What Is The Good Life? Exploring Concepts Of Meaning And Purpose

Table of Contents
Defining the "Good Life": Philosophical Perspectives
The concept of the "good life" has been interpreted differently throughout history. Several prominent philosophical perspectives offer valuable insights:
Hedonism: Pleasure as the Ultimate Good
Hedonism posits that pleasure is the ultimate good and the primary goal of life. Thinkers like Epicurus advocated for a life of moderate pleasures, minimizing pain and maximizing enjoyment. However, critics argue that a purely hedonistic approach can lead to shallowness and a lack of long-term fulfillment. The pursuit of fleeting pleasures, like excessive indulgence in food or material possessions, can often lead to disappointment and addiction.
- Examples of hedonistic pursuits: Overindulgence in food, excessive shopping, substance abuse.
- Potential drawbacks: Addiction, fleeting pleasure, lack of lasting fulfillment, potential for neglecting other important aspects of life.
Virtue Ethics: Character and Moral Excellence
Virtue ethics, championed by Aristotle, emphasizes the importance of developing virtuous character traits as the path to a good life. It focuses less on specific actions and more on cultivating moral excellence. Virtues like courage, honesty, justice, and compassion are seen as essential for flourishing. By consistently acting in accordance with these virtues, individuals cultivate a strong moral character that contributes to both personal well-being and the well-being of society.
- Examples of virtues: Honesty, kindness, courage, justice, compassion.
- How developing virtues contributes to a good life: Stronger relationships, increased self-respect, greater resilience, a more meaningful existence.
Eudaimonia: Flourishing and Living Well
Eudaimonia, a central concept in Aristotelian ethics, translates roughly to "flourishing" or "living well." It emphasizes the importance of living a life of purpose and meaning, realizing one's full potential, and contributing to something greater than oneself. Eudaimonia isn't simply about happiness; it's about living a life of excellence and fulfilling one's unique capabilities.
- Activities that contribute to eudaimonia: Meaningful work, strong relationships, contributing to community, pursuing personal growth, engaging in activities that bring a sense of purpose.
The Role of Meaning and Purpose in the Good Life
A fulfilling life is rarely achieved without a sense of meaning and purpose. These elements act as guiding stars, illuminating our path and providing motivation to overcome challenges.
Finding Your Purpose: Identifying Your Values and Passions
Discovering your purpose involves deep self-reflection and identifying your core values and passions. What truly matters to you? What activities bring you joy and a sense of fulfillment? Aligning your actions with your values is crucial for creating a meaningful life.
- Methods for discovering your purpose: Journaling, introspection, exploring different experiences, talking to mentors, seeking feedback from others.
The Importance of Relationships: Social Connection and Belonging
Strong social connections are essential for well-being. Love, friendship, and community provide support, belonging, and a sense of shared experience. These relationships enrich our lives, providing emotional sustenance and a sense of belonging.
- Benefits of strong relationships: Increased happiness, reduced stress, improved physical health, a sense of belonging, support during challenging times.
- Strategies for building meaningful connections: Nurturing existing relationships, actively seeking out new connections, engaging in activities you enjoy with others, practicing empathy and compassion.
Contribution and Legacy: Making a Difference in the World
Finding meaning often involves contributing to something larger than ourselves. Whether it’s volunteering, pursuing a career that benefits others, or engaging in activism, making a difference in the world can profoundly impact our sense of purpose and fulfillment. The desire to leave a positive legacy also contributes significantly to a meaningful life.
- Examples of contributing to society: Volunteering, charitable giving, mentoring, advocating for social justice, pursuing a career that benefits others.
- The positive impact on personal well-being: Increased sense of purpose, improved self-esteem, greater happiness, increased life satisfaction.
Practical Steps Towards a Good Life
While philosophical perspectives provide a framework, practical steps are necessary to cultivate a good life.
Mindfulness and Self-Awareness: Cultivating Present Moment Awareness
Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and yoga, cultivate present moment awareness, reducing stress and increasing self-awareness. This heightened self-awareness allows for better decision-making and a greater understanding of your own needs and desires.
- Mindfulness techniques: Meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, mindful walking.
- Benefits for mental and emotional well-being: Reduced stress, increased self-awareness, improved focus, greater emotional regulation.
Goal Setting and Action: Creating a Roadmap for a Fulfilling Life
Setting meaningful goals aligned with your values and purpose provides direction and motivation. Breaking down large goals into smaller, manageable steps makes the journey less daunting and more rewarding.
