What Is The Great Decoupling And Why Does It Matter?
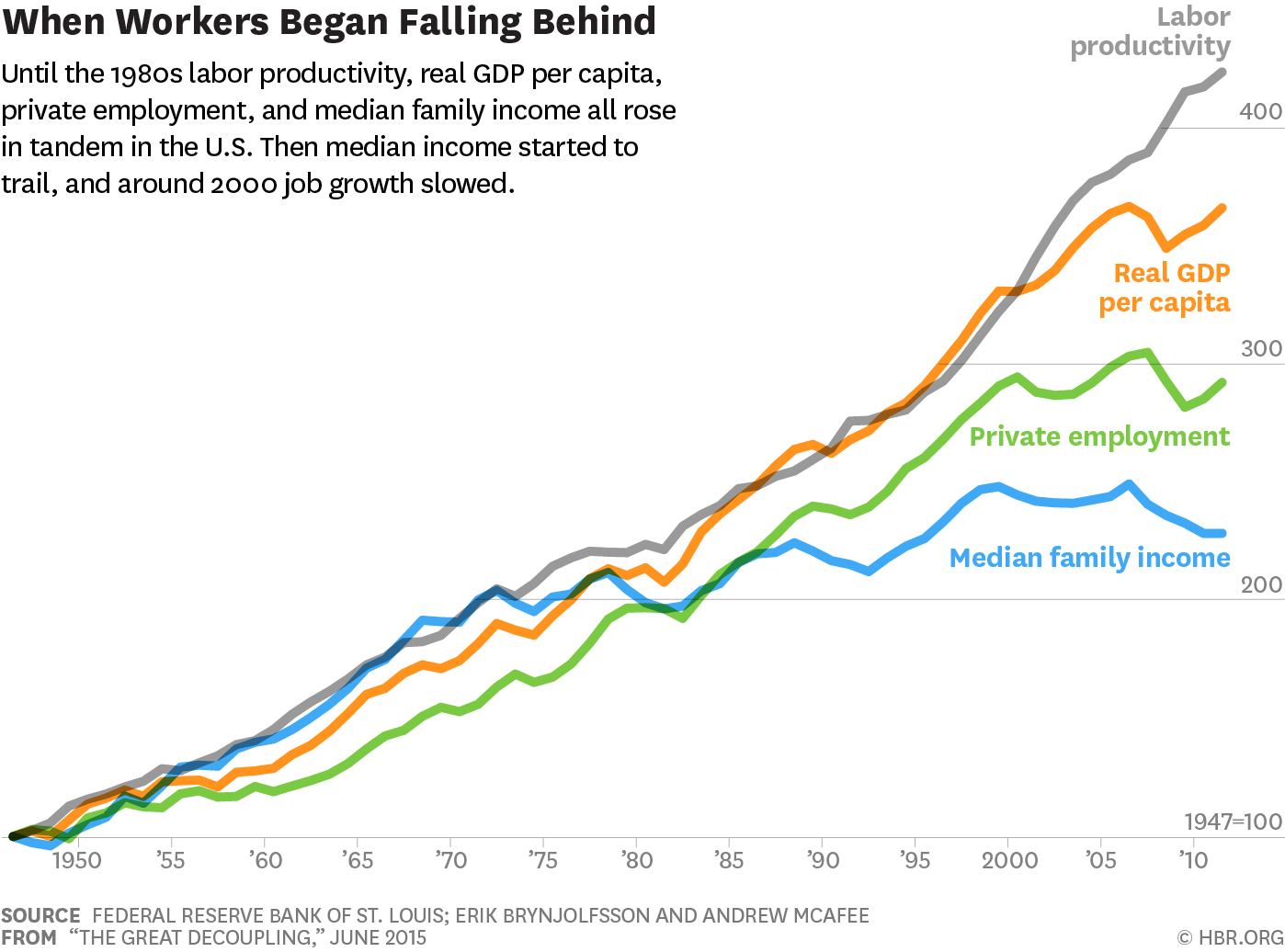
Table of Contents
The Drivers of the Great Decoupling
Several interconnected factors fuel the Great Decoupling, creating a complex web of challenges and opportunities.
Geopolitical Tensions and Trade Wars
Increasing US-China rivalry is a primary driver. Trade disputes, characterized by escalating tariffs and sanctions, have significantly strained the relationship. This protectionist environment disrupts established global supply chains and fosters uncertainty.
- Examples: The US-China trade war initiated in 2018, with tariffs imposed on hundreds of billions of dollars worth of goods; sanctions targeting specific Chinese companies over national security concerns.
- Impact: Supply chain disruptions, increased production costs, and a shift towards regionalization of manufacturing.
- Keywords: Geopolitical risks, trade wars, tariffs, sanctions, supply chain disruptions, protectionism.
Technological Competition and National Security Concerns
Concerns over intellectual property theft, the pursuit of technological dominance, and national security are exacerbating the decoupling. Both nations are investing heavily in critical technologies, leading to a competition for leadership in areas like semiconductors and artificial intelligence.
