Canadian Dollar's High Value: Economic Implications And Necessary Reforms
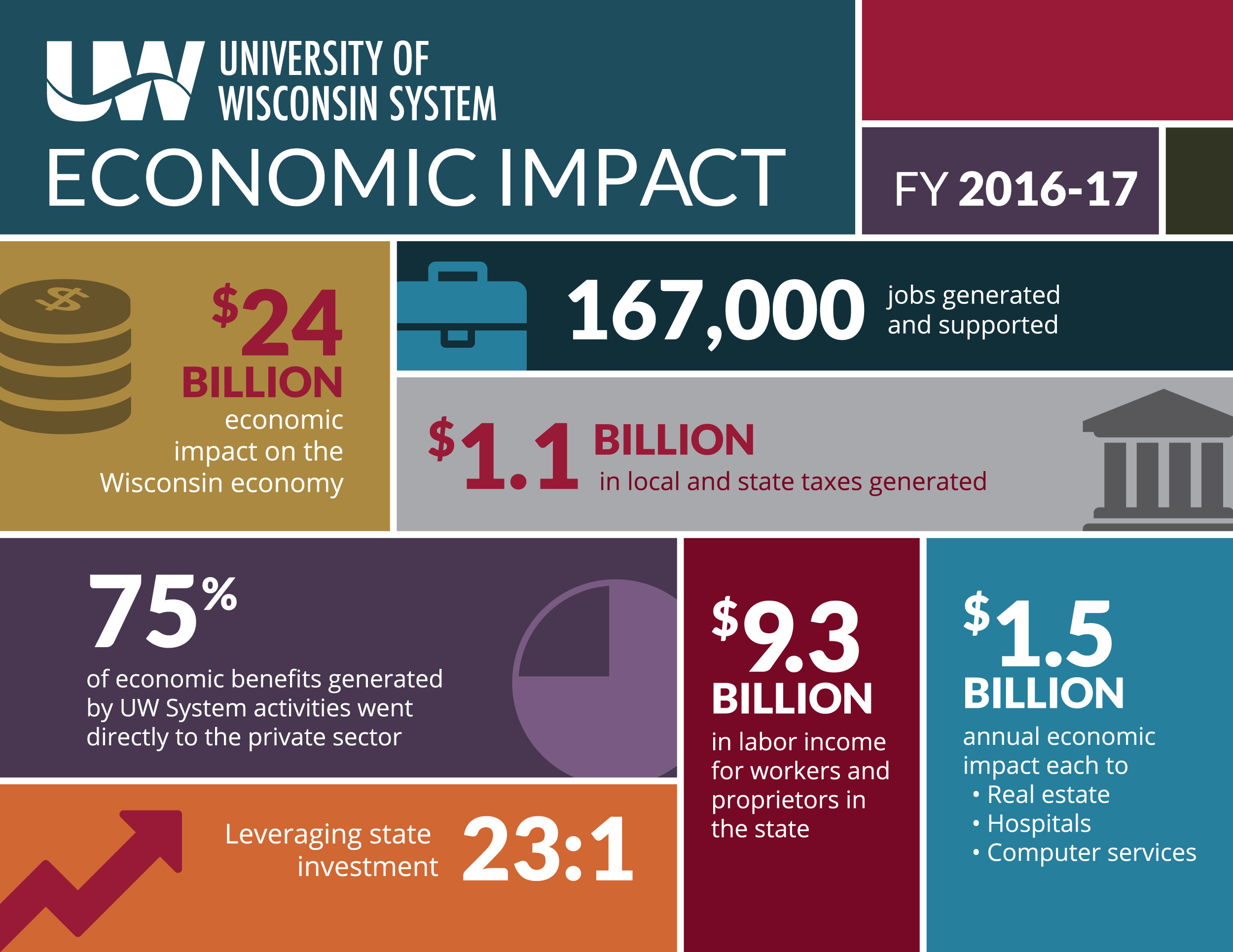
Table of Contents
Impact on Exports
A strong Canadian dollar directly impacts the competitiveness of Canadian exports. Increased value makes Canadian goods more expensive for international buyers, potentially leading to reduced demand and lost market share. This weakening of the Canadian dollar's competitiveness in the global market necessitates a thorough understanding of its effects.
Reduced Export Revenue
Higher prices for Canadian goods resulting from a high Canadian dollar can result in lower sales volumes and decreased export revenue for Canadian businesses. This decreased profitability directly affects several key areas:
- Reduced profitability for export-oriented industries: Companies relying heavily on exports face shrinking profit margins, forcing them to adapt or risk closure.
