China's Push For US Drug Import Substitutes: A National Strategy

Table of Contents
Motivations Behind China's Import Substitution Strategy
China's drive to reduce dependence on US drug imports stems from a multifaceted strategy rooted in national security, economic growth, and improved healthcare accessibility.
National Security Concerns
Relying heavily on foreign pharmaceutical suppliers poses a significant national security risk. This vulnerability becomes acutely apparent during times of geopolitical tension or global crises.
- Potential disruptions to supply chains: Geopolitical instability or unexpected events can easily disrupt the import of essential medicines, potentially leading to shortages and impacting public health.
- Vulnerability during conflicts: International conflicts or trade disputes can severely restrict access to crucial medications, jeopardizing the health and well-being of the Chinese population.
- Control over essential medicines: Securing a domestic supply chain ensures national control over essential medicines, reducing dependence on foreign powers and mitigating potential leverage in diplomatic or economic negotiations.
Economic Independence and Growth
Developing a robust domestic pharmaceutical industry offers substantial economic advantages for China.
- Reducing reliance on foreign currency expenditure: Manufacturing drugs domestically reduces the need for foreign currency, strengthening the nation's economic independence and stability.
- Fostering innovation in the domestic pharmaceutical sector: Investment in research and development stimulates innovation, leading to advancements in drug discovery and manufacturing technologies.
- Promoting economic growth: A thriving pharmaceutical industry creates numerous jobs, attracts foreign investment, and contributes significantly to national economic growth.
Improving Healthcare Accessibility and Affordability
A key driver of China's import substitution strategy is the desire to improve healthcare accessibility and affordability for its vast population.
- Developing generic and biosimilar drugs: Focusing on generic and biosimilar medications significantly reduces medication costs, making essential drugs more accessible to a broader segment of the population.
- Reducing medication costs for patients: Lower drug prices alleviate the financial burden of healthcare on individuals and families, improving overall healthcare outcomes.
- Enhancing healthcare equity: Increased access to affordable medications promotes greater healthcare equity, ensuring that all citizens have access to the essential drugs they need.
Key Strategies Employed by China
China's strategy to replace US drug imports involves a multi-pronged approach focusing on investment, industry support, and intellectual property rights.
Investment in R&D and Infrastructure
Massive investments are being channeled into bolstering China's pharmaceutical capabilities.
- Government funding for pharmaceutical research: Significant government funding is directed towards research and development, accelerating innovation in drug discovery and development.
- Construction of advanced manufacturing plants: China is investing heavily in building state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities to produce high-quality pharmaceuticals domestically.
- Training and recruitment of skilled professionals: Efforts are focused on training and attracting skilled professionals to build a highly competent workforce within the pharmaceutical industry.
Promoting Domestic Pharmaceutical Companies
The Chinese government actively supports the growth of its domestic pharmaceutical companies.
- Tax incentives: Tax breaks and other financial incentives encourage domestic pharmaceutical companies to invest in research, development, and expansion.
- Streamlined regulatory approvals for domestic drugs: Faster approval processes for domestically produced drugs accelerate their entry into the market.
- Government procurement policies favoring local companies: Government agencies prioritize purchasing drugs from domestic manufacturers, supporting their growth and market share.
Intellectual Property Rights and Biosimilars
China's approach to intellectual property rights (IPR) concerning biosimilars and generic drugs is a delicate balancing act.
- Balancing innovation incentives with affordable access: China aims to strike a balance between protecting innovation through IPR and ensuring affordable access to essential medications for its population.
- Debates surrounding patent protection and biosimilar development: The debate surrounding patent protection and the development of biosimilars is ongoing, reflecting the complexities involved in balancing innovation and affordability.
- Impact on global pharmaceutical companies: China's approach to IPR significantly impacts global pharmaceutical companies, creating both opportunities and challenges for their operations in the Chinese market.
Challenges and Obstacles
Despite ambitious goals, China faces significant challenges in its pursuit of pharmaceutical independence.
