Zebra Mussel Infestation Discovered In Casper

Table of Contents
The Threat of Zebra Mussels in Casper's Waterways
Understanding Zebra Mussels
Zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) are small, fingernail-sized mollusks native to Eurasia. Their remarkable ability to reproduce quickly, with a single female producing up to one million eggs per year, makes them a formidable invasive species. Their filter-feeding habits, while beneficial to water clarity in some cases, dramatically impact native aquatic life. They consume vast quantities of phytoplankton, depriving native species of food, and they can also attach to and smother native mussels and other organisms.
- Origin: Eurasia
- Rapid Reproduction: Up to one million eggs per female per year.
- Filter-Feeding Habits: Consume vast quantities of phytoplankton.
- Impact on Native Species: Competition for food and habitat, smothering of native mussels.
- Clogging of Pipes and Infrastructure: Attachment to pipes and infrastructure causes blockages and damage.
Impact on Casper's Ecosystem
The presence of zebra mussels in Casper's waterways poses a serious threat to the local ecosystem. Specific lakes and rivers are now at risk, with potential disruptions to the aquatic food web already underway. The impact on native species, such as fish and other invertebrates, could be catastrophic. The economic consequences are also significant, potentially affecting fishing and recreational activities that are vital to the Casper economy.
- Specific Lakes and Rivers Affected: [Insert specific names of affected water bodies here, if available. If not, mention general areas.]
- Endangered Native Species: [List specific endangered species at risk, if known.]
- Potential Impact on Fishing and Recreation: Reduced fish populations, potential closure of recreational areas.
- Economic Cost of Control Measures: Significant costs associated with monitoring, control, and mitigation efforts.
Spread and Pathways
Zebra mussels are notorious for their ability to spread rapidly. In Casper, several pathways facilitate their spread, including recreational boating, ballast water discharge from ships, and unintentional transport on fishing gear or other equipment. Preventing the further spread relies heavily on responsible behavior and diligent preventative measures.
- Common Vectors for Spread: Recreational boats, trailers, fishing gear, ballast water.
- Importance of Cleaning Boats and Equipment: Thoroughly cleaning and drying boats and equipment before and after use in infested waters.
- Role of Human Activity in Spreading the Infestation: Unintentional transport on improperly cleaned boats and equipment is a primary driver of spread.
Response and Mitigation Efforts
Local and State Response
Local authorities and state agencies in Wyoming are working diligently to contain the zebra mussel infestation in Casper. This includes implementing robust monitoring programs, conducting surveys to assess the extent of the infestation, and launching public awareness campaigns to educate residents. Control measures, such as chemical treatments in localized areas and physical removal where feasible, are also being considered. Collaboration between various agencies is vital for a coordinated response.
- Surveys: Ongoing assessments of the extent of the infestation.
- Monitoring Programs: Continuous monitoring of water quality and zebra mussel populations.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educational efforts to inform the public about the threat and prevention measures.
- Control Measures: Chemical treatments, physical removal, and other methods.
- Collaboration between Agencies: Coordination between local, state, and federal agencies.
Community Involvement and Prevention
Community involvement is crucial in preventing the further spread of zebra mussels. Every individual can play a vital role by diligently cleaning their boats and equipment, thoroughly inspecting gear after use, and reporting any sightings of zebra mussels immediately to the relevant authorities. Supporting local initiatives and accessing educational resources are also important contributions to this fight.
- Cleaning Boats: Thoroughly cleaning and drying boats and trailers before and after use.
- Inspecting Gear: Carefully checking fishing gear, anchors, and other equipment for zebra mussels.
- Reporting Sightings: Immediately reporting any sightings to the Wyoming Game and Fish Department or other relevant authorities.
- Supporting Local Initiatives: Contributing to local efforts to control and prevent the spread of zebra mussels.
- Educational Resources: Seeking information and educational resources on zebra mussel identification and prevention strategies.
Long-Term Implications and Future Outlook
Ecological Long-Term Impacts
The long-term ecological consequences of the zebra mussel infestation in Casper could be far-reaching. Changes in species composition, altered nutrient cycling, and potential cascading effects throughout the food web are all possible outcomes. The impact on biodiversity could be severe, potentially leading to the decline or extinction of native species.
- Changes in Species Composition: Displacement of native species by zebra mussels.
- Altered Nutrient Cycling: Changes in nutrient availability and water quality.
- Potential for Cascading Effects: Impacts on higher trophic levels in the food web.
Economic and Social Consequences
The long-term economic and social implications of the infestation are significant. The cost of ongoing control and mitigation efforts will be substantial, placing a burden on taxpayers and potentially impacting local budgets. The impact on tourism and recreation could also be severe, reducing visitor numbers and harming local businesses that rely on these activities. Developing long-term management strategies is crucial for minimizing these impacts.
- Costs Associated with Mitigation: Significant costs associated with monitoring, control, and management.
- Potential Impact on Tourism: Reduced visitor numbers due to concerns about water quality and recreational opportunities.
- Long-Term Management Strategies: Development of sustainable strategies for long-term control and management of the infestation.
Conclusion
The zebra mussel infestation in Casper represents a serious threat to Wyoming's waterways. The rapid reproductive rate and devastating ecological impact of this invasive species demand immediate and sustained action. Local, state, and community efforts are crucial to control the spread and mitigate the long-term consequences.
Help protect Casper's waterways from the devastating effects of zebra mussel infestation. Report sightings immediately to the Wyoming Game and Fish Department [insert link here] and take action to prevent further spread. Learn more about prevention strategies and how you can help at [insert link to relevant resources here]. Your participation is vital in safeguarding Casper's valuable aquatic ecosystems.

