Fuel Costs Soar: 20-Cent Increase In Average Gas Price
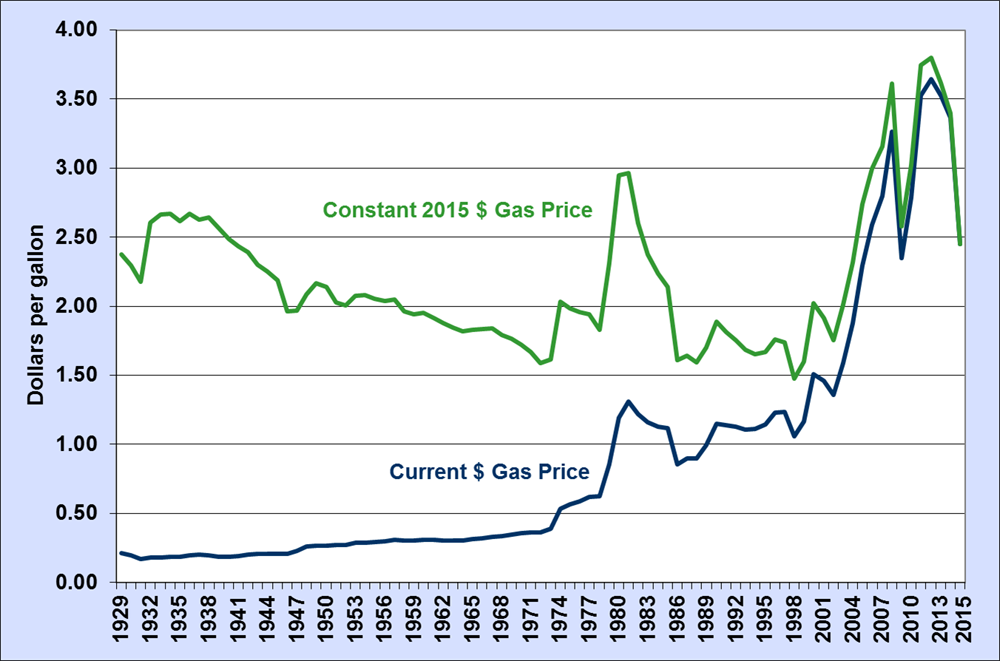
Table of Contents
Understanding the 20-Cent Increase: Causes and Contributing Factors
The 20-cent increase in the average gas price isn't an isolated incident; it's a symptom of several interconnected factors affecting the global and national fuel market.
Global Oil Market Volatility
Global events significantly influence crude oil prices, directly impacting gas prices at the pump. Geopolitical instability, such as the ongoing conflict in Ukraine, creates uncertainty and disruption in the global oil supply chain. Decisions made by OPEC (Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries) regarding oil production quotas also play a crucial role.
- Recent Events Contributing to Volatility: The war in Ukraine, sanctions on Russian oil, and OPEC+ production cuts have all contributed to increased oil prices.
- Specific Countries/Organizations: Russia's role as a major oil producer, and OPEC+'s influence on global supply, are key factors impacting prices.
- Data Points: Crude oil prices have increased by X% in the past Y months, directly correlating to the rise in gas prices.
Refinery Capacity and Production
The capacity and operational efficiency of refineries are critical in determining gasoline supply. Reduced refinery capacity due to maintenance, unexpected shutdowns, or other operational challenges can lead to gasoline shortages and subsequent price increases.
- Refinery Maintenance/Shutdowns: Planned and unplanned refinery maintenance can temporarily reduce gasoline output. Recent examples include [mention specific recent refinery issues].
- Effect on Gasoline Availability: Reduced refinery output translates to less gasoline available, driving up prices due to increased demand.
- Statistics on Refinery Output/Capacity: [Insert statistics on refinery output and capacity utilization, if available. Cite sources.]
Increased Demand and Seasonal Factors
Increased driving during certain seasons, particularly the summer travel season, leads to higher demand for gasoline. This surge in demand, coupled with other factors, contributes to price increases.
- Seasonal Trends: Summer months typically see a higher demand for fuel due to increased road trips and vacations.
- Consumer Behavior: Consumer behavior significantly impacts fuel demand. Increased economic activity can also lead to higher gas consumption.
- Data on Seasonal Fluctuations: [Include data showcasing seasonal variations in gas prices, if available. Cite sources.]
The Impact of Rising Gas Prices on Consumers and the Economy
The 20-cent increase in fuel costs has wide-ranging consequences for consumers and the overall economy.
Increased Transportation Costs
Rising gas prices directly impact transportation costs for individuals and businesses alike. Commuting becomes more expensive, impacting household budgets. The increased cost of transporting goods also leads to higher prices for groceries and other consumer products.
- Increased Cost of Commuting: A 20-cent increase can significantly increase annual commuting costs, depending on distance and frequency.
- Grocery Prices: Transportation costs are factored into the final price of goods, leading to higher prices at the grocery store.
