Gambling On Climate Change: The Case Of The LA Wildfires
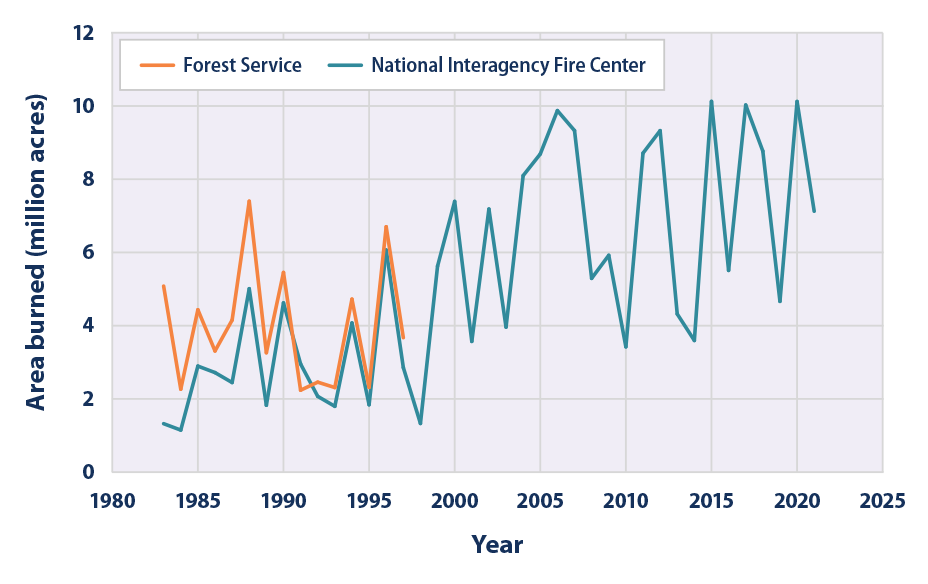
Table of Contents
H2: The Link Between Climate Change and Increased Wildfire Risk in LA
The connection between climate change and the worsening LA wildfires is undeniable. The intensifying environmental impact is evident in several key ways:
H3: Rising Temperatures and Drought Conditions
Climate change is supercharging the conditions that fuel wildfires. We're seeing:
- Increased average temperatures: Data from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) shows a clear upward trend in average temperatures in the LA region over the past century.
- Prolonged droughts: Longer and more severe droughts are depleting soil moisture, turning vast areas into tinderboxes.
- Decreased soil moisture: This reduction in soil moisture makes vegetation more susceptible to ignition and rapid fire spread.
For example, the years leading up to the 2020 wildfire season were characterized by exceptionally low rainfall and record-high temperatures, creating a perfect storm for catastrophic wildfires. Leading climate scientists, such as [Insert name and affiliation of a relevant climate scientist], confirm this trend and predict even more extreme conditions in the future.
H3: Changes in Vegetation and Fuel Loads
Changes in vegetation patterns are exacerbating the problem. We observe:
- Increased invasive species: Invasive plants often outcompete native species, creating denser, more flammable underbrush.
- Overgrown brush: Years of drought and fire suppression have led to the accumulation of significant fuel loads in many areas.
- Lack of forest management: Insufficient forest thinning and prescribed burns leave landscapes vulnerable to intense and rapid fire spread.
The combination of these factors creates a highly combustible environment, increasing the risk of larger, more destructive wildfires. The Woolsey Fire of 2018, for instance, rapidly spread through densely vegetated areas, highlighting the danger of unchecked fuel buildup.
H3: The Role of Santa Ana Winds
Climate change may also be influencing the infamous Santa Ana winds, known for their role in fueling devastating wildfires. While research is ongoing, some studies suggest that:
- Increased wind speeds: Climate change models predict an increase in the intensity of these powerful winds.
- Longer duration: The Santa Ana wind season might become longer and more frequent.
- Drier air: Warmer temperatures lead to drier air, further increasing the flammability of vegetation.
While the exact relationship needs further investigation, the potential for more intense and frequent Santa Ana winds significantly increases the wildfire risk in LA.
H2: The Economic and Social Costs of LA Wildfires
The cost of LA wildfires extends far beyond the immediate damage. The economic and social impact is profound:
H3: Direct Costs
The financial burden is staggering:
- Firefighting costs: The cost of battling large wildfires is enormous, requiring significant resources and personnel.
- Insurance claims: Property damage from wildfires leads to massive insurance payouts, straining the system.
