Western Massachusetts Rainfall: Climate Change Trends And Impacts
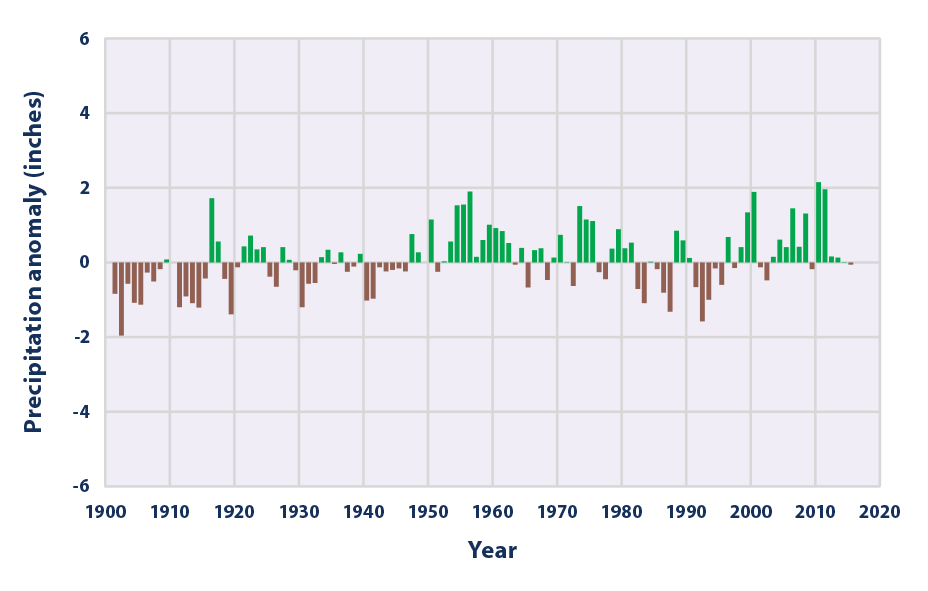
Table of Contents
Observed Trends in Western Massachusetts Rainfall
The most striking observation regarding Western Massachusetts rainfall is the increasing variability in both the amount and distribution of precipitation throughout the year. This unpredictability poses significant challenges for residents and businesses alike.
Increasing Variability
The region is experiencing more intense rain events leading to widespread flooding, interspersed with longer periods of drought. This creates a volatile situation where water resources are strained by both excess and scarcity. Seasonal precipitation is becoming increasingly unpredictable, making long-term planning difficult.
- More intense rain events: Leading to flash floods and damage to infrastructure.
- Longer periods of drought: Stressing water resources and impacting agriculture.
- Unpredictable seasonal precipitation: Making it difficult to plan for water management and agricultural activities.
Data from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) shows a statistically significant increase in the intensity of rainfall events in Western Massachusetts over the past three decades, while overall annual rainfall totals remain relatively consistent in some areas, but variable in others. Specific locations like the Connecticut River Valley have seen dramatic shifts in both drought and flood frequency.
Changes in Seasonal Precipitation
Significant shifts are occurring in the distribution of rainfall across the seasons. While precise changes vary across the region, some areas are observing drier springs and wetter autumns, altering snowmelt patterns and impacting water availability during crucial growing seasons.
- Changes in spring snowmelt: Leading to earlier runoff and reduced water availability later in the year.
- Impacts on water availability during crucial growing seasons: Affects crop yields and necessitates changes in agricultural practices.
These changes correlate with rising temperatures and shifts in atmospheric circulation patterns, indicative of broader climate change influences. Analyzing historical data alongside temperature records paints a clearer picture of the interconnectedness of these changes. Graphs illustrating these trends, readily available from sources like NOAA and the University of Massachusetts Amherst, show clear evidence of these seasonal shifts.
Contributing Factors: The Role of Climate Change
The observed changes in Western Massachusetts rainfall are strongly linked to the effects of climate change, driven largely by increased greenhouse gas emissions.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions and the Hydrological Cycle
Increased concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are fundamentally altering the hydrological cycle. Warmer temperatures lead to greater evaporation, resulting in more moisture in the atmosphere. This, in turn, can fuel more intense rainfall events when atmospheric conditions are favorable. Changes in atmospheric circulation patterns also contribute to shifts in precipitation distribution.