- Potential job losses in export-dependent sectors: Reduced profitability can lead to layoffs and restructuring as businesses struggle to maintain operations.
- Increased vulnerability to global economic downturns: A reliance on exports makes the Canadian economy more susceptible to external shocks and global recessions.
Increased Competition from Foreign Importers
Conversely, a strong Canadian dollar makes imports cheaper. This increased competition from cheaper foreign imports can put pressure on domestic producers, further impacting profitability and employment within Canada. This increased competition puts significant pressure on Canadian businesses, requiring significant adaptations:
- Loss of market share to foreign competitors: Domestic businesses struggle to compete with lower-priced imports, leading to market share erosion.
- Pressure on domestic pricing strategies: Canadian businesses might be forced to lower their prices to remain competitive, squeezing profit margins.
- Need for increased efficiency and innovation to compete: To survive, Canadian businesses must enhance productivity and develop innovative products and services.
Impact on Imports
While a strong Canadian dollar makes imports cheaper for consumers, this benefit also has potential downsides for the Canadian economy.
Increased Consumer Spending on Imports
Lower import prices can lead to increased consumer spending on foreign goods, potentially shifting consumer behavior and preferences significantly:
- Potential shift in consumer preferences towards imported goods: Consumers may opt for cheaper foreign products over domestically produced alternatives.
- Reduced demand for domestically produced goods: This shift in consumer preference can hurt domestic industries and lead to job losses.
- Impact on domestic industries competing with imports: Domestic producers face increased pressure to compete, potentially leading to business closures.
Dependence on Foreign Goods and Services
Increased reliance on imports creates vulnerabilities in the supply chain, threatening the stability of the Canadian economy:
- Risk of supply disruptions due to global events: Dependence on foreign suppliers makes Canada susceptible to global disruptions like pandemics or geopolitical instability.
- Potential for inflation if import costs rise: If the cost of imports increases for any reason, it can lead to inflation within Canada.
- Need for diversification of supply chains: Canada needs to diversify its import sources to reduce its vulnerability to disruptions.
Necessary Economic Reforms
Addressing the challenges posed by a high Canadian dollar requires a multi-pronged approach involving government policies and proactive business strategies.
Diversification of Export Markets
Reducing reliance on specific export markets through diversification can mitigate the impact of currency fluctuations. This crucial element of economic resilience requires several key actions:
- Exploring new markets and trade agreements: Canada needs to actively seek new trade partners and agreements to reduce its reliance on existing ones.
- Investing in market research and promotion of Canadian goods abroad: Government support is needed to help Canadian businesses explore and enter new markets.
- Supporting small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in expanding their international reach: SMEs are a vital part of the Canadian economy and need assistance to compete globally.
Investment in Innovation and Productivity
Improving productivity and innovation can enhance the competitiveness of Canadian businesses, allowing them to better withstand currency fluctuations. This involves a significant commitment to:
- Investing in research and development (R&D): Increased investment in R&D is critical for developing innovative products and services.
- Supporting the adoption of new technologies: Businesses need support to adopt and implement new technologies to improve efficiency and productivity.
- Implementing policies to attract and retain skilled workers: A skilled workforce is essential for innovation and economic growth.
Fiscal and Monetary Policy Adjustments
Government policies can play a crucial role in managing the impact of a high Canadian dollar. This might include measures to stimulate domestic demand or to support specific industries affected by the currency's appreciation. Effective policy adjustments can include:
- Targeted subsidies or tax incentives: Providing financial support to specific industries struggling with the high Canadian dollar.
- Infrastructure investment to boost domestic demand: Investing in infrastructure projects can stimulate economic activity and create jobs.
- Monetary policy adjustments to manage inflation and interest rates: The Bank of Canada can use monetary policy tools to manage inflation and interest rates in response to the high Canadian dollar.
Conclusion
The high value of the Canadian dollar presents a complex economic challenge, impacting both exports and imports. While offering some benefits for consumers, it poses significant risks to Canadian businesses and employment. Addressing this requires a comprehensive strategy including diversification of export markets, investment in innovation and productivity, and well-considered fiscal and monetary policy adjustments. Understanding the complexities of the Canadian dollar's high value and implementing appropriate reforms is crucial for ensuring long-term economic stability and growth. Proactive strategies to manage the Canadian dollar's high value are essential for a healthy and resilient Canadian economy. Effective management of the Canadian dollar's high value is vital for Canada's continued economic prosperity.

