Decreased Earthquake Frequency In Santorini: Scientists Analyze The Outlook
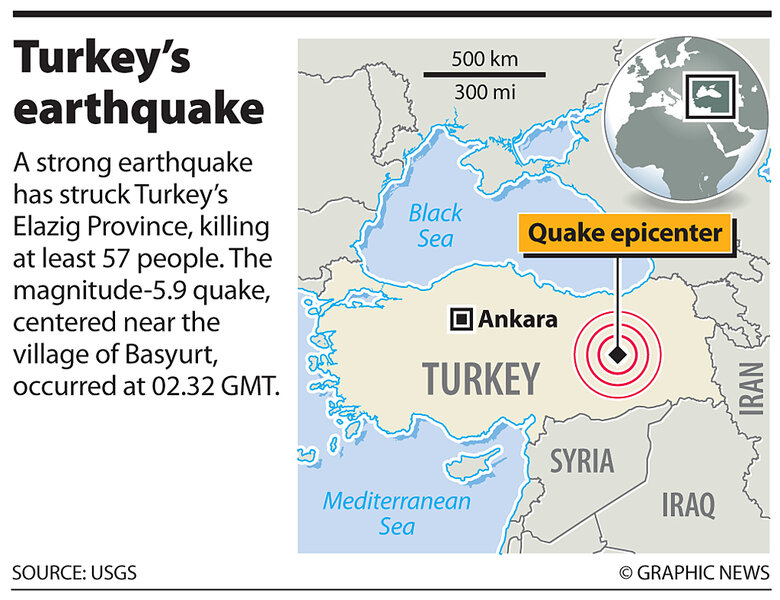
Table of Contents
Analyzing the Recent Decline in Santorini Seismic Activity
The observed decrease in Santorini earthquake frequency is a significant development requiring careful analysis. While Santorini has always experienced seismic events, recent data, spanning approximately the last [Insert Time Period, e.g., three years], reveals a statistically significant reduction in both the frequency and magnitude of earthquakes. [Cite specific sources here, e.g., "According to a study published in the Bulletin of Volcanology...", or "Data from the National Observatory of Athens shows..."].
- Specific examples of reduced seismic activity: For instance, the number of earthquakes registering above magnitude 3.0 has decreased by [Insert Percentage or specific number] compared to the previous [Insert Time Period, e.g., five-year] average.
- Comparison to historical earthquake data for Santorini: Historical records show periods of both increased and decreased seismic activity. However, the current decline appears to be more pronounced than previously observed short-term fluctuations.
- Specific monitoring techniques used: This observation is based on data from a sophisticated network of seismic monitoring stations deployed across Santorini, supplemented by GPS measurements to detect subtle ground deformation and other advanced geodetic techniques.
Potential Geological Explanations for Reduced Earthquake Activity
Several geological hypotheses attempt to explain the reduced Santorini earthquake frequency. The most prominent theories center around changes in the island's magma chamber dynamics and regional tectonic forces.
- Magma chamber dynamics and their relation to earthquakes: Fluctuations in magma chamber pressure are a primary driver of seismic activity. A decrease in pressure, perhaps due to degassing or a shift in magma flow, could explain the reduced earthquake frequency. This hypothesis needs further investigation through detailed geochemical analysis of volcanic gases.
- Tectonic plate interactions and their impact on Santorini's seismicity: The Aegean Sea region is tectonically complex, with the African and Eurasian plates colliding. Changes in the stress field resulting from subtle shifts in plate movements could potentially influence Santorini's seismic activity.
- Alternative geological explanations: Other possibilities include changes in hydrothermal activity within the volcanic system. Alterations in the circulation of heated groundwater could influence the stress on the surrounding rocks and subsequently affect earthquake frequency.
Implications for Volcanic Risk Assessment and Future Predictions
The decreased Santorini earthquake frequency significantly impacts volcanic risk assessment. While a reduction in seismic activity might initially suggest a lower risk of eruption, this interpretation is not straightforward.
- Earthquake frequency in volcanic risk models: Earthquake frequency is a crucial parameter in volcanic risk models. However, it's only one factor among many. Other indicators, such as ground deformation, gas emissions, and geochemical changes, must be considered holistically.
- Uncertainties in volcanic forecasting: Predicting volcanic eruptions remains a complex challenge. The current reduction in seismic activity doesn't necessarily imply a reduced volcanic hazard. The volcano could be accumulating pressure silently.
- Lower or higher risk of future eruptions: The current scientific consensus is that the decreased earthquake frequency does not definitively indicate a lower or higher risk of future eruptions. Continued monitoring is essential to assess the situation accurately. Continuous monitoring and research are vital for understanding the island's complex geological processes.
The Role of Advanced Monitoring Technologies in Understanding Santorini's Seismic Activity
Advanced monitoring technologies play a crucial role in understanding the changes in Santorini's seismicity. These tools provide high-resolution data crucial for refining models and predictions.
- Description of different monitoring technologies and their applications: This includes dense seismic networks, GPS networks for measuring ground deformation, satellite imagery for detecting subtle changes in the landscape, and geochemical monitoring of volcanic gases to understand magma movement and composition.
- Data collected improving understanding of volcanic processes: Combining data from these various sources allows scientists to build a more comprehensive picture of the volcanic system's behavior. This integrated approach aids in the interpretation of seemingly contradictory data, like the reduced earthquake frequency.
- Importance of international collaboration: International collaboration in data sharing and analysis is paramount in enhancing the accuracy of volcanic hazard assessments and ensuring timely warnings.
Conclusion
The recent decrease in Santorini earthquake frequency is a compelling observation that requires continued investigation. While several geological hypotheses attempt to explain this phenomenon, including changes in magma chamber pressure and tectonic plate interactions, the implications for volcanic risk remain complex and require careful consideration. The reduction in seismic activity does not necessarily equate to a reduced volcanic hazard.
Further research into Santorini earthquake frequency is crucial for refining volcanic hazard models and ensuring public safety. Stay informed on the latest developments regarding Santorini's seismic activity and volcanic outlook by regularly checking reputable scientific sources and government advisories. Understanding Santorini earthquake frequency is vital for mitigating potential risks.

Featured Posts
-
 A Simple Path To Profitable Dividends
May 11, 2025
A Simple Path To Profitable Dividends
May 11, 2025 -
 Lily Collins Stars In Sexy Calvin Klein Campaign See The Photos
May 11, 2025
Lily Collins Stars In Sexy Calvin Klein Campaign See The Photos
May 11, 2025 -
 Aaron Judges 1 000 Game Milestone Hall Of Fame Bound
May 11, 2025
Aaron Judges 1 000 Game Milestone Hall Of Fame Bound
May 11, 2025 -
 Ufc Champion Valentina Shevchenkos Custom Dragon Themed Gear Unveiled
May 11, 2025
Ufc Champion Valentina Shevchenkos Custom Dragon Themed Gear Unveiled
May 11, 2025 -
 Weekend Usmnt Recap Dest And Pulisic Lead The Charge
May 11, 2025
Weekend Usmnt Recap Dest And Pulisic Lead The Charge
May 11, 2025
