Understanding The Scale Of The Current Bond Crisis
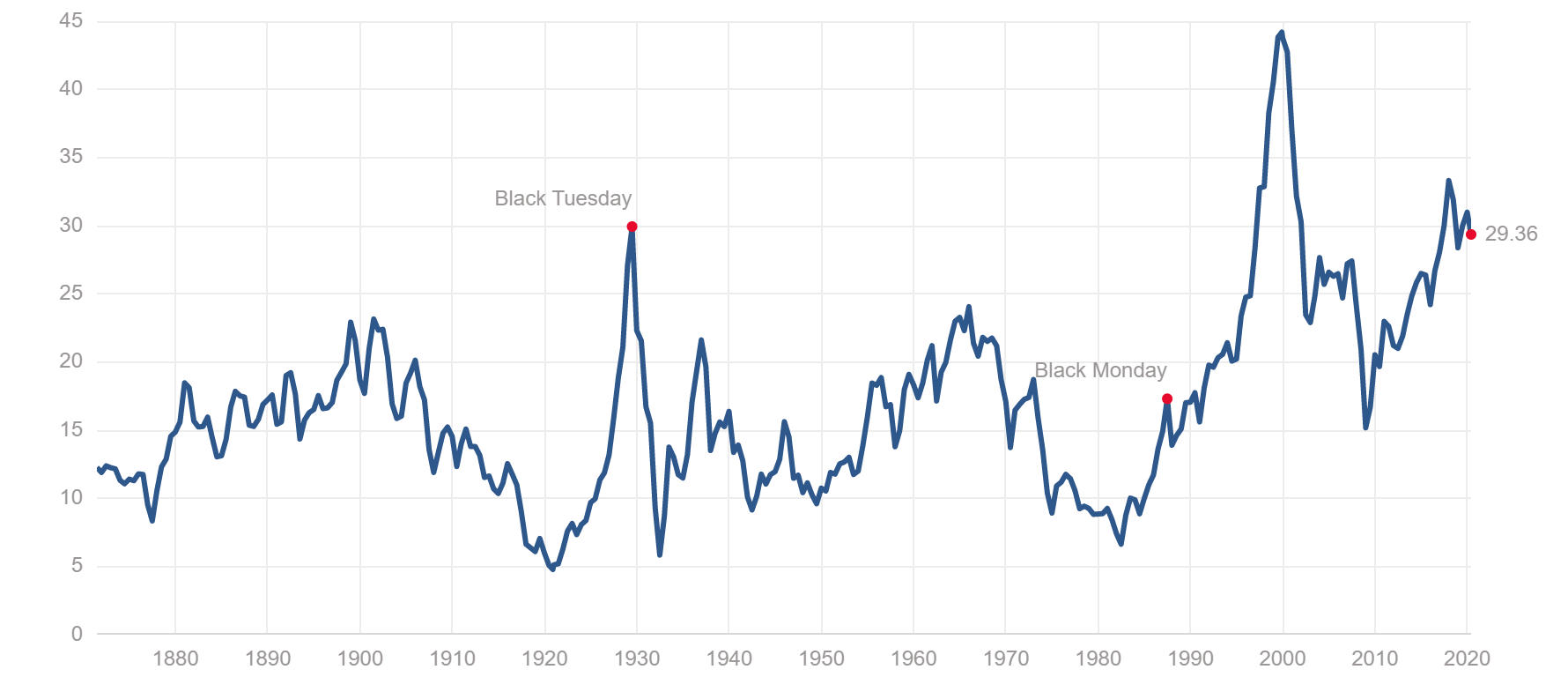
Table of Contents
Rising Interest Rates and Their Impact on Bond Prices
The relationship between interest rates and bond prices is inversely proportional. When interest rates rise, the value of existing bonds falls, and vice versa. This is because newly issued bonds offer higher yields, making older bonds with lower coupon payments less attractive.
The Mechanics of Bond Price Depreciation
Rising interest rates directly impact bond valuation. The yield curve, which illustrates the relationship between interest rates and maturities, steepens as short-term rates increase faster than long-term rates. This impacts the present value of future cash flows from a bond, leading to depreciation. Duration risk, a measure of a bond's sensitivity to interest rate changes, becomes crucial in understanding the magnitude of price fluctuations.
- Reinvestment Risk: When interest rates rise, the coupon payments from existing bonds cannot be reinvested at the same high rate, reducing overall returns.
- Impact on Bond Types: Government bonds, generally considered safer, are affected, although less severely than higher-risk corporate bonds. High-yield corporate bonds, with their higher coupon rates, experience more significant price drops due to increased credit risk.
- Central Bank Role: Central banks play a pivotal role through monetary policy. Rate hikes, aimed at controlling inflation, directly influence bond prices and yields.
Inflation's Role in the Bond Market Crisis
High inflation erodes the real return of bonds. Even if a bond offers a positive nominal yield, if inflation outpaces that yield, the investor experiences a loss of purchasing power. This is a significant concern for fixed-income investors.
Inflation Expectations and Bond Yields
Inflation expectations are crucial in shaping bond yields and investor behavior. If investors anticipate high inflation, they demand higher yields to compensate for the erosion of purchasing power. This drives bond prices down. Keywords: inflation hedge, real interest rates, inflation-protected securities (TIPS).