Technological Gaps
A crucial hurdle is the technological gap between Chinese and US pharmaceutical companies.
- Need for further investment in cutting-edge technologies: Significant investment is still needed to bridge the gap in cutting-edge technologies used in drug discovery and manufacturing.
- Challenges in producing complex drugs: Producing complex biologics and other advanced medications requires sophisticated technologies and expertise that China is still developing.
- Knowledge transfer limitations: Acquiring the necessary technological know-how and expertise from international partners can be challenging.
Regulatory Hurdles and Quality Control
Ensuring high-quality and safe domestically produced drugs is paramount.
- Stricter regulatory oversight: Strengthening regulatory oversight and enforcement is crucial to maintaining high quality and safety standards in drug manufacturing.
- Improvements in manufacturing processes: Continuous improvements in manufacturing processes are essential to guarantee consistent product quality and meet international standards.
- Building international trust in the quality of Chinese pharmaceuticals: Gaining international recognition and trust in the quality and safety of Chinese-made pharmaceuticals is essential for expanding exports.
Global Market Competition
Competing in the global pharmaceutical market presents formidable challenges.
- Competing with established global players: Chinese pharmaceutical companies face intense competition from established multinational pharmaceutical companies.
- Meeting international regulatory standards: Meeting stringent international regulatory standards is crucial for gaining access to global markets.
- Building a strong brand reputation: Establishing a strong international brand reputation built on quality, safety, and innovation is essential for success in the global market.
Conclusion
China's push for US drug import substitutes is a multifaceted national strategy with far-reaching implications. Driven by national security concerns, economic ambitions, and a commitment to improved healthcare accessibility, this strategy involves substantial investments, policy reforms, and a focus on building a domestically competitive pharmaceutical industry. While significant challenges remain in areas such as technological advancements, regulatory hurdles, and global market competition, China's determination to achieve pharmaceutical independence is undeniable. Understanding China's strategy regarding US drug import substitutes is vital for navigating the evolving global pharmaceutical landscape. Continued analysis of this ambitious national strategy is critical for all stakeholders—from global pharmaceutical companies to policymakers—to effectively respond to the shifting dynamics within the global pharmaceutical market and the future of drug accessibility.

Featured Posts
-
 Ofc U 19 Womens Championship 2025 Tonga Earns Qualification
May 01, 2025
Ofc U 19 Womens Championship 2025 Tonga Earns Qualification
May 01, 2025 -
