Deadly Fungi: The Emerging Superbug Crisis
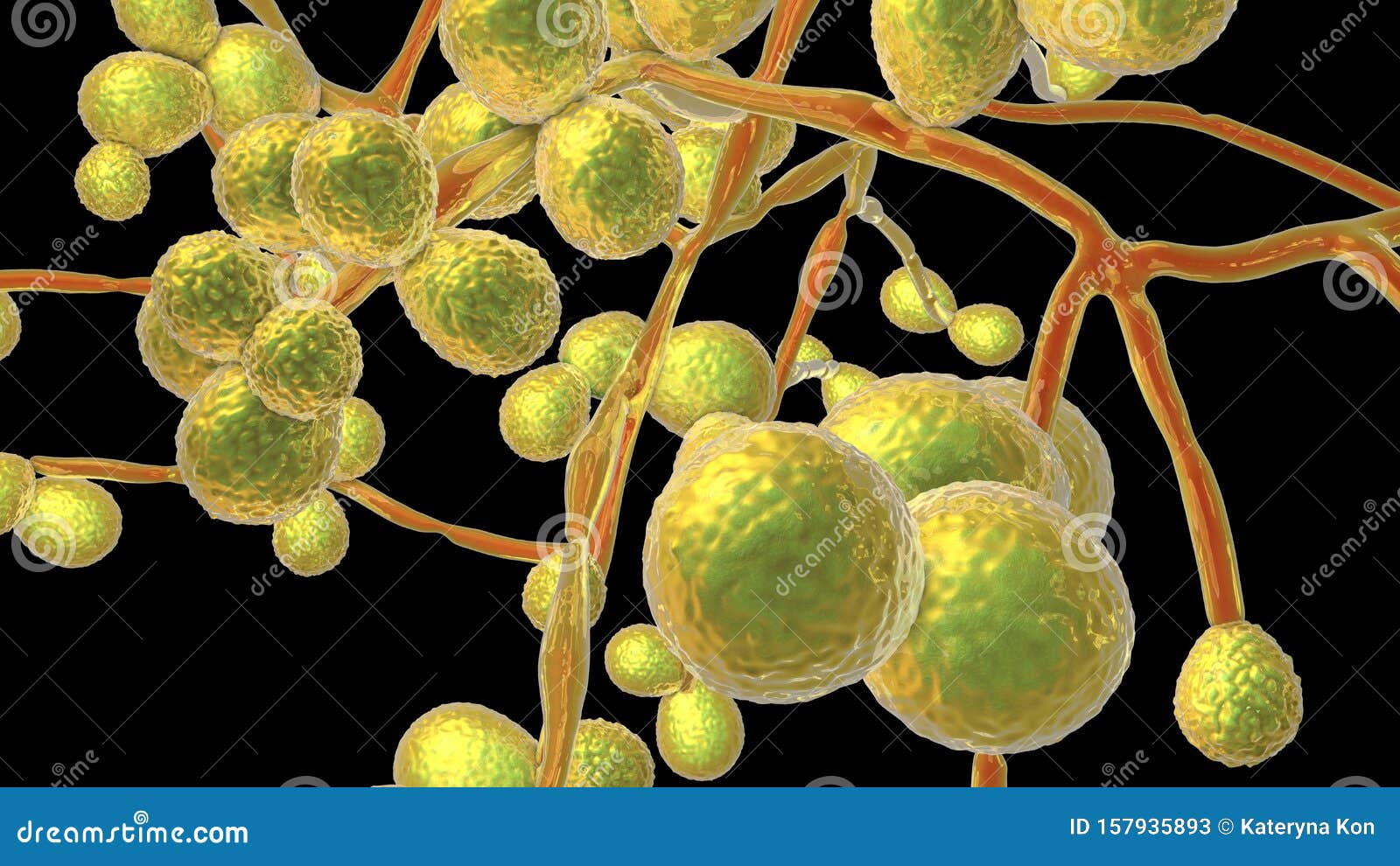
Table of Contents
The Rise of Antifungal Resistance
The overuse and misuse of antifungals in both human and agricultural settings have driven the evolution of resistant fungal strains. This resistance renders existing treatments ineffective, leading to prolonged illness, increased mortality, and significant healthcare costs. The current arsenal of antifungal drugs is limited, primarily consisting of azoles, echinocandins, and polyenes. The emergence of resistance to these classes poses a significant challenge.
- Increased use of antifungals in agriculture: The widespread use of antifungals in agriculture to protect crops contributes significantly to the spread of resistance genes. These genes can then transfer to human pathogens, exacerbating the problem.