- Examples: US restrictions on the sale of advanced semiconductor manufacturing equipment to China; increased investment in domestic semiconductor production in both countries; export controls on sensitive technologies like 5G.
- Keywords: Technology decoupling, intellectual property theft, national security, semiconductor industry, AI development, 5G technology.
Ideological Differences and Diverging Values
Fundamental differences in political systems and values further complicate the relationship. Contrasting approaches to human rights, data privacy, and cybersecurity create friction and hinder cooperation.
- Examples: Differing views on human rights in Xinjiang and Hong Kong; contrasting approaches to data privacy regulations; concerns over Chinese influence in global technology standards.
- Keywords: Ideological differences, political systems, human rights, data privacy, cybersecurity.
The Economic Impacts of the Great Decoupling
The Great Decoupling is causing significant economic ripples worldwide.
Restructuring Global Supply Chains
Companies are diversifying their supply chains to reduce reliance on either China or the US, a process impacting global supply chains significantly. This “de-risking” strategy, while potentially enhancing resilience, increases costs and complexity.
- Examples: Companies relocating production to Southeast Asia, India, or Mexico ("friend-shoring" and "nearshoring"); increased logistics costs due to longer and more complex supply chains; a rise in "reshoring" – bringing manufacturing back to the home country.
- Keywords: Supply chain diversification, friend-shoring, nearshoring, reshoring, global supply chains, logistics costs.
Investment Implications and Market Volatility
Geopolitical uncertainty stemming from the Great Decoupling leads to increased market volatility and shifts in global investment flows. Investors are reevaluating risk premiums and seeking diversification strategies.
- Examples: Increased volatility in stock markets; shifts in foreign direct investment towards regionalized economies; higher risk premiums for investments in countries perceived as vulnerable to geopolitical risks.
- Keywords: Global investment, market volatility, geopolitical uncertainty, regionalization, risk premiums, portfolio diversification.
Impact on Innovation and Technological Advancement
The Great Decoupling presents a double-edged sword for innovation. While competition can spur technological advancement, fragmentation of research and development efforts could hinder progress.
- Arguments for increased innovation: Increased competition between two major technological powers can lead to faster innovation.
- Arguments for slower innovation: Fragmented research efforts and reduced collaboration may slow technological advancement in certain areas.
- Keywords: Technological innovation, R&D investment, competition, fragmentation, technological advancement.
Adapting to the Great Decoupling
Navigating the complexities of the Great Decoupling requires proactive strategies.
Strategies for Businesses
Businesses must develop resilient strategies to mitigate risks and capitalize on new opportunities. This includes diversifying supply chains, conducting thorough geopolitical risk assessments, and adapting to changing regulations.
- Examples: Investing in automation and technology to reduce reliance on specific suppliers; developing multiple sourcing options; building stronger relationships with governments and regulatory bodies.
- Keywords: Business strategies, risk management, geopolitical risk assessment, supply chain resilience, regulatory compliance.
Policy Responses and International Cooperation
Governments and international organizations play a vital role in shaping the trajectory of the Great Decoupling. Policy responses can either exacerbate the separation or foster cooperation.
- Examples: Government subsidies for domestic production; the development of new trade agreements focused on specific regions; attempts at international cooperation to address shared challenges.
- Keywords: Government policies, international cooperation, trade agreements, economic sanctions, regulatory frameworks.
Conclusion
The Great Decoupling is a multifaceted phenomenon driven by geopolitical tensions, technological competition, and ideological differences. Its economic consequences are far-reaching, impacting global supply chains, investment flows, and technological innovation. Understanding the nuances of US-China decoupling and broader economic decoupling is critical for businesses and investors to adapt and mitigate risks. Learn more about the Great Decoupling, stay informed about its implications, and proactively develop strategies to navigate this evolving global landscape. The future of global economics hinges on our ability to understand and effectively respond to this significant shift.

Featured Posts
-
 Neymar En Prelista De Brasil Regreso Ante Argentina
May 08, 2025
Neymar En Prelista De Brasil Regreso Ante Argentina
May 08, 2025 -
 Understanding Ubers Shift To Subscription Plans For Drivers
May 08, 2025
Understanding Ubers Shift To Subscription Plans For Drivers
May 08, 2025 -
 110 Potential Gains Analyzing The Black Rock Etf Billionaires Are Buying
May 08, 2025
110 Potential Gains Analyzing The Black Rock Etf Billionaires Are Buying
May 08, 2025 -
 Glen Powells The Running Man Transformation Diet Fitness And Mindset
May 08, 2025
Glen Powells The Running Man Transformation Diet Fitness And Mindset
May 08, 2025 -
 Aj Aym Aym Ealm Ky 12 Wyn Brsy Yadgar Tqaryb Ka Aneqad
May 08, 2025
Aj Aym Aym Ealm Ky 12 Wyn Brsy Yadgar Tqaryb Ka Aneqad
May 08, 2025