Featured Posts
-
 Dwps Increased Home Visits Impact On Benefit Claimants
May 08, 2025
Dwps Increased Home Visits Impact On Benefit Claimants
May 08, 2025 -
 Papal Election Cardinals Review Candidate Dossiers
May 08, 2025
Papal Election Cardinals Review Candidate Dossiers
May 08, 2025 -
 Savage Land Showdown Rogue Comic 2 Preview Featuring Ka Zar
May 08, 2025
Savage Land Showdown Rogue Comic 2 Preview Featuring Ka Zar
May 08, 2025 -
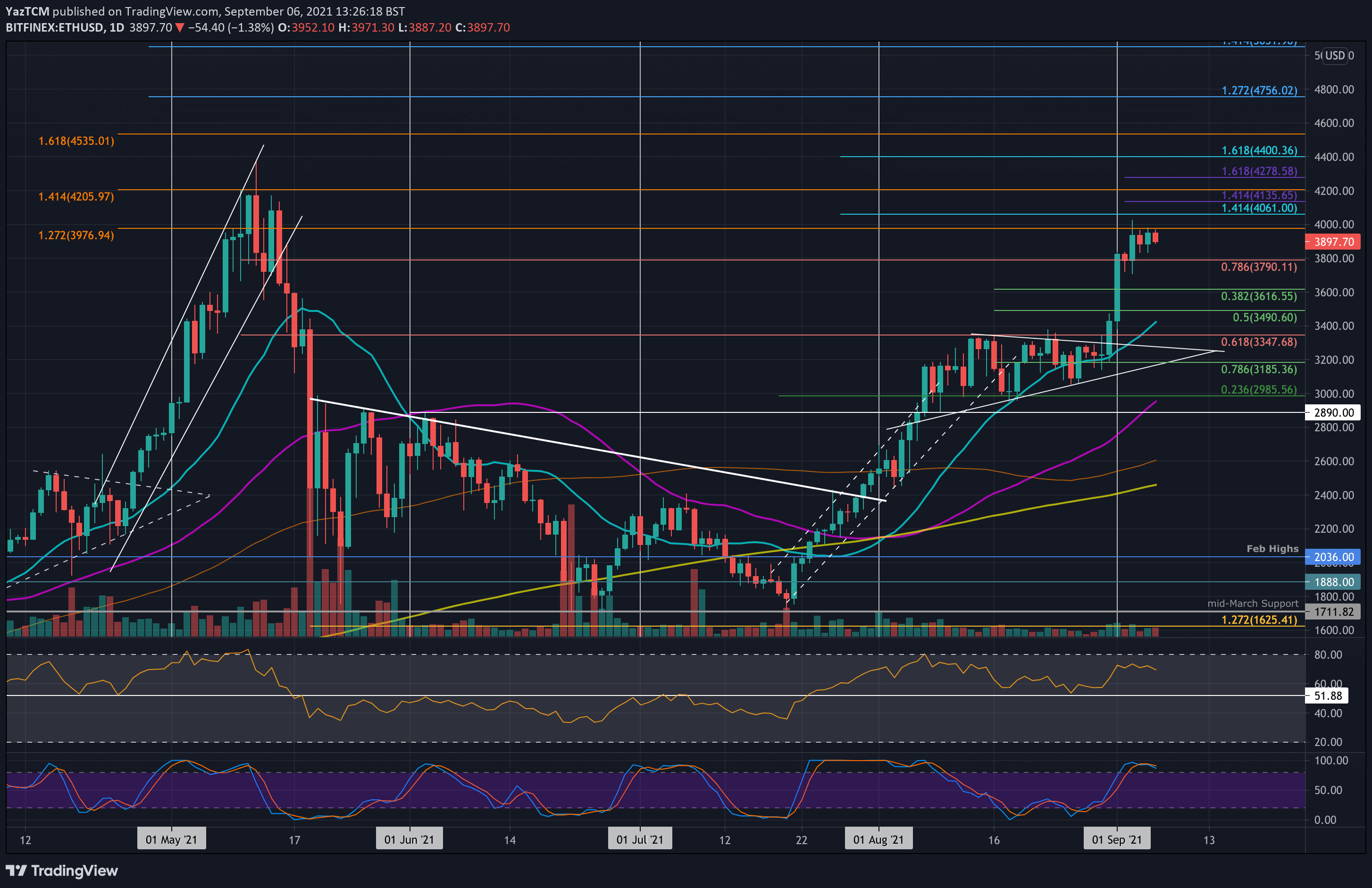 Is This Ethereum Buy Signal Real Weekly Chart Deep Dive
May 08, 2025
Is This Ethereum Buy Signal Real Weekly Chart Deep Dive
May 08, 2025 -
 Dossier On Papal Candidates Cardinals Weigh Options
May 08, 2025
Dossier On Papal Candidates Cardinals Weigh Options
May 08, 2025