- Rebuilding efforts: Rebuilding homes and infrastructure after a wildfire is a costly and time-consuming process.
- Loss of tourism revenue: Wildfires can devastate tourism, impacting local economies significantly.
The combined cost of recent LA wildfires runs into billions of dollars, placing a substantial strain on public resources and individual finances.
H3: Indirect Costs
The indirect consequences are equally devastating:
- Air pollution related health issues: Wildfire smoke causes respiratory problems and other health complications, affecting vulnerable populations disproportionately.
- Homelessness: Wildfires can displace residents, leading to homelessness and exacerbating existing inequalities.
- Trauma: The experience of wildfire can have lasting psychological effects on survivors.
- Economic disruption: Wildfires disrupt businesses, supply chains, and employment opportunities.
H2: Mitigating the Risk: Investing in Climate Action and Wildfire Prevention
Addressing the LA wildfire crisis requires a two-pronged approach:
H3: Climate Change Mitigation
Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is paramount:
- Transitioning to renewable energy: Shifting away from fossil fuels towards renewable energy sources is crucial.
- Improving energy efficiency: Reducing energy consumption through better efficiency measures lowers carbon emissions.
- Sustainable transportation: Promoting public transit, cycling, and electric vehicles reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
Stronger policies at local, state, and national levels are essential to accelerate this transition and curb emissions effectively.
H3: Wildfire Prevention Strategies
Proactive measures are crucial to reduce wildfire risk:
- Improved forest management practices: Implementing regular forest thinning, prescribed burns, and other forest management techniques can significantly reduce fuel loads.
- Controlled burns: Conducting controlled burns under specific conditions can help reduce the risk of uncontrolled wildfires.
- Community preparedness programs: Educating communities about wildfire risks and developing evacuation plans is essential.
- Building codes: Enacting stricter building codes that incorporate fire-resistant materials can minimize property damage.
Successful wildfire prevention initiatives in other regions can serve as models for LA, demonstrating the effectiveness of proactive strategies.
3. Conclusion
The increasing severity of LA wildfires is not a matter of chance; it's a direct consequence of climate change. We are literally gambling on climate change, and the stakes are devastating wildfires that cost billions and displace communities. Continuing to ignore climate action is a gamble we cannot afford to lose. Stop gambling on climate change. Demand climate action now to protect our communities from devastating LA wildfires. Learn more about climate change mitigation and wildfire prevention strategies in LA. Support organizations dedicated to wildfire preparedness and environmental protection. Contact your elected officials and demand action on climate change. The future of LA, and indeed the planet, depends on it.

Featured Posts
-
 Azmt Jdydt Albwlysaryw Twqf Tyara Ajnbya
May 07, 2025
Azmt Jdydt Albwlysaryw Twqf Tyara Ajnbya
May 07, 2025 -
 Wwe Smack Down La Emotiva Reaparicion De Lewis Capaldi Despues De Problemas De Salud
May 07, 2025
Wwe Smack Down La Emotiva Reaparicion De Lewis Capaldi Despues De Problemas De Salud
May 07, 2025 -
 Deconstructing The Glossy Mirage
May 07, 2025
Deconstructing The Glossy Mirage
May 07, 2025 -
 Rihannas Savage X Fenty Lingerie Perfect For Your Wedding Night
May 07, 2025
Rihannas Savage X Fenty Lingerie Perfect For Your Wedding Night
May 07, 2025 -
 Papa Francisco Fieis Dormem Nas Ruas Para A Missa De Seu Funeral
May 07, 2025
Papa Francisco Fieis Dormem Nas Ruas Para A Missa De Seu Funeral
May 07, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Deadly Fungi The Emerging Superbug Crisis
May 08, 2025
Deadly Fungi The Emerging Superbug Crisis
May 08, 2025 -
 Motorcycle Hit By Van In Apparent Road Rage Incident Cnn
May 08, 2025
Motorcycle Hit By Van In Apparent Road Rage Incident Cnn
May 08, 2025 -
 Proposed Doj Changes Could Severely Damage User Trust In Google Search
May 08, 2025
Proposed Doj Changes Could Severely Damage User Trust In Google Search
May 08, 2025 -
 Cnn Reports Van Involved In Road Rage Motorcycle Collision
May 08, 2025
Cnn Reports Van Involved In Road Rage Motorcycle Collision
May 08, 2025 -
 Cardinals Dossier Influences Next Pope Selection
May 08, 2025
Cardinals Dossier Influences Next Pope Selection
May 08, 2025
