Improving Mental Healthcare: Addressing Systemic Issues And Funding Gaps

Table of Contents
Systemic Barriers to Mental Healthcare Access
The current mental healthcare landscape is riddled with obstacles that prevent many from receiving the help they need. These systemic barriers significantly impact access to quality care and contribute to the ongoing mental health crisis.
Lack of Access to Qualified Professionals
A critical barrier is the lack of access to qualified mental health professionals. This shortage manifests in several ways:
- Geographic disparities: Rural communities often face severe shortages of psychiatrists, psychologists, and therapists, leaving residents with limited options and potentially long travel distances to access care. This creates a significant disparity in access to mental healthcare services between urban and rural populations, further exacerbating existing health inequalities.
- Long wait times: Even in areas with sufficient professionals, long wait times for appointments and therapy sessions are common, leading to delays in treatment and worsening symptoms for those in need. This delay in access directly impacts treatment outcomes and can contribute to increased severity of mental health conditions.
- Specialty shortages: There's a critical shortage of specialists in certain areas, such as child and adolescent psychiatry, leaving vulnerable populations without adequate support. This lack of specialized care necessitates a more concerted effort to recruit and train mental health professionals specializing in these areas.
- High cost of treatment: The high cost of mental healthcare, including therapy sessions, medication, and hospitalization, makes treatment inaccessible to many, particularly those without adequate health insurance or financial resources. This economic barrier reinforces existing inequalities and disproportionately affects low-income individuals and families.
- Stigma: The pervasive stigma surrounding mental health prevents many individuals from seeking help, fearing judgment, discrimination, or social isolation. Addressing this deeply rooted stigma requires public awareness campaigns and education initiatives to normalize seeking mental healthcare.
Inefficient and Fragmentated Healthcare Systems
The current healthcare system often lacks coordination and integration, making it difficult for individuals to navigate and access the services they need.
- Lack of coordination: There is often a lack of communication and coordination between different healthcare providers, such as primary care physicians, psychiatrists, and therapists, leading to fragmented and inefficient care. Better communication and information sharing between providers are crucial for seamless and integrated care.
- Navigational challenges: Patients often face significant challenges in navigating the complex healthcare system to access mental health services. Simplifying the process and providing clear pathways to care are essential steps to improving access.
- Data silos: The lack of integrated data systems prevents comprehensive patient care and outcome tracking. A unified system for sharing relevant patient information across providers would enable better monitoring of treatment effectiveness and facilitate more personalized care.
- Need for integrated care: Integrated care models that address both physical and mental health needs are crucial. Many mental health conditions are comorbid with physical health issues, requiring a holistic approach to treatment.
Inadequate Mental Health Policies and Legislation
Inadequate mental health policies and legislation further exacerbate the challenges.
- Lack of comprehensive national strategies: Many countries lack comprehensive national mental health strategies outlining clear goals, priorities, and resource allocation plans. A national strategy ensures coordinated efforts and a cohesive approach to addressing mental health needs.
- Insufficient funding: Insufficient funding allocated to mental health initiatives directly impacts the availability and quality of services. Increased funding is essential to address the existing resource gaps.
- Inadequate insurance coverage: Inadequate insurance coverage for mental health services leaves many individuals with substantial out-of-pocket expenses, creating a significant financial barrier to access. Expanding insurance coverage to include comprehensive mental health benefits is critical.
- Need for stronger policy to destigmatize: Stronger policies aimed at destigmatizing mental illness are needed to encourage help-seeking behavior and create a more supportive environment for those struggling with mental health conditions.
The Critical Role of Funding in Improving Mental Healthcare
Increased and strategic funding is paramount to improving mental healthcare. Underfunding severely limits the capacity to address systemic issues and provide quality care.
Underfunding of Mental Health Services
Mental health services are consistently underfunded compared to other healthcare sectors.
- Spending disparities: A comparison of mental health spending with spending on other healthcare areas reveals significant disparities, highlighting the urgent need for increased investment. This disparity reflects a chronic under prioritization of mental health within the broader healthcare system.