- SMART goal setting techniques: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound.
- Strategies for staying motivated: Celebrating milestones, seeking support from others, focusing on progress rather than perfection.
Gratitude and Appreciation: Focusing on the Positive Aspects of Life
Practicing gratitude involves focusing on the positive aspects of life, fostering appreciation for what you have. This simple practice can significantly boost happiness and well-being.
- Positive psychological effects of gratitude: Increased happiness, improved physical health, stronger relationships, increased resilience.
- Simple ways to incorporate it into daily life: Keeping a gratitude journal, expressing thanks to others, noticing and appreciating the small things.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the good life is not a single destination but an ongoing journey of self-discovery and growth. By incorporating philosophical insights, cultivating meaning and purpose, and taking practical steps towards self-awareness and gratitude, you can create a life rich in happiness, fulfillment, and lasting joy. Start your journey towards a more meaningful and purposeful life today. Begin exploring what truly matters to you and build your own version of the good life, focusing on living a good life filled with meaning and purpose. Embrace the journey of purposeful living and discover your own unique path towards a truly meaningful and fulfilling life.

Featured Posts
-
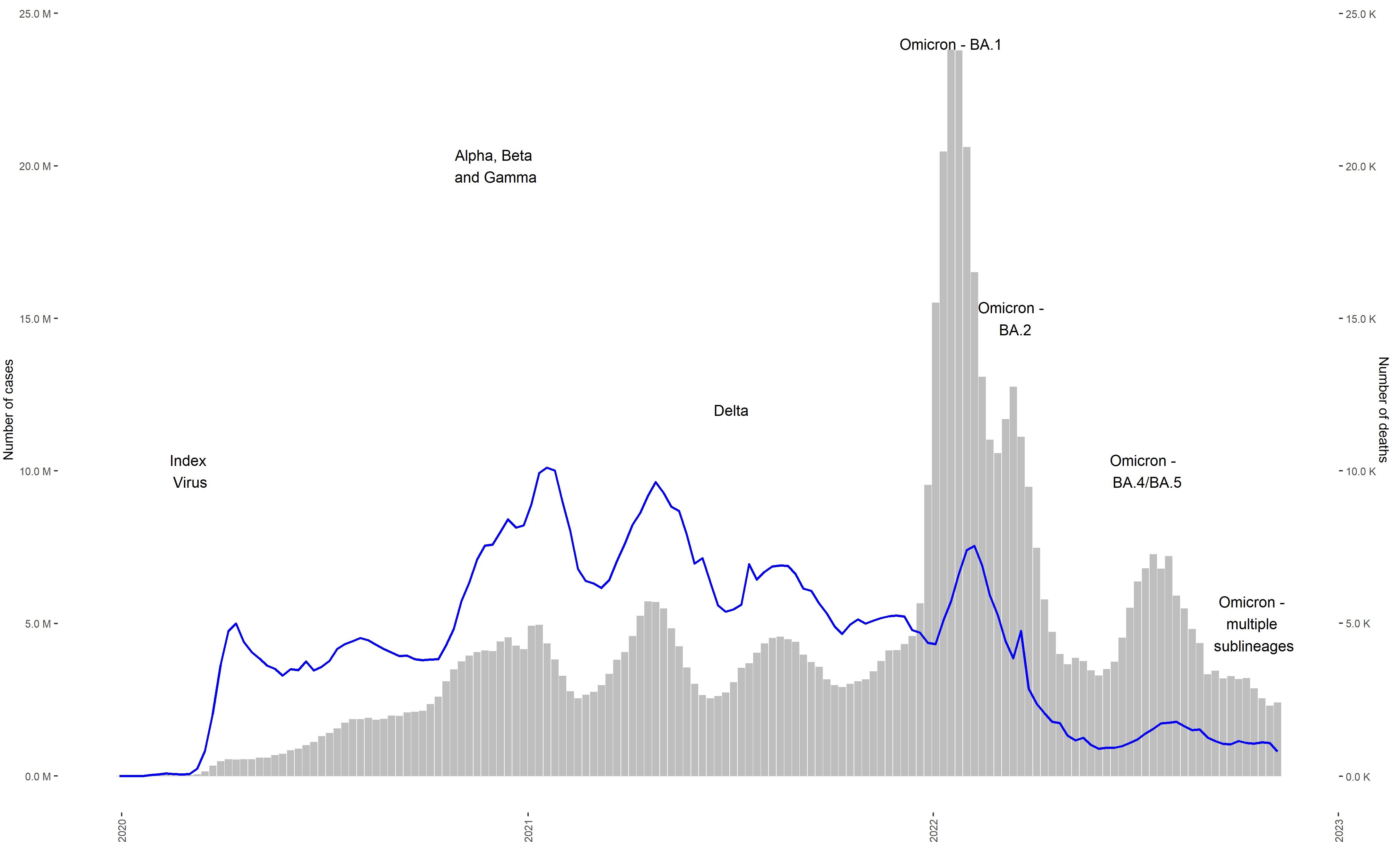 New Covid 19 Variant A Global Health Concern
May 31, 2025
New Covid 19 Variant A Global Health Concern
May 31, 2025 -
 Life Or Death The Conditions For An Iconic Rock Bands Glastonbury Return
May 31, 2025
Life Or Death The Conditions For An Iconic Rock Bands Glastonbury Return
May 31, 2025 -
 Isabelle Autissier L Urgence Environnementale Et L Unite Face Au Defi Climatique
May 31, 2025
Isabelle Autissier L Urgence Environnementale Et L Unite Face Au Defi Climatique
May 31, 2025 -
 Grigor Dimitrov 15 To Uchastie Na Rolan Garos
May 31, 2025
Grigor Dimitrov 15 To Uchastie Na Rolan Garos
May 31, 2025 -
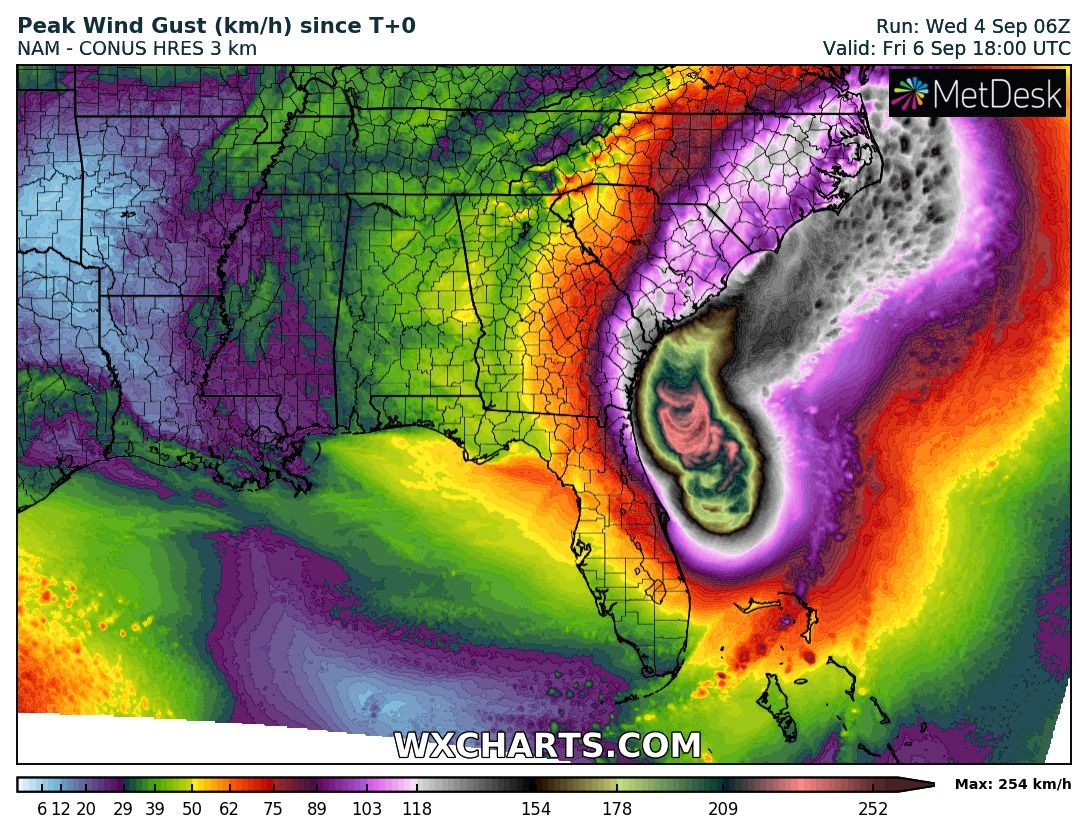 Carolinas Severe Weather A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding Storm Alerts
May 31, 2025
Carolinas Severe Weather A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding Storm Alerts
May 31, 2025