- Impact on Household Budgets: Increased fuel costs put a strain on household budgets, particularly for low-income families.
Economic Implications
The impact of soaring gas prices extends beyond individual consumers, affecting the broader economy. Inflation rates may increase, as fuel costs are embedded in the prices of numerous goods and services. Businesses experience increased operating costs, potentially impacting profitability and job growth. Governments may consider measures such as fuel tax relief to mitigate the effects.
- Impact on Inflation: Increased fuel costs contribute to inflation, impacting the purchasing power of consumers.
- Business Operating Costs: Higher fuel costs increase the cost of transportation for businesses, affecting their bottom line.
- Potential Government Intervention: Governments might implement policies such as fuel tax cuts or subsidies to alleviate the burden on consumers and businesses.
Strategies for Coping with Higher Fuel Costs
While we can't control global oil prices, we can take steps to mitigate the impact of higher fuel costs.
Fuel Efficiency Tips
Improving fuel economy can significantly reduce your expenses at the pump. Simple steps can make a big difference.
- Regular Vehicle Maintenance: Keeping your vehicle well-maintained (regular oil changes, tire rotations, etc.) ensures optimal fuel efficiency.
- Optimal Driving Habits: Avoiding aggressive acceleration and braking, and maintaining a consistent speed, can improve fuel economy.
- Proper Tire Inflation: Maintaining the correct tire pressure improves fuel efficiency and tire longevity.
Alternative Transportation Options
Consider exploring alternative transportation options to reduce your reliance on personal vehicles.
- Public Transportation: Utilizing buses, trains, or subways can significantly reduce fuel consumption and costs.
- Cycling/Walking: For shorter distances, cycling or walking is a healthy and cost-effective alternative.
- Carpooling: Sharing rides with colleagues or friends can reduce individual fuel costs.
- Electric Vehicles: Investing in an electric vehicle, while having upfront costs, can save on fuel expenses in the long run.
Budgeting and Financial Planning
Effective budgeting and financial planning are essential to manage increased fuel costs.
- Adjusting Budgets: Re-evaluate your budget and identify areas where you can cut expenses to accommodate higher fuel costs.
- Prioritizing Expenses: Prioritize essential expenses and consider postponing non-essential purchases.
- Emergency Funds: Having an emergency fund can help you manage unexpected expenses related to rising fuel costs.
Conclusion
The 20-cent increase in the average gas price is a significant event with far-reaching consequences. The rise is attributed to a complex interplay of factors including global oil market volatility, refinery capacity issues, and increased demand. This increase impacts consumers through higher transportation costs and affects the economy through inflationary pressures and increased business operating costs. To manage this increase in fuel costs, drivers should adopt fuel-saving strategies, explore alternative transportation options, and implement effective budgeting practices. Stay informed about fluctuations in fuel costs and adapt your driving habits and financial planning to mitigate the impact of rising gas prices. Monitor the average gas price in your area and consider adopting fuel-saving strategies to manage this significant increase in fuel costs.

Featured Posts
-
 Vstup Ukrayini Do Nato Ostanni Peregovori Ta Pozitsiya Yevrokomisiyi
May 22, 2025
Vstup Ukrayini Do Nato Ostanni Peregovori Ta Pozitsiya Yevrokomisiyi
May 22, 2025 -
 Thursdays Core Weave Crwv Stock Decline A Detailed Explanation
May 22, 2025
Thursdays Core Weave Crwv Stock Decline A Detailed Explanation
May 22, 2025 -
 Emergency Responders Tackle Significant Used Car Fire
May 22, 2025
Emergency Responders Tackle Significant Used Car Fire
May 22, 2025 -
 Juergen Klopp Transferi En Guencel Gelismeler Ve Spekuelatif Haberler
May 22, 2025
Juergen Klopp Transferi En Guencel Gelismeler Ve Spekuelatif Haberler
May 22, 2025 -
 Jackson Elk Herd Hunt Season Deeper Cuts After Public Feedback
May 22, 2025
Jackson Elk Herd Hunt Season Deeper Cuts After Public Feedback
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 The Israeli Diplomat Shooting In Washington A Developing Story
May 22, 2025
The Israeli Diplomat Shooting In Washington A Developing Story
May 22, 2025 -
 German Chancellor Merz Denounces Violent Washington Attack
May 22, 2025
German Chancellor Merz Denounces Violent Washington Attack
May 22, 2025 -
 Israeli Diplomat Shootings In Washington What We Know
May 22, 2025
Israeli Diplomat Shootings In Washington What We Know
May 22, 2025 -
 Israeli Embassy Confirms Identities Of Couple Killed In Dc Shooting
May 22, 2025
Israeli Embassy Confirms Identities Of Couple Killed In Dc Shooting
May 22, 2025 -
 Merz Condemns Washington Attack German Chancellors Strong Response
May 22, 2025
Merz Condemns Washington Attack German Chancellors Strong Response
May 22, 2025
