US Solar Tariff Hikes: Southeast Asia's Response And Future Outlook

Table of Contents
Impact of US Solar Tariffs on Southeast Asian Solar Industries
The US solar tariff increases have had a multifaceted negative impact on Southeast Asian solar industries.
Increased Costs and Reduced Competitiveness
The tariffs directly increase the cost of US-made solar components, making them less competitive globally. This disproportionately affects Southeast Asia because:
- Reliance on US Components: Many Southeast Asian countries depend on US-sourced solar panels or crucial components for their renewable energy projects.
- Project Cost Increases: Higher component costs translate directly to higher project costs, leading to project delays and cancellations, especially for smaller-scale projects. This slows down the overall adoption of solar energy in the region.
- Reduced Competitiveness: Both solar panel manufacturers and solar energy project developers in Southeast Asia face reduced competitiveness in the global and regional markets, struggling to compete with projects using less expensive components sourced elsewhere. This can lead to job losses and economic setbacks.
Supply Chain Disruptions
The tariffs have introduced considerable disruptions to the global solar supply chain, impacting Southeast Asia in several ways:
- Project Delays: Sourcing difficulties due to tariff-related constraints cause significant delays in project timelines. This impacts project completion dates and investor confidence.
- Increased Reliance on Alternative Suppliers: Southeast Asian nations are forced to seek alternative suppliers, which can lead to quality and reliability concerns, as well as potential increases in transportation costs. Finding reliable and cost-effective alternatives is a critical challenge.
- Government Pressure: Southeast Asian governments are under pressure to find new and secure sources of solar components, requiring significant adjustments to their energy policies and international trade relationships.
Southeast Asia's Response Strategies
Faced with these challenges, Southeast Asian nations are implementing several strategies to mitigate the impact of US solar tariffs:
Diversification of Supply Chains
Southeast Asian countries are aggressively diversifying their supply chains to reduce reliance on US components:
- New Partnerships: They are actively exploring partnerships with solar panel manufacturers in China, India, and Europe, seeking more stable and diverse sourcing options.
- Domestic Manufacturing: Many nations are investing heavily in developing domestic solar manufacturing capabilities. This reduces import dependence and creates local jobs.
- Regional Cooperation: Strengthening regional cooperation within ASEAN and beyond is crucial to create a more resilient and integrated solar energy supply network, allowing for greater access to resources and technologies.
Policy Adjustments and Incentives
Governments are implementing policy changes to foster the growth of their solar sectors:
- Financial Incentives: Offering financial incentives, tax breaks, and subsidies to stimulate domestic solar manufacturing and project development.
- Streamlined Permitting: Simplifying and accelerating permitting processes for solar projects to reduce bureaucratic hurdles and encourage faster deployment.
- R&D Investment: Investing in research and development to advance solar technologies and increase efficiency, leading to long-term cost reductions.
- Trade Agreements: Negotiating bilateral trade agreements to secure preferential access to affordable solar components from other countries.
The Future Outlook for Solar Energy in Southeast Asia
Despite the challenges posed by US tariffs, the long-term outlook for solar energy in Southeast Asia remains positive:
Continued Growth Despite Challenges
Several factors point towards continued growth:
- Strong Government Support: Governments in the region continue to strongly support renewable energy development as a key part of their national energy strategies.
- Growing Energy Demand: The region's rapidly expanding economies and growing populations necessitate sustainable energy solutions, making solar power increasingly critical.
- Decreasing Costs: The cost of solar technology continues to decline globally, offsetting some of the impacts of the tariffs.
Potential for Regional Leadership
Southeast Asia has the potential to become a regional leader in solar energy, capitalizing on its strategic location and growing manufacturing capacity:
- Infrastructure Investment: Continued investment in renewable energy infrastructure is key to establishing a robust and competitive solar energy market.
- Effective Policy Implementation: Successful implementation of supportive policies and regulations is essential to attract investment and drive growth.