Featured Posts
-
 Ea Fc 24 Fut Birthday Ultimate Team Player Tier List And Ratings
May 22, 2025
Ea Fc 24 Fut Birthday Ultimate Team Player Tier List And Ratings
May 22, 2025 -
 Is Blake Lively Involved In This Alleged Scandal A Deep Dive
May 22, 2025
Is Blake Lively Involved In This Alleged Scandal A Deep Dive
May 22, 2025 -
 The Risky Business Of Ceo Relationships A Case Study
May 22, 2025
The Risky Business Of Ceo Relationships A Case Study
May 22, 2025 -
 Invest Smart A Guide To The Countrys Newest Business Hotspots
May 22, 2025
Invest Smart A Guide To The Countrys Newest Business Hotspots
May 22, 2025 -
 Fastest Australian Foot Crossing A New Record Is Set
May 22, 2025
Fastest Australian Foot Crossing A New Record Is Set
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Dong Nai Kien Nghi Duong Cao Toc 4 Lan Xe Xuyen Rung Ma Da Den Binh Phuoc
May 22, 2025
Dong Nai Kien Nghi Duong Cao Toc 4 Lan Xe Xuyen Rung Ma Da Den Binh Phuoc
May 22, 2025 -
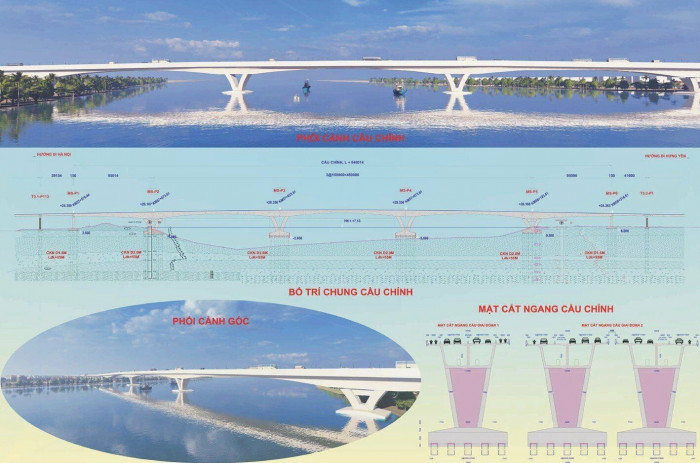 De Xuat Xay Dung Duong 4 Lan Xe Xuyen Rung Ma Da Ket Noi Dong Nai Va Binh Phuoc
May 22, 2025
De Xuat Xay Dung Duong 4 Lan Xe Xuyen Rung Ma Da Ket Noi Dong Nai Va Binh Phuoc
May 22, 2025 -
 7 Du An Ket Noi Giao Thong Tp Hcm Long An Uu Tien Dau Tu
May 22, 2025
7 Du An Ket Noi Giao Thong Tp Hcm Long An Uu Tien Dau Tu
May 22, 2025 -
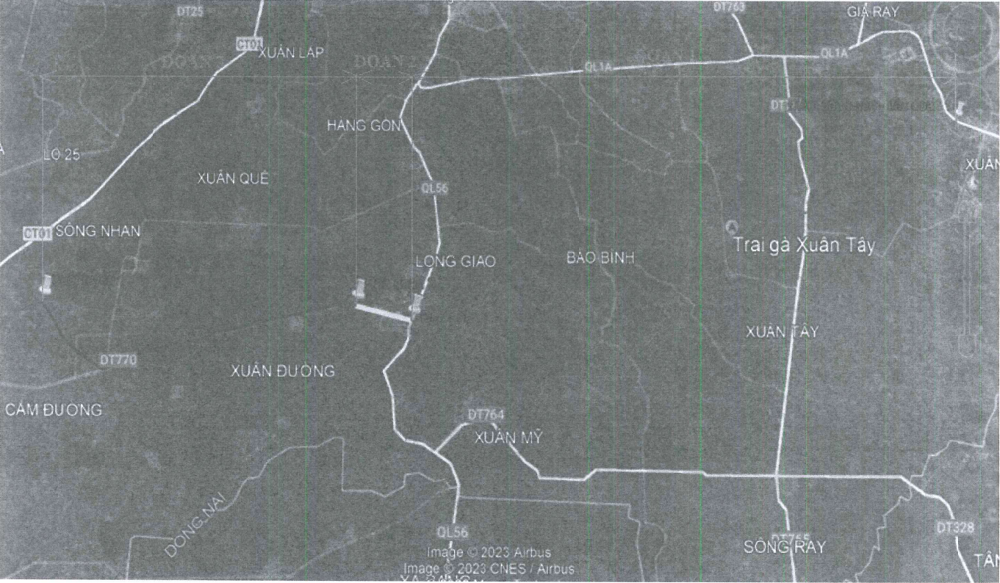 Dong Nai Kien Nghi Xay Dung Duong 4 Lan Xe Xuyen Rung Ma Da Noi Binh Phuoc
May 22, 2025
Dong Nai Kien Nghi Xay Dung Duong 4 Lan Xe Xuyen Rung Ma Da Noi Binh Phuoc
May 22, 2025 -
 Phan Tich 7 Vi Tri Ket Noi Hap Dan Tp Hcm Long An
May 22, 2025
Phan Tich 7 Vi Tri Ket Noi Hap Dan Tp Hcm Long An
May 22, 2025
