Identifying The Country's Next Big Business Hubs: A Geographic Analysis

Table of Contents
A "business hub" is defined as a geographic location exhibiting a confluence of factors conducive to business success. These include robust infrastructure, a skilled and readily available talent pool, high levels of economic activity, and supportive government policies. Understanding these components is critical for identifying promising locations for investment and business expansion. This analysis will help clarify which areas are poised for significant growth and offer lucrative investment opportunities within the country's dynamic economic environment.
Analyzing Demographic Trends and Population Growth
Understanding demographic trends is paramount when identifying the country's next big business hubs. Rapid population growth, particularly in urban areas, fuels demand for goods and services, creating a fertile ground for business expansion. This section will explore the relationship between population dynamics and the emergence of new business centers.
Population Density and Urbanization
Population density and urbanization rates are strongly correlated with business growth. Cities experiencing rapid population growth often see a surge in economic activity, as increased demand necessitates more businesses to satisfy consumer needs.
- Examples of high-growth cities: City A, with a 15% annual population increase, has seen a boom in the tech and service sectors. City B's rapid urbanization has attracted significant foreign direct investment (FDI) in infrastructure and manufacturing.
- Analysis of migration patterns: Internal migration from rural areas to urban centers fuels the growth of cities like City C and City D, creating a young, dynamic workforce.
- Impact of young populations: A large young population, as seen in City E, represents a significant consumer base and a pool of skilled workers, driving innovation and entrepreneurship.
Education and Skills Development
A skilled workforce is essential for attracting businesses. The availability of qualified workers significantly impacts a region's competitiveness. Education levels and the alignment of skills training with industry needs are critical factors.
- Statistics on educational attainment: Region X boasts a high rate of tertiary education completion, leading to a robust talent pool. In contrast, Region Y needs to improve its vocational training programs to meet the demands of a growing manufacturing sector.
- Examples of successful skills development initiatives: Government-funded apprenticeship programs in Region Z have successfully filled the skills gap in the renewable energy sector. Private sector initiatives in City F have focused on upskilling existing workers to meet the demands of the digital economy.
- Comparison of different regions' skill bases: A comparison across regions highlights the disparities in the availability of skilled labor and the need for targeted interventions to address skill gaps in specific industries.
Assessing Infrastructure and Connectivity
Robust infrastructure is crucial for business operations. Efficient transportation networks and reliable digital infrastructure are essential for supporting business growth and competitiveness.
Transportation Networks
Efficient transportation networks—roads, rail, airports, and ports—are critical for logistics and the movement of goods and services. Well-developed infrastructure reduces transportation costs and improves efficiency, making a region more attractive to businesses.
- Examples of well-developed and underdeveloped transportation networks: Region A's modern highway system and international airport contribute to its economic success, unlike Region B, where poor road infrastructure hinders business operations and increases costs.
- Analysis of their impact on business costs and efficiency: The cost of transporting goods significantly impacts profitability. Efficient transportation networks directly contribute to cost reduction and improved efficiency.
Digital Infrastructure and Connectivity
Access to high-speed internet, reliable electricity, and digital technologies is increasingly essential for business growth. Digital literacy and the adoption of digital tools are also key factors.
- Statistics on internet penetration: High internet penetration rates in City G have fostered the growth of digital businesses and attracted tech companies.
- Analysis of digital literacy rates: Improved digital literacy in Region C has enabled businesses to adopt new technologies and enhance productivity.
- Examples of successful digital infrastructure projects: Government investments in broadband infrastructure have facilitated economic growth in City H.
Evaluating Economic Factors and Government Policies
Government policies, tax incentives, access to capital, and the overall regulatory environment significantly influence business investment and development.
Tax Incentives and Regulatory Environment
Favorable tax policies and a streamlined regulatory environment attract businesses. Regions with excessive bureaucracy or unfavorable tax structures may struggle to attract investment.
- Comparison of different regions' tax policies: Region D's competitive corporate tax rates have attracted numerous multinational corporations.
- Analysis of regulatory burdens: Excessive regulations in Region E create obstacles for businesses and hinder growth.
- Examples of successful government initiatives to attract businesses: Tax breaks and streamlined approval processes in City I have been instrumental in stimulating investment.
Access to Capital and Funding
Access to venture capital, loans, and other funding sources is crucial for businesses, especially startups. Regions with a well-developed financial ecosystem tend to experience greater entrepreneurial activity.
- Analysis of investment trends: Increased venture capital investment in Region F reflects investor confidence in its growth potential.
- Comparison of different regions' access to funding: The availability of government grants and loans in Region G makes it attractive for new businesses.
- Examples of successful crowdfunding or venture capital initiatives: City J's thriving startup ecosystem benefits from the availability of angel investors and venture capital firms.
Identifying the Country's Next Big Business Hubs – Key Takeaways and Call to Action
Our geographic analysis highlights that identifying the country's next big business hubs requires a holistic approach considering demographic trends, infrastructure, and economic factors. Regions demonstrating rapid population growth, a skilled workforce, robust infrastructure, and supportive government policies are likely to experience significant business growth. Our analysis suggests Cities A, B, E, G, I, and J, and Regions D, F, and G show substantial potential.
