Market Volatility: When Professionals Sell, Individuals Buy

Table of Contents
The Psychology of Market Volatility
Market volatility triggers powerful emotional responses, particularly fear and greed. These emotions, central to behavioral finance, significantly impact investment decisions. During market downturns, the prevalent market sentiment often shifts to panic, leading to what's known as "fear-based selling." Individual investors, often lacking the experience and long-term perspective of professionals, are more susceptible to this emotional reaction.
- Fear-based selling: This is the instinctual reaction to falling prices, leading investors to sell assets to avoid further losses, often at the worst possible time.
- Herd mentality: The tendency to follow the actions of others, amplified during volatile periods, exacerbates market reactions. When everyone is selling, the pressure to join the exodus is immense.
- Emotional vs. Disciplined Investing: Professional investors typically approach market volatility with a more disciplined and analytical mindset, focusing on long-term value rather than short-term fluctuations. They understand that market corrections are a normal part of the market cycle.
- Behavioral Finance: This field of study explores the psychological factors that influence investor decisions, highlighting the impact of emotions on market outcomes. Understanding behavioral finance is crucial for mitigating emotional biases.
Professional Investors' Strategies During Volatility
Professional investors often view market volatility as an opportunity, not a threat. Their strategies are rooted in long-term perspectives and sophisticated risk management techniques.
- Value Investing: This approach focuses on identifying undervalued assets, often overlooked during market panics. Professionals see volatility as a chance to buy quality companies at discounted prices.
- Hedging Strategies: These techniques are used to mitigate potential losses. Professional investors may employ hedging to protect their portfolios from significant downturns.
- Diversification: A well-diversified portfolio, spread across different asset classes and geographies, can cushion the impact of market volatility. This reduces the overall risk exposure.
- Fundamental Analysis: Professionals rely heavily on fundamental analysis, thoroughly researching a company's financial health and prospects before investing. This helps them identify fundamentally strong companies that are temporarily undervalued.
Why Individuals Should Consider a Contrarian Approach
While acknowledging the inherent risks, individual investors can benefit from adopting a more contrarian approach to market volatility. This involves resisting the urge to panic sell and instead considering buying during dips.
- Buy the Dip: This strategy involves purchasing assets when prices are depressed, anticipating a future rebound. It's a core tenet of contrarian investing.
- Dollar-Cost Averaging (DCA): DCA involves investing a fixed amount of money at regular intervals, regardless of market fluctuations. This mitigates the risk of investing a lump sum at a market peak.
- Long-Term Growth Perspective: Investing for the long term minimizes the impact of short-term market fluctuations. Volatility becomes less significant when focusing on long-term growth potential.
- Thorough Research and Risk Assessment: Before implementing a contrarian strategy, it's crucial to conduct thorough research, understanding your risk tolerance, and assessing the potential risks and rewards.
Managing Risk During Volatility
Even with a contrarian approach, managing risk is paramount.
- Risk Tolerance: Understand your own risk tolerance before making any investment decisions. Don't invest money you can't afford to lose.
- Portfolio Rebalancing: Regularly rebalancing your portfolio can help mitigate risk by adjusting asset allocations based on market movements.
- Stop-Loss Orders: These orders automatically sell an asset if it falls below a predetermined price, limiting potential losses.
Conclusion
Market volatility presents both challenges and opportunities. While fear often drives individual investors to sell, professional investors frequently view it as a chance to acquire undervalued assets. By understanding the psychological factors at play and adopting a more disciplined, contrarian approach, individual investors can potentially leverage market volatility to their advantage. This involves thorough research, a long-term perspective, and effective risk management techniques like diversification and dollar-cost averaging. Don't let market volatility dictate your investment decisions. Learn more about effective strategies for navigating market fluctuations and discover how to potentially profit from periods of uncertainty. Mastering market volatility can lead to significant long-term growth in your portfolio. Start learning today!