- Over-prescription of antifungals in healthcare settings: Over-prescription of antifungals in hospitals and other healthcare settings accelerates the development of resistant strains. This is further compounded by the often-difficult diagnosis of fungal infections, leading to broad-spectrum antifungal use.
- Limited development of new antifungal drugs: The pharmaceutical industry has historically invested less in antifungal drug development compared to antibacterial drugs. This lack of investment has resulted in a limited pipeline of new antifungal agents, leaving us vulnerable to resistant strains.
- Mechanisms of antifungal resistance are diverse and complex: Fungi employ a variety of mechanisms to resist antifungal drugs, including target modification, drug efflux pumps, and altered cell wall biosynthesis. Understanding these complex mechanisms is crucial for developing new strategies to combat resistance.
High-Risk Fungal Pathogens
Several fungal species pose significant threats due to their inherent virulence and increasing resistance to antifungal therapies. These deadly fungi represent a major challenge to global health security.
- Candida auris: This multi-drug resistant yeast is a leading cause of bloodstream infections, particularly in healthcare settings. C. auris is notorious for its high mortality rates and its ability to rapidly spread in hospitals, making infection control extremely challenging.
- Aspergillus fumigatus: This common mold causes invasive aspergillosis, a serious infection primarily affecting immunocompromised individuals. The increasing resistance of A. fumigatus to azoles, a key class of antifungal drugs, makes treatment more difficult and less effective.
- Cryptococcus neoformans: This fungus causes cryptococcal meningitis, a devastating infection primarily affecting individuals with weakened immune systems, including those with HIV/AIDS. Resistance to fluconazole, a commonly used antifungal, is a growing concern, increasing mortality rates.
- Mucormycosis: This rare but serious fungal infection, often called "black fungus," typically affects individuals with weakened immune systems, particularly those with diabetes or those undergoing chemotherapy. Mucormycosis has a high mortality rate and requires aggressive treatment.
Impact on Healthcare Systems
The emergence of deadly fungi significantly impacts healthcare systems globally. The increased prevalence of these resistant strains places an enormous strain on resources and leads to poorer patient outcomes.
- Increased burden on intensive care units (ICUs): Patients with severe fungal infections often require intensive care, placing a significant burden on already strained ICU resources.
- Strain on healthcare resources due to prolonged treatment: Treatment of resistant fungal infections is often prolonged and complex, requiring significant healthcare resources and increasing costs.
- Challenges in infection control measures: Controlling the spread of these highly resistant fungi in healthcare settings is extremely challenging, demanding rigorous infection control protocols.
- Need for advanced diagnostic tools for rapid identification: Rapid and accurate diagnosis of fungal infections is crucial for timely and effective treatment. Investment in advanced diagnostic tools is essential.
Strategies for Combating the Deadly Fungi Crisis
Addressing this crisis requires a multi-pronged approach that includes improved infection prevention, the development of new antifungal drugs, and responsible antifungal stewardship. A global collaborative effort is essential.
- Implementation of strict infection control protocols in healthcare settings: Strengthened infection control protocols, including hand hygiene, environmental cleaning, and contact precautions, are critical in preventing the spread of deadly fungi within healthcare facilities.
- Development of rapid diagnostic tests to enable early detection and treatment: Rapid and accurate diagnostic tools are crucial for early detection and prompt initiation of appropriate therapy.
- Prioritization of research and development of new antifungal agents: Increased investment in research and development is essential to discover and develop new antifungal drugs with novel mechanisms of action to overcome resistance.
- Promoting responsible use of antifungals to prevent resistance: Antimicrobial stewardship programs are necessary to promote the judicious use of antifungals, minimizing the risk of resistance development.
- Increased public health awareness and education: Public health campaigns are needed to educate healthcare professionals and the public about the dangers of antifungal resistance and the importance of infection prevention.
Conclusion
The emergence of deadly fungi, resistant to existing treatments, presents a serious and growing global health threat. This "superbug" crisis necessitates a collaborative effort involving researchers, healthcare professionals, and policymakers to develop and implement effective strategies to combat this challenge. By prioritizing research into new antifungal drugs, implementing stringent infection control measures, and promoting responsible antifungal use, we can mitigate the devastating impact of these deadly fungi and prevent a future where even common fungal infections become life-threatening. Understanding the threat of deadly fungi and taking proactive measures is critical to safeguarding global health. We must act now to prevent a future where these emerging superbugs overwhelm our healthcare systems.

