Core Inflation Surge Forces Bank Of Canada Into Difficult Decision

Table of Contents
Understanding the Core Inflation Surge in Canada
Defining Core Inflation and its Significance
Core inflation measures the rate of price increases in the economy, excluding volatile components like food and energy prices. It provides a clearer picture of underlying inflationary pressures than headline inflation, making it a crucial indicator for monetary policy decisions. Understanding core inflation trends is vital for the Bank of Canada to gauge the effectiveness of its interventions.
- Methodology: Statistics Canada employs various methods to calculate core inflation, including the trimmed mean and median measures, which remove the most extreme price changes to better reflect the underlying trend.
- Contributing Factors: Several factors have fueled the recent core inflation surge:
- Supply chain bottlenecks continue to constrain production and drive up costs.
- Strong consumer demand, boosted by government stimulus and pent-up demand, is putting upward pressure on prices.
- Wage pressures, driven by a tight labor market, are contributing to higher production costs and inflationary pressures.
Analyzing the Recent Data
Statistics Canada's recent data paints a concerning picture. [Insert Chart/Graph visualizing recent core inflation data]. The surge in core inflation surpasses the Bank of Canada's 2% target, exceeding forecasts and highlighting the urgency of the situation.
- Key Data Points: The data reveals a consistent upward trend in core inflation over the past year, exceeding expectations and raising serious concerns.
- Historical Context: Comparing the current surge to historical data reveals its severity and significance. [Insert comparative data points].
- Forecasts: While forecasts vary, most economists predict sustained elevated core inflation in the near term.
The Bank of Canada's Policy Dilemma
The Balancing Act
The Bank of Canada's mandate is to maintain price stability and full employment. However, the current situation forces a trade-off: aggressive measures to control inflation risk slowing economic growth and potentially triggering a recession, while inaction risks allowing inflation to become entrenched.
- Raising Interest Rates: Increasing interest rates cools down the economy by making borrowing more expensive, reducing consumer spending and investment. However, it also risks slowing economic growth, increasing unemployment, and impacting the housing market.
- Maintaining Low Rates: Keeping interest rates low supports economic activity and employment. However, it allows inflation to persist and potentially accelerate, eroding purchasing power and creating uncertainty.
Exploring Potential Policy Options
The Bank of Canada has several options at its disposal to address the core inflation surge.
- Further Interest Rate Hikes: This remains the most likely option, aiming to curb demand and cool inflation. The magnitude and timing of further hikes will depend on incoming economic data.
- Quantitative Tightening: This involves reducing the Bank of Canada's balance sheet by selling government bonds, further tightening monetary conditions.
- Unconventional Monetary Policies: While less likely in the current context, unconventional measures like negative interest rates or other targeted interventions could be considered as last resorts.
Market Reactions and Economic Forecasts
Impact on the Canadian Dollar
The core inflation surge and the Bank of Canada's policy response will significantly impact the Canadian dollar. Higher interest rates generally attract foreign investment, strengthening the currency. However, a weakening economy might offset this effect.
- Currency Fluctuations: A stronger Canadian dollar can make exports more expensive and imports cheaper, potentially impacting the trade balance and overall economic growth.
- International Trade: Fluctuations in the Canadian dollar's value have important implications for Canadian businesses engaged in international trade.
Predictions from Economists and Analysts
Economists hold diverse views on the future trajectory of inflation and the Bank of Canada's response. Some predict a sharp slowdown in growth, potentially leading to a recession, while others foresee a "soft landing" with inflation gradually returning to target.
- Range of Potential Outcomes: Forecasts vary widely, reflecting the inherent uncertainty surrounding economic developments.
- Diverse Opinions: Leading economists and financial analysts offer differing perspectives on the efficacy of various policy options and their potential economic consequences.
Conclusion: Navigating the Core Inflation Challenge
This article highlights the severity of the core inflation surge in Canada and the complex dilemma facing the Bank of Canada. The central challenge remains balancing inflation control with the need for sustainable economic growth. The Bank's response to this core inflation surge will significantly shape Canada's economic future, impacting everything from employment to the value of the Canadian dollar. Stay informed about the Bank of Canada's decisions and their impact on the Canadian economy. Follow our blog for updates on the Bank of Canada's response to the core inflation surge and gain deeper insights into the complexities of managing core inflation in Canada.

Featured Posts
-
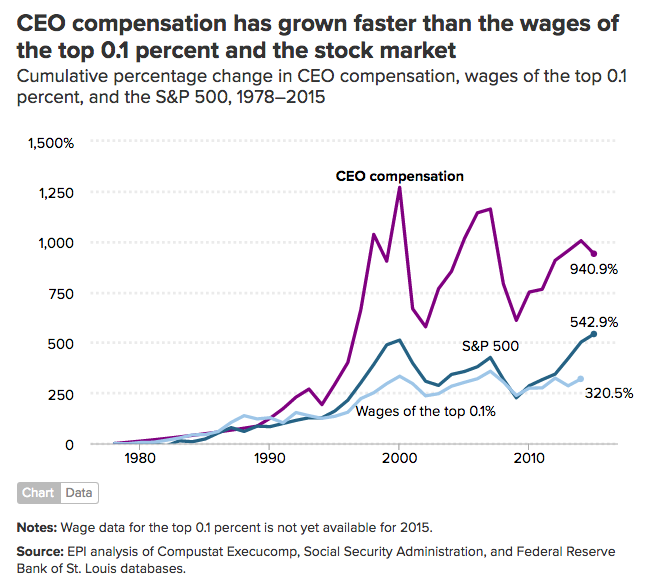 Analysis Of Bps 31 Reduction In Ceo Compensation
May 22, 2025
Analysis Of Bps 31 Reduction In Ceo Compensation
May 22, 2025 -
 Reduced Jackson Elk Hunting Permits Following Public Outcry
May 22, 2025
Reduced Jackson Elk Hunting Permits Following Public Outcry
May 22, 2025 -
 Trans Australia Run A Race To Rewrite History
May 22, 2025
Trans Australia Run A Race To Rewrite History
May 22, 2025 -
 Cassis Blackcurrant Liqueur A Comprehensive Guide
May 22, 2025
Cassis Blackcurrant Liqueur A Comprehensive Guide
May 22, 2025 -
 Thong Tin Chinh Thuc Cau Ma Da Dong Nai Binh Phuoc Khoi Cong Thang 6
May 22, 2025
Thong Tin Chinh Thuc Cau Ma Da Dong Nai Binh Phuoc Khoi Cong Thang 6
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Emergency Responders Tackle Significant Used Car Fire
May 22, 2025
Emergency Responders Tackle Significant Used Car Fire
May 22, 2025 -
 Used Car Dealer Fire Extensive Damage Reported
May 22, 2025
Used Car Dealer Fire Extensive Damage Reported
May 22, 2025 -
 Large Fire Engulfs Used Car Dealership Crews On Scene
May 22, 2025
Large Fire Engulfs Used Car Dealership Crews On Scene
May 22, 2025 -
 Crews Battle Blaze At Used Car Dealership
May 22, 2025
Crews Battle Blaze At Used Car Dealership
May 22, 2025 -
 Recent Susquehanna Valley Storm Damage Reports And Resources
May 22, 2025
Recent Susquehanna Valley Storm Damage Reports And Resources
May 22, 2025