- Innovation: Fostering innovation in solar technologies, particularly in areas like energy storage and efficiency improvements, will enhance the region’s competitive edge.
Opportunities for Investment
The challenges presented by the US tariffs create significant investment opportunities:
- Domestic Manufacturing: Investment in domestic solar manufacturing facilities offers strong returns and contributes to regional economic development.
- Alternative Supply Chains: Investing in alternative supply chain solutions, particularly those that enhance regional cooperation, offers significant potential.
- Renewable Energy Projects: The need for renewable energy sources creates numerous opportunities for investment in solar energy projects across Southeast Asia.
Conclusion
The US solar tariff hikes present significant obstacles to Southeast Asia's burgeoning solar energy sector, resulting in higher costs, supply chain disruptions, and reduced competitiveness. However, Southeast Asian nations are actively responding with diversification strategies, policy adjustments, and investments in domestic manufacturing. The long-term outlook remains positive, with opportunities for regional leadership and substantial investment. To effectively navigate this complex landscape and capitalize on the potential of this dynamic market, staying informed about the impacts of US solar tariffs Southeast Asia is paramount. For insightful analysis and the latest industry updates, continue to follow relevant news and research.

Featured Posts
-
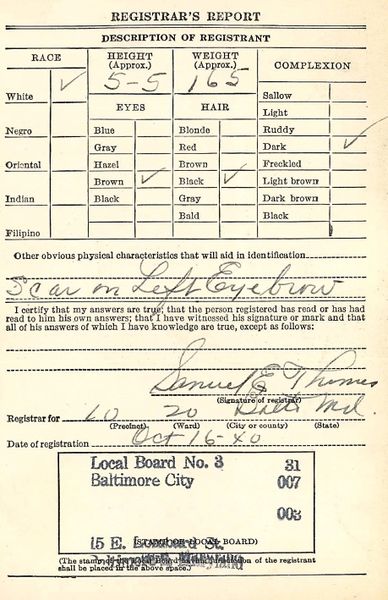 Virginias Revenue Loss Addressing The Issue Of Maryland Vehicle Registrations
May 30, 2025
Virginias Revenue Loss Addressing The Issue Of Maryland Vehicle Registrations
May 30, 2025 -
 Fikret Hakan In Ilk Goeruentuesue Pinar Deniz Ve Kaan Yildirim Dan Mutluluk Pozu
May 30, 2025
Fikret Hakan In Ilk Goeruentuesue Pinar Deniz Ve Kaan Yildirim Dan Mutluluk Pozu
May 30, 2025 -
 Andre Agassi Joins The Pickleball Pro Tour Debut Match Review
May 30, 2025
Andre Agassi Joins The Pickleball Pro Tour Debut Match Review
May 30, 2025 -
 French Open Djokovic Opens With A Win
May 30, 2025
French Open Djokovic Opens With A Win
May 30, 2025 -
 Alcaraz From Behind To Champion In Monte Carlo
May 30, 2025
Alcaraz From Behind To Champion In Monte Carlo
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Estevan Road Sweeping Dates Complete List Now Available
May 31, 2025
Estevan Road Sweeping Dates Complete List Now Available
May 31, 2025 -
 City Of Estevan Announces Full 2024 Street Sweeping Schedule
May 31, 2025
City Of Estevan Announces Full 2024 Street Sweeping Schedule
May 31, 2025 -
 Estevan Street Sweeping Schedule Released
May 31, 2025
Estevan Street Sweeping Schedule Released
May 31, 2025 -
 Life Changing Impact Duncan Bannatynes Philanthropy In Morocco
May 31, 2025
Life Changing Impact Duncan Bannatynes Philanthropy In Morocco
May 31, 2025 -
 Simple Recipes Using Rosemary And Thyme
May 31, 2025
Simple Recipes Using Rosemary And Thyme
May 31, 2025