- Impact of underfunding: Underfunding directly impacts service availability, quality, and accessibility. It restricts the ability to hire qualified professionals, develop effective programs, and expand access to care.
- Investment needs: Increased investment in research, prevention, and treatment is crucial to develop more effective treatments, improve early intervention strategies, and enhance the overall quality of care.
Prioritizing Prevention and Early Intervention Programs
Investing in prevention and early intervention programs is cost-effective and yields significant long-term benefits.
- Cost-effectiveness: Early intervention and prevention programs are significantly more cost-effective than treating severe mental illness later in life. Investing in these programs prevents the escalation of mental health conditions and reduces the long-term burden on the healthcare system.
- School-based services: Expanding school-based mental health services provides early identification and intervention for young people, improving outcomes and reducing stigma.
- Community-based support: Expanding access to community-based mental health support networks provides crucial resources and reduces isolation, improving the overall mental wellbeing of individuals and communities.
- Targeting at-risk populations: Focusing on preventative care for at-risk populations through targeted programs can significantly reduce the incidence and prevalence of mental health conditions.
Strategic Allocation of Funds for Maximum Impact
Strategic allocation of increased funding is crucial for maximizing impact.
- Training and education: Investing in the training and education of mental health professionals is essential to ensure a skilled workforce capable of providing high-quality care.
- Telehealth infrastructure: Improving infrastructure to support telehealth and remote services expands access to care, particularly for individuals in remote or underserved areas.
- Innovative approaches: Supporting innovative approaches to mental health treatment, such as technology-based interventions and personalized care models, improves the efficacy and accessibility of care.
- Research funding: Investing in research into the causes and effective treatments of mental illness accelerates advancements in treatment and prevention strategies.
