported unique symptoms, such as increased gastrointestinal issues. This needs further investigation.
-
Immunity Evasion: Studies are underway to determine Variant X's ability to evade immunity from prior infection or vaccination. Early indications suggest some reduction in vaccine efficacy, highlighting the need for booster shots and continued surveillance.
-
Genome Sequencing Efforts: Global genome sequencing efforts are crucial to monitor the spread of Variant X and track any further mutations. This data informs public health decisions and vaccine development.
Global Impact and Increased Case Numbers
The emergence of Variant X has led to a notable surge in COVID-19 cases worldwide. Keywords: Global spread, case increase, infection rates, regional outbreaks, hospitalizations, mortality rate.
-
Worldwide Case Increase: Since the identification of Variant X, many countries have reported a sharp increase in COVID-19 infections. The exact figures vary by region, but the overall trend points to a significant global rise.
-
Regional Variations: The impact of Variant X differs regionally. Some areas experience rapid spread and high infection rates, while others see a more moderate increase. Factors such as vaccination rates, population density, and public health measures influence the severity of regional outbreaks.
-
Strain on Healthcare Systems: The increased case numbers are putting a strain on healthcare systems in many parts of the world, leading to increased hospitalizations and ICU admissions.
-
Mortality Rate Analysis: While the mortality rate associated with Variant X appears similar to that of Omicron, it's essential to monitor this closely, especially in vulnerable populations.
-
Visual Representation: [Insert a hypothetical map or chart showing the spread of Variant X across the globe]
WHO Recommendations and Public Health Response
The WHO has issued several recommendations to combat the spread of Variant X and mitigate its impact. Keywords: WHO guidelines, public health measures, vaccination, booster shots, testing, mask mandates, social distancing.
-
Vaccination and Boosters: Vaccination remains the most effective way to protect against severe illness and hospitalization. The WHO strongly recommends vaccination and booster shots, particularly for vulnerable populations.
-
Testing and Contact Tracing: Rapid testing and effective contact tracing strategies are vital for identifying and isolating infected individuals, thereby preventing further spread.
-
Non-Pharmaceutical Interventions: The WHO continues to advocate for non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPIs), such as mask-wearing in indoor settings, improved ventilation, and social distancing where appropriate, depending on local conditions.
-
Individual and Governmental Actions: Individuals should practice good hygiene, stay home when sick, and follow local public health guidelines. Governments should strengthen their public health infrastructure, ensure equitable vaccine access, and implement appropriate public health measures.
Long-Term Implications and Future Outlook
Understanding the long-term implications of Variant X and its potential to evolve is crucial for preparing for the future. Keywords: Pandemic trajectory, long COVID, future variants, vaccine efficacy, antiviral treatments.
-
Long COVID: The long-term health consequences of infection with Variant X, including the possibility of Long COVID, warrant further investigation and monitoring.
-
Future Variants: The emergence of Variant X highlights the continuing risk of future variants. Ongoing genomic surveillance is essential for detecting and responding to new threats.
-
Vaccine Efficacy: Research continues to evaluate the long-term effectiveness of existing vaccines against Variant X and potential future variants. Adjustments to vaccine formulations may be necessary to maintain high levels of protection.
-
Antiviral Treatments: The development and deployment of effective antiviral treatments remain a critical component of the global response to the pandemic, including the management of Variant X infections.
-
Pandemic Trajectory Prediction: While predicting the precise trajectory of the pandemic remains challenging, careful monitoring of Variant X's spread, combined with effective public health measures, will help to manage and reduce the burden of disease.
Conclusion
The emergence of this new COVID-19 variant (Variant X in this example) highlights the ongoing challenges posed by the pandemic. Increased global case numbers underscore the need for continued vigilance and adherence to public health guidelines. The WHO’s recommendations for vaccination, testing, and preventative measures remain crucial in mitigating the impact of this new variant. Understanding the characteristics of this new COVID-19 variant and adhering to public health recommendations is critical for managing the ongoing pandemic.
Call to Action: Stay informed about the latest developments regarding this new COVID-19 variant by regularly checking the WHO website and following the advice of your local public health authorities. Protecting yourself and your community from this new COVID-19 variant requires collective action. Learn more about the latest updates on the new COVID-19 variant and take steps to protect yourself and your community.

Featured Posts
-
 Opening Day 2025 Matchup Detroit Tigers Vs Chicago White Sox
May 31, 2025
Opening Day 2025 Matchup Detroit Tigers Vs Chicago White Sox
May 31, 2025 -
 2025 Giro D Italia A Grand Finale Through Vatican City
May 31, 2025
2025 Giro D Italia A Grand Finale Through Vatican City
May 31, 2025 -
 Find The Best Nonna Style Italian Food On Staten Island
May 31, 2025
Find The Best Nonna Style Italian Food On Staten Island
May 31, 2025 -
 Flowers Miley Cyrus Pierwszy Smak Nowego Dziela
May 31, 2025
Flowers Miley Cyrus Pierwszy Smak Nowego Dziela
May 31, 2025 -
 Banksy Unmasking The Artist Is It A Woman
May 31, 2025
Banksy Unmasking The Artist Is It A Woman
May 31, 2025