- Warmer temperatures: Leading to increased evaporation and more intense rainfall events.
- Changes in atmospheric circulation patterns: Altering the pathways of storm systems and precipitation distribution.
The overwhelming scientific consensus, supported by reports from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and numerous peer-reviewed studies, confirms the link between greenhouse gas emissions and alterations in rainfall patterns globally, including Western Massachusetts.
Local Impacts and Feedback Loops
While global climate change is the primary driver, local factors also influence rainfall patterns in Western Massachusetts.
- Changes in land use: Deforestation and urbanization alter local water cycles, influencing runoff and evapotranspiration.
- Local topography: The complex terrain of Western Massachusetts significantly influences precipitation distribution, with some areas receiving more rainfall than others.
These local feedback loops complicate the picture, necessitating detailed regional studies to fully understand the interplay of global and local factors affecting rainfall patterns.
Impacts of Altered Rainfall Patterns
The altered rainfall patterns in Western Massachusetts have significant consequences for the region's water resources, agriculture, and infrastructure.
Impacts on Water Resources
The increasing variability in rainfall poses substantial challenges to water resource management. The region faces an increased risk of both droughts and severe flooding, creating a precarious balance in water availability for drinking water, agriculture, and industry.
- Increased risk of droughts: Stressing water supplies and potentially leading to water restrictions.
- Challenges for water management: Requiring innovative solutions for water storage, conservation, and distribution.
- Potential for water conflicts: As competition for limited water resources intensifies.
The implications for reservoirs and water infrastructure are substantial, requiring investments in adaptation measures to ensure water security.
Agricultural Impacts
Changes in rainfall patterns significantly affect farming practices and crop yields in Western Massachusetts.
- Increased risk of crop failure: Due to both drought and flooding.
- Changes in growing seasons: Requiring farmers to adapt their planting and harvesting schedules.
These changes have considerable economic implications for the agricultural sector, demanding innovative strategies for climate-resilient agriculture.
Impacts on Infrastructure
The increasing frequency of extreme weather events, including both intense rainfall and drought, puts significant strain on the region's infrastructure.
- Damage from flooding: Including damage to roads, bridges, and buildings.
- Increased erosion: Threatening soil stability and infrastructure integrity.
- Costs associated with infrastructure repair and adaptation: Demanding significant public investment.
Conclusion
The observed trends in Western Massachusetts rainfall clearly demonstrate the significant impact of climate change on the region. The increasing variability in precipitation, with more intense rainfall events and prolonged droughts, poses substantial challenges to water resources, agriculture, and infrastructure. Understanding and adapting to these changing patterns is crucial for ensuring the region's resilience to climate change. Further research, improved water management strategies, and community preparedness are vital steps to mitigate the effects of altered rainfall patterns. Learn more about climate change impacts and how you can contribute to sustainable water management in Western Massachusetts. Stay informed on the latest research on Western Massachusetts rainfall and climate change.

Featured Posts
-
 Allegations Nypd Detective On Mayor Adams Security Detail Involved In Crypto Kidnapping
May 31, 2025
Allegations Nypd Detective On Mayor Adams Security Detail Involved In Crypto Kidnapping
May 31, 2025 -
 Understanding The Increased Rainfall In Western Massachusetts A Climate Change Perspective
May 31, 2025
Understanding The Increased Rainfall In Western Massachusetts A Climate Change Perspective
May 31, 2025 -
 The Nintendo Switchs Legacy A Look At Its Indie Game Partnerships
May 31, 2025
The Nintendo Switchs Legacy A Look At Its Indie Game Partnerships
May 31, 2025 -
 Sanofi Acquires Dren Bios Bispecific Myeloid Cell Engager
May 31, 2025
Sanofi Acquires Dren Bios Bispecific Myeloid Cell Engager
May 31, 2025 -
 Gran Incendio Forestal En Constanza Bomberos Combaten Las Llamas
May 31, 2025
Gran Incendio Forestal En Constanza Bomberos Combaten Las Llamas
May 31, 2025