 Nvidias Geopolitical Risks A Look Beyond The China Factor
May 01, 2025
Nvidias Geopolitical Risks A Look Beyond The China Factor
May 01, 2025 -
 Geen Tbs Voor Erasmusschutter Fouad L De Redenen Achter De Levenslange Gevangenisstraf
May 01, 2025
Geen Tbs Voor Erasmusschutter Fouad L De Redenen Achter De Levenslange Gevangenisstraf
May 01, 2025 -
 Dragons Den Preparing Your Pitch For Success
May 01, 2025
Dragons Den Preparing Your Pitch For Success
May 01, 2025 -
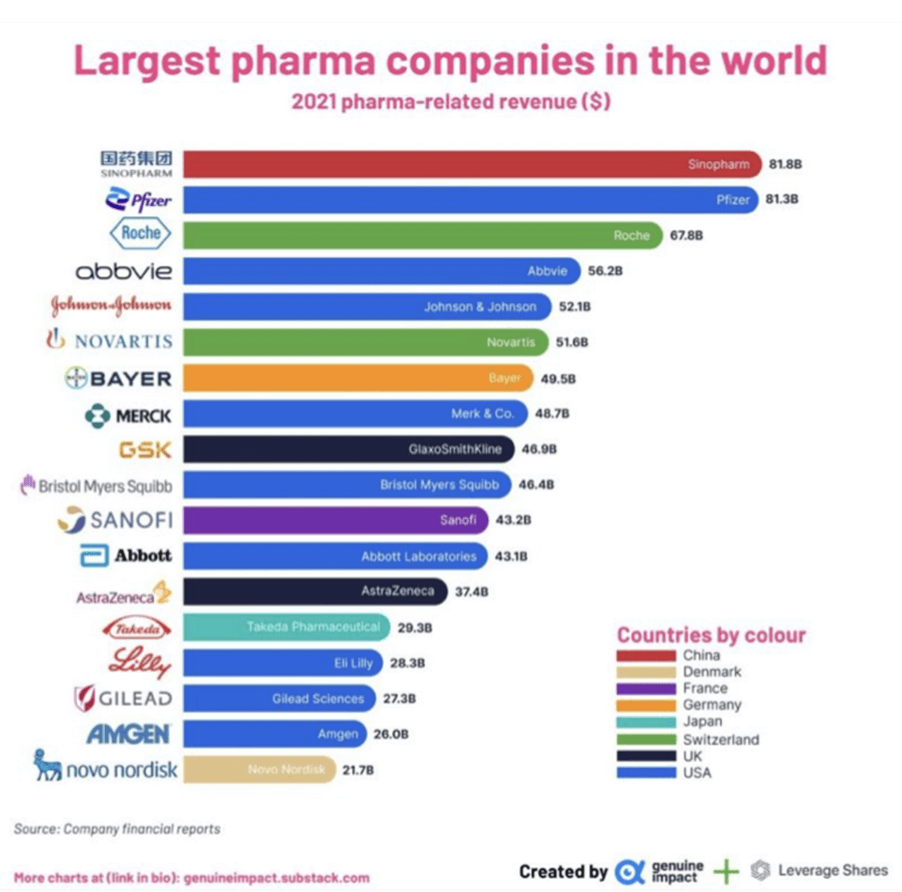 Finding Alternatives Chinas Response To Us Pharmaceutical Imports
May 01, 2025
Finding Alternatives Chinas Response To Us Pharmaceutical Imports
May 01, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Discover The Best New Southern Cruises For 2025
May 01, 2025
Discover The Best New Southern Cruises For 2025
May 01, 2025 -
 Analyzing Nclh Stock What Are Hedge Funds Doing
May 01, 2025
Analyzing Nclh Stock What Are Hedge Funds Doing
May 01, 2025 -
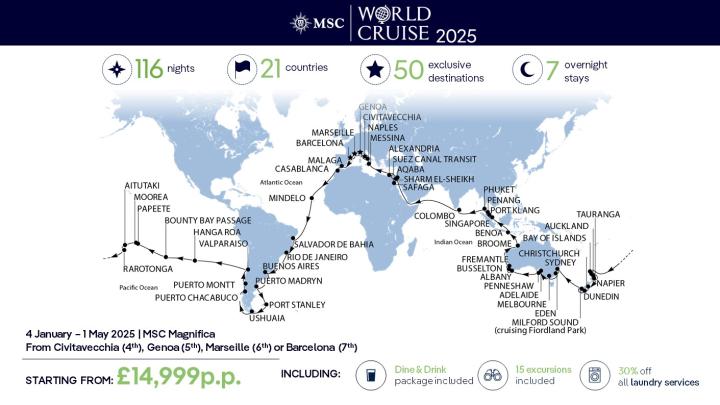 2025 Southern Cruises Your Guide To The Best New Ships And Routes
May 01, 2025
2025 Southern Cruises Your Guide To The Best New Ships And Routes
May 01, 2025 -
 Hedge Fund Activity And The Norwegian Cruise Line Nclh Stock Price
May 01, 2025
Hedge Fund Activity And The Norwegian Cruise Line Nclh Stock Price
May 01, 2025 -
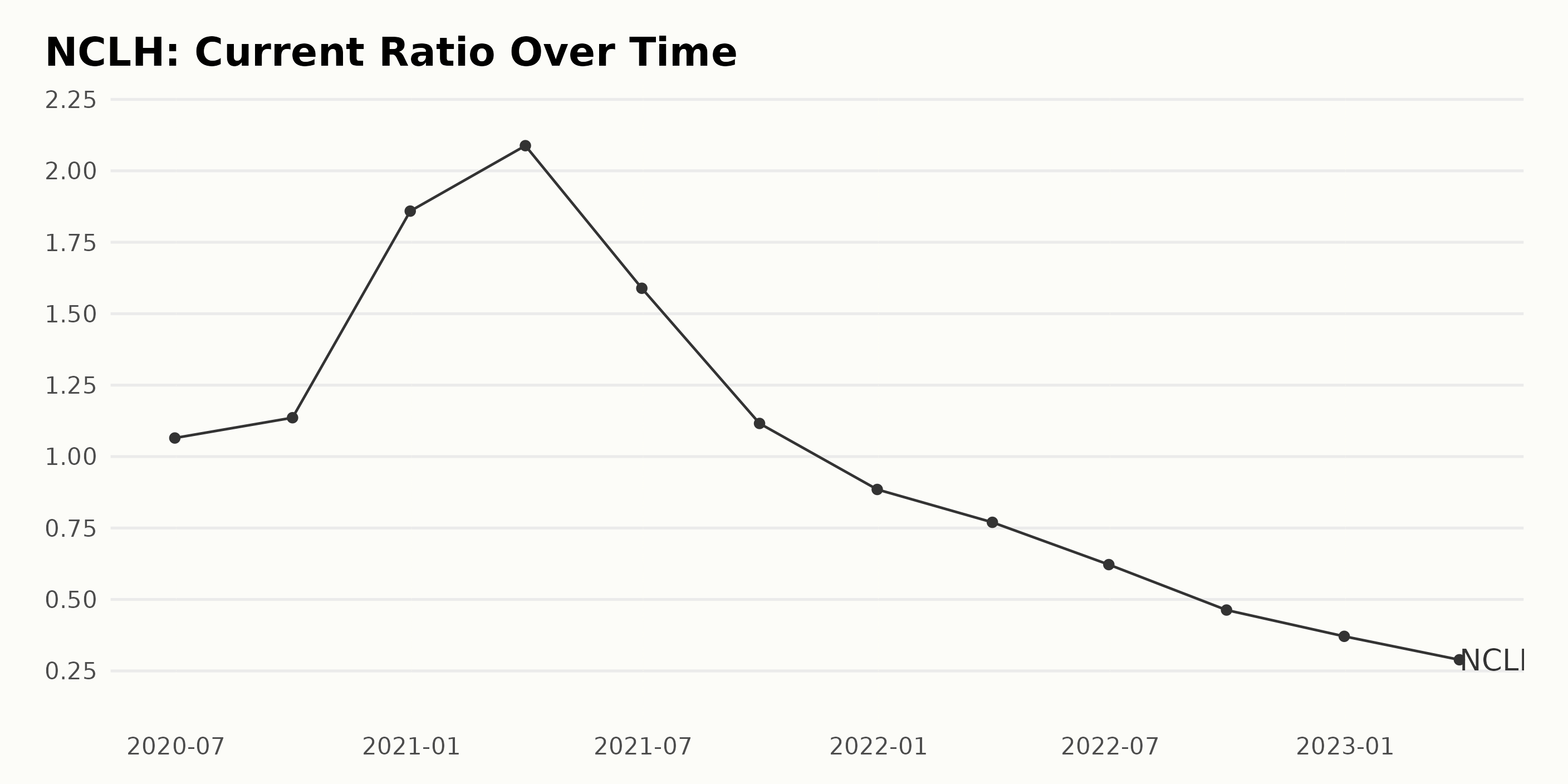 Norwegian Cruise Line Nclh A Hedge Fund Perspective On Investment
May 01, 2025
Norwegian Cruise Line Nclh A Hedge Fund Perspective On Investment
May 01, 2025