Conclusion
The systemic barriers and significant funding gaps in mental healthcare are undeniably impacting millions globally. Improving mental healthcare access requires a multifaceted approach addressing the issues outlined above. By acknowledging the critical need for increased investment and advocating for policy changes that prioritize mental health, we can create a system that provides equitable access to quality care for all. Let us work together to advocate for better mental health services, increased funding for improving mental healthcare, and systemic reforms that ensure everyone has the support they need to thrive. The long-term benefits of investing in mental well-being are immeasurable. Let's make improving mental healthcare a top priority.

Featured Posts
-
 Pasifika Sipoti In Brief April 4th Key Events
May 02, 2025
Pasifika Sipoti In Brief April 4th Key Events
May 02, 2025 -
 Automakers In China Understanding The Current Market Landscape And Future Outlook
May 02, 2025
Automakers In China Understanding The Current Market Landscape And Future Outlook
May 02, 2025 -
 Rare And Retired Fortnite Skins A Collectors Guide
May 02, 2025
Rare And Retired Fortnite Skins A Collectors Guide
May 02, 2025 -
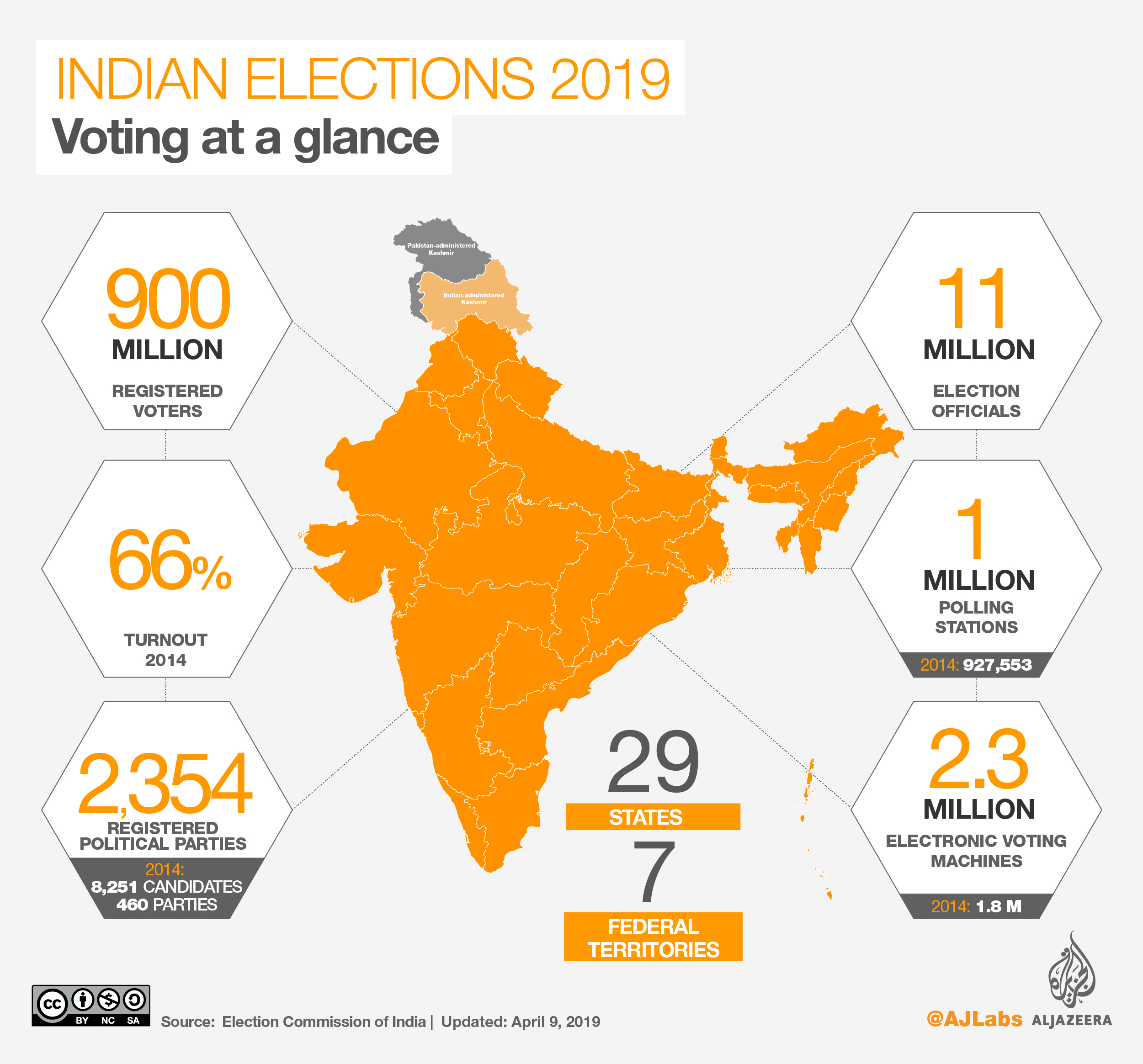 Robust Poll Data System Preventing Election Errors
May 02, 2025
Robust Poll Data System Preventing Election Errors
May 02, 2025 -
 Australias Opposition A 9 Billion Budget Improvement Plan
May 02, 2025
Australias Opposition A 9 Billion Budget Improvement Plan
May 02, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Reform Partys Local Election Performance A Test For Farages Influence
May 03, 2025
Reform Partys Local Election Performance A Test For Farages Influence
May 03, 2025 -
 Evaluating Reform Uks Commitment To Uk Farmers
May 03, 2025
Evaluating Reform Uks Commitment To Uk Farmers
May 03, 2025 -
 Nigel Farages Reform Party A Crucial Uk Local Election Test
May 03, 2025
Nigel Farages Reform Party A Crucial Uk Local Election Test
May 03, 2025 -
 Thlyl Shaml Lwrqt Syasat Alastthmar Alty Asdrtha Aljbht Alwtnyt
May 03, 2025
Thlyl Shaml Lwrqt Syasat Alastthmar Alty Asdrtha Aljbht Alwtnyt
May 03, 2025 -
 Examining Reform Uks Plans For The Uk Farming Industry
May 03, 2025
Examining Reform Uks Plans For The Uk Farming Industry
May 03, 2025