Identifying the country's next big business hubs is essential for investors, entrepreneurs, and policymakers alike. By understanding the drivers of economic growth, stakeholders can make informed decisions about investment, business expansion, and policy development.
By understanding the factors contributing to the emergence of new business hubs, you can strategically position yourself for success. Start your exploration of the country's next big business hubs today!

Featured Posts
-
 Ja Morant Under Nba Investigation What We Know So Far
Apr 24, 2025
Ja Morant Under Nba Investigation What We Know So Far
Apr 24, 2025 -
 John Travolta Shares A Photo To Remember His Late Son Jett On His Birthday
Apr 24, 2025
John Travolta Shares A Photo To Remember His Late Son Jett On His Birthday
Apr 24, 2025 -
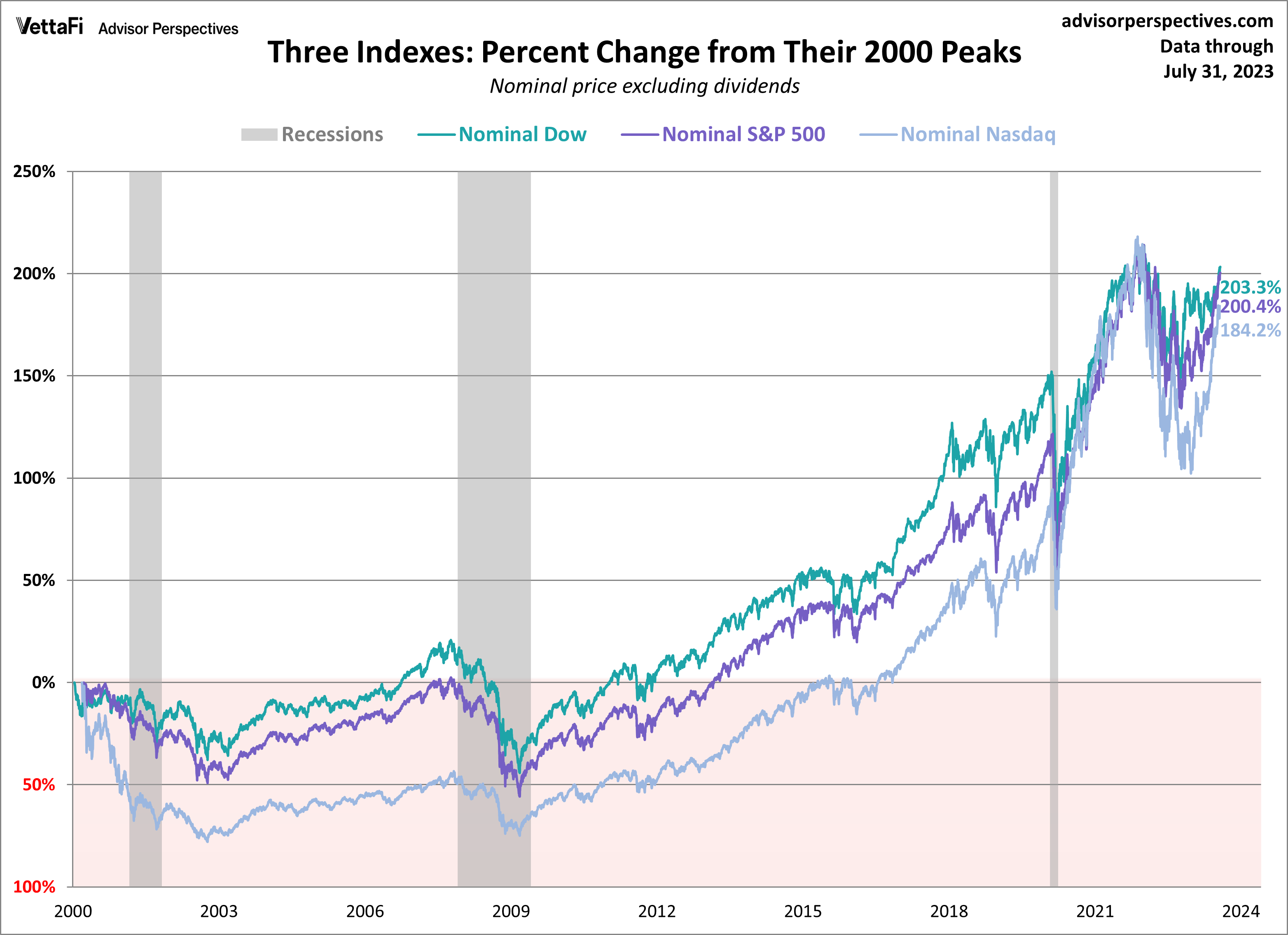 Stock Market Data Dow S And P 500 And Nasdaq April 23rd 2024
Apr 24, 2025
Stock Market Data Dow S And P 500 And Nasdaq April 23rd 2024
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Golden States Bench Duo Hield And Payton Key To Win Vs Portland
Apr 24, 2025
Golden States Bench Duo Hield And Payton Key To Win Vs Portland
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Navigate The Private Credit Boom 5 Essential Dos And Don Ts
Apr 24, 2025
Navigate The Private Credit Boom 5 Essential Dos And Don Ts
Apr 24, 2025