Featured Posts
-
 Cowherds Persistent Attacks On Jayson Tatum
May 08, 2025
Cowherds Persistent Attacks On Jayson Tatum
May 08, 2025 -
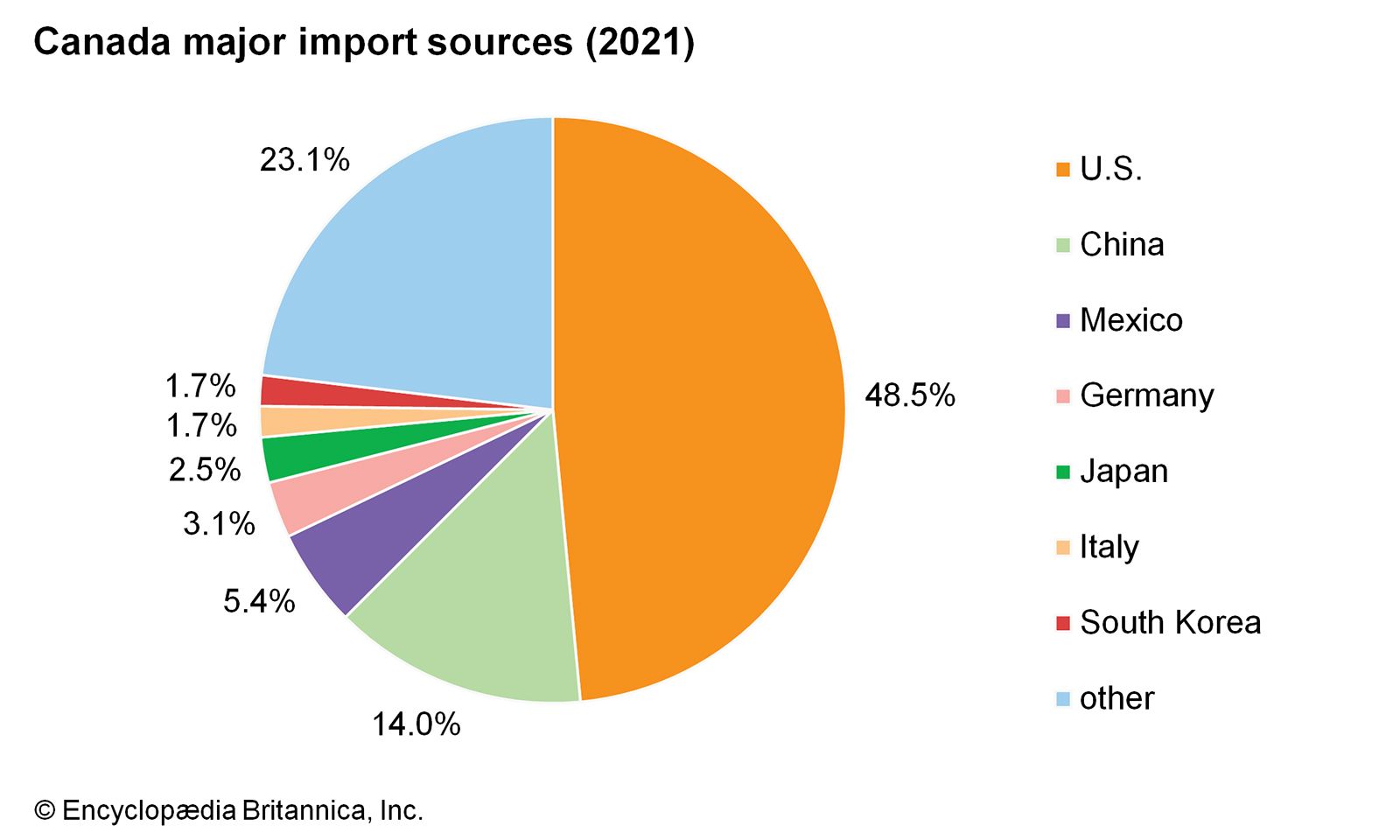 Us Canada Trade A Path Towards Coherence And Cooperation
May 08, 2025
Us Canada Trade A Path Towards Coherence And Cooperation
May 08, 2025 -
 Thunder Vs Pacers Injury Update Key Players Out On March 29th
May 08, 2025
Thunder Vs Pacers Injury Update Key Players Out On March 29th
May 08, 2025 -
 Ripples Xrp Three Factors Suggesting A Potential Price Surge
May 08, 2025
Ripples Xrp Three Factors Suggesting A Potential Price Surge
May 08, 2025 -
 Path Of Exile 2 Everything You Need To Know About Rogue Exiles
May 08, 2025
Path Of Exile 2 Everything You Need To Know About Rogue Exiles
May 08, 2025