Featured Posts
-
 Unionized Starbucks Employees Turn Down Companys Guaranteed Raise Offer
Apr 28, 2025
Unionized Starbucks Employees Turn Down Companys Guaranteed Raise Offer
Apr 28, 2025 -
 The Future Of Search Perplexitys Ceo On Competing With Googles Ai
Apr 28, 2025
The Future Of Search Perplexitys Ceo On Competing With Googles Ai
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Specific Us Products Exempted From Chinese Tariffs
Apr 28, 2025
Specific Us Products Exempted From Chinese Tariffs
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Harvard Researchers Deportation Hearing In Louisiana
Apr 28, 2025
Harvard Researchers Deportation Hearing In Louisiana
Apr 28, 2025 -
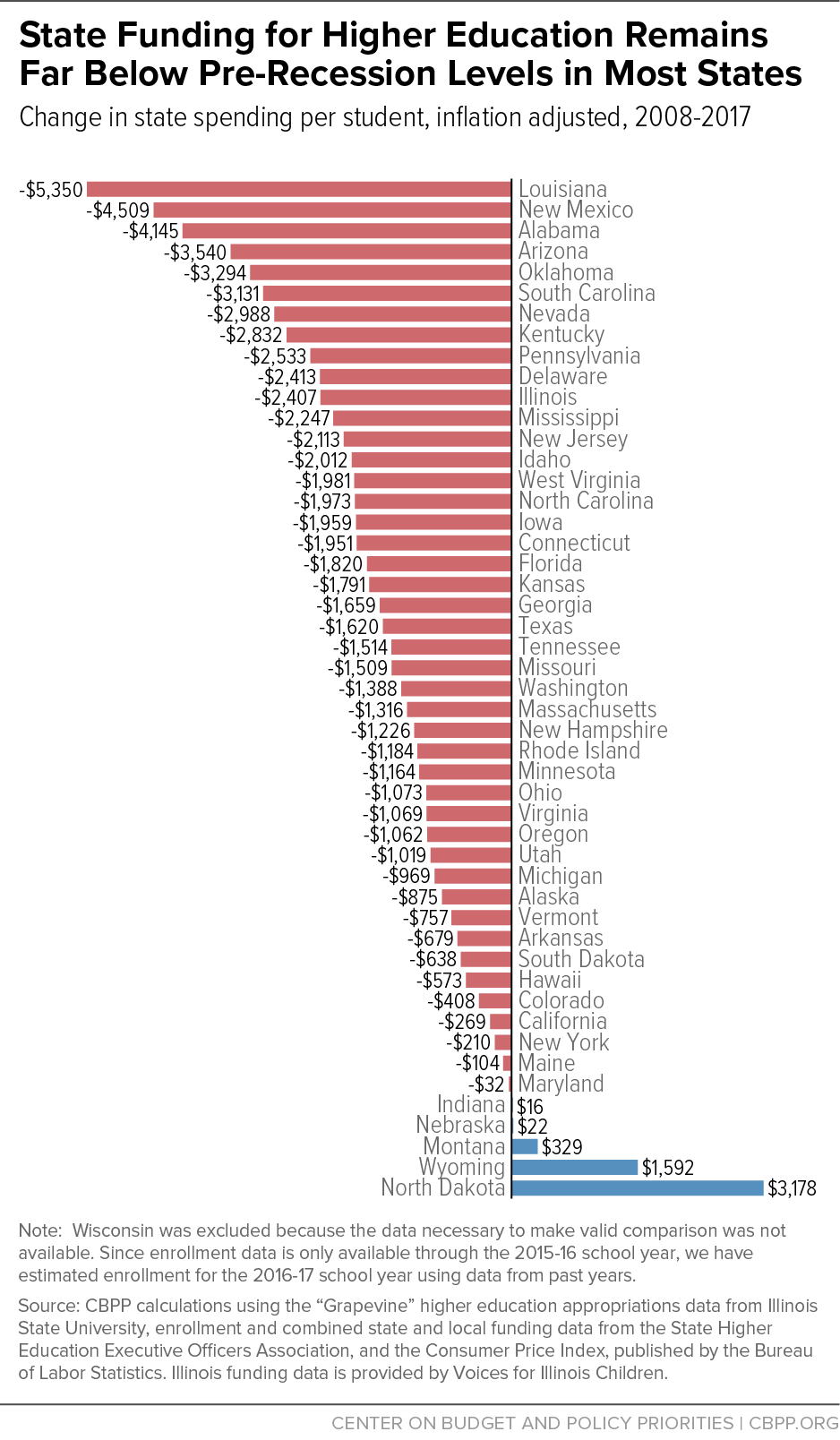 Trump Administrations Impact On Higher Education A Nationwide Analysis
Apr 28, 2025
Trump Administrations Impact On Higher Education A Nationwide Analysis
Apr 28, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Red Sox Lineup Overhaul Outfielders Return Impacts Casas Position
Apr 28, 2025
Red Sox Lineup Overhaul Outfielders Return Impacts Casas Position
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Jarren Duran 2 0 This Red Sox Outfielders Potential For A Breakout Year
Apr 28, 2025
Jarren Duran 2 0 This Red Sox Outfielders Potential For A Breakout Year
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Is This Red Sox Outfielder The Next Jarren Duran A Breakout Season Prediction
Apr 28, 2025
Is This Red Sox Outfielder The Next Jarren Duran A Breakout Season Prediction
Apr 28, 2025 -
 This Red Sox Outfielder Poised For A Duran Like Breakout
Apr 28, 2025
This Red Sox Outfielder Poised For A Duran Like Breakout
Apr 28, 2025 -
 The End Of An Era Orioles Hit Streak Ends At 160 Games
Apr 28, 2025
The End Of An Era Orioles Hit Streak Ends At 160 Games
Apr 28, 2025