- Unexpected Inflation Surges: Sudden, unexpected increases in inflation cause significant volatility in the bond market, as investors reassess their risk and return expectations.
- Inflation and Central Bank Policy: Central banks attempt to manage inflation through monetary policy, often influencing bond yields and market stability.
- Inflation Expectations and Volatility: The uncertainty surrounding future inflation is a major driver of the current bond market volatility.
Assessing the Severity of the Current Bond Crisis
The current bond market crisis is significant when compared to historical events. While not yet at the scale of past crises, the rapid rise in interest rates and the persistent inflationary pressures present a considerable challenge.
Key Indicators of Market Stress
Several metrics highlight the stress in the market:
-
Credit Spreads: The difference between yields on corporate bonds and government bonds is widening, indicating increasing credit risk.
-
Bond Yields: Global bond yields have increased substantially, reflecting investor concerns and the impact of higher interest rates.
-
Investor Sentiment: Negative investor sentiment is palpable, contributing to selling pressure and further price declines.
-
Geographic Spread: The crisis is global in nature, impacting developed and emerging markets alike.
-
Sectoral Impact: Various sectors, particularly those with high debt levels, are experiencing significant pressure.
-
Contagion Risk: The potential for the crisis to spread to other financial markets, such as the stock market, is a considerable concern.
Potential Consequences and Mitigation Strategies
Economic Ripple Effects
The bond market crisis has significant potential for broader economic consequences:
- Increased Borrowing Costs: Higher interest rates translate to increased borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, potentially dampening economic activity.
- Government Debt Management: Governments face higher costs in managing their debt, potentially impacting fiscal policy and government spending.
- Government Intervention: Governments may intervene through fiscal or monetary policy to mitigate the crisis's impact.
Strategies for Investors
For investors, navigating this challenging environment requires careful consideration:
- Portfolio Diversification: Diversifying investments across asset classes can help reduce exposure to bond market risks.
- Risk Management: Understanding the duration and credit risk of individual bond holdings is critical for effective risk management.
- Professional Advice: Seeking professional financial advice is crucial for developing a robust investment strategy in this volatile market.
Conclusion
The current bond market crisis is a complex situation driven by a confluence of factors, primarily rising interest rates and persistent inflation. The severity of this situation warrants close monitoring, as it carries significant potential for impacting economic growth, investment, and consumer spending. The interconnectedness of global financial markets increases the risk of contagion, emphasizing the need for proactive risk management. Understanding the bond market dynamics and the interplay of these factors is crucial. To effectively navigate the bond crisis and manage bond portfolio risk, staying informed and seeking professional financial advice is paramount. Continue your research by exploring topics like "credit default swaps (CDS)," "high-yield bonds," "investment-grade bonds," "monetary policy," and "fiscal policy" to gain a deeper understanding of this evolving situation.

Featured Posts
-
 Cuaca Besok Di Denpasar Dan Sekitarnya Bali
May 29, 2025
Cuaca Besok Di Denpasar Dan Sekitarnya Bali
May 29, 2025 -
 Las Carreras Sprint De Moto Gp Mucho Riesgo Poca Ganancia
May 29, 2025
Las Carreras Sprint De Moto Gp Mucho Riesgo Poca Ganancia
May 29, 2025 -
 Quatro Jogadores Do Real Madrid Incluindo Mbappe E Vinicius Jr Investigados Pela Uefa
May 29, 2025
Quatro Jogadores Do Real Madrid Incluindo Mbappe E Vinicius Jr Investigados Pela Uefa
May 29, 2025 -
 Ma Meilleure Ennemie Remix Coldplay Joins Forces With Stromae And Pomme
May 29, 2025
Ma Meilleure Ennemie Remix Coldplay Joins Forces With Stromae And Pomme
May 29, 2025 -
 Space X Starship Launch Faa Issues Flight Restrictions
May 29, 2025
Space X Starship Launch Faa Issues Flight Restrictions
May 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Free Housing For Two Weeks A German Citys Recruitment Drive
May 31, 2025
Free Housing For Two Weeks A German Citys Recruitment Drive
May 31, 2025 -
 Gratis Wohnungen Diese Deutsche Stadt Wirbt Um Neue Einwohner
May 31, 2025
Gratis Wohnungen Diese Deutsche Stadt Wirbt Um Neue Einwohner
May 31, 2025 -
 Diese Deutsche Gemeinde Bietet Kostenlose Unterkuenfte Fuer Neubuerger
May 31, 2025
Diese Deutsche Gemeinde Bietet Kostenlose Unterkuenfte Fuer Neubuerger
May 31, 2025 -
 Hospitalization Of Former Nypd Commissioner Bernard Kerik Full Recovery Anticipated
May 31, 2025
Hospitalization Of Former Nypd Commissioner Bernard Kerik Full Recovery Anticipated
May 31, 2025 -
 Wohnungsknappheit Ade Deutsche Kleinstadt Lockt Mit Freiem Wohnen
May 31, 2025
Wohnungsknappheit Ade Deutsche Kleinstadt Lockt Mit Freiem Wohnen
May 31, 2025
