Understanding The Recent Increase In Bitcoin Mining Difficulty And Hashrate
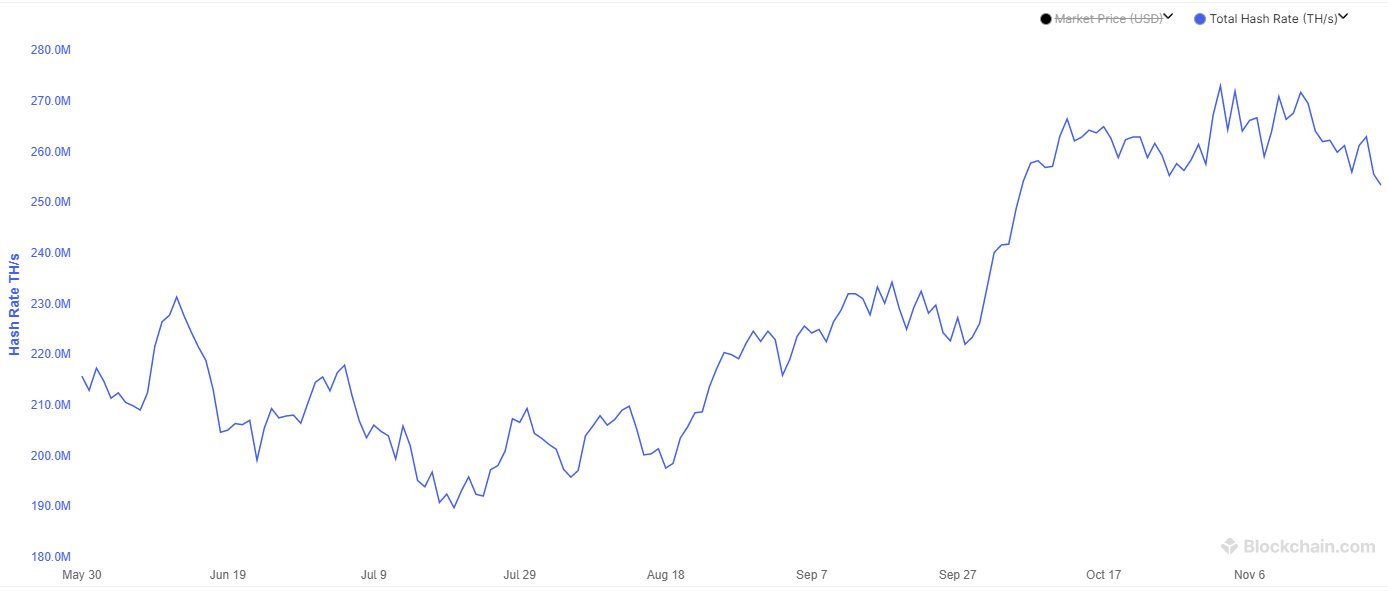
Table of Contents
The Interplay Between Bitcoin Mining Difficulty and Hashrate
The relationship between Bitcoin mining difficulty and hashrate is fundamentally intertwined. They are two sides of the same coin, constantly adjusting to maintain the network's integrity and stability. A higher hashrate, representing the total computational power dedicated to mining Bitcoin, leads to a more frequent discovery of new blocks. To counteract this and maintain the intended block generation time of approximately 10 minutes, the mining difficulty automatically adjusts upwards. Conversely, a decrease in hashrate results in a lower difficulty adjustment.
- Difficulty adjusts to maintain a consistent block generation time (approximately 10 minutes). This ensures predictable block creation, preventing network instability caused by wildly fluctuating block times.
- Hashrate represents the total computational power dedicated to mining Bitcoin. A higher hashrate indicates a more secure and robust network.
- An increase in hashrate necessitates a difficulty adjustment to prevent excessively fast block creation. This prevents miners from finding blocks too quickly, disrupting the intended pace of the blockchain.
- Difficulty adjustments occur roughly every two weeks. This periodic adjustment allows the network to adapt to changes in the total hashrate.
Factors Contributing to the Recent Hashrate Increase
Several factors have contributed to the recent increase in Bitcoin's hashrate. These factors are complex and interconnected, reflecting both technological advancements and macroeconomic influences.
-
Increased miner adoption of more efficient ASICs: The development of more powerful and energy-efficient Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs) has significantly boosted the hashrate. These advancements allow miners to process more transactions per unit of energy, increasing their profitability and incentivizing further investment in mining hardware. The ongoing innovation in ASIC technology continues to push the boundaries of Bitcoin mining capacity.
-
Institutional investment in mining: Large-scale mining operations, often backed by institutional investors, are playing an increasingly significant role. These operations possess the resources to deploy vast numbers of mining rigs, contributing substantially to the overall hashrate. This institutional interest signifies a growing confidence in Bitcoin's long-term viability.
-
Government regulations and their impact: Government regulations regarding cryptocurrency mining vary widely across different jurisdictions. Some regions have embraced Bitcoin mining, offering incentives or favorable regulatory environments that attract miners. Others have imposed restrictions, impacting the overall hashrate. The impact of regulatory changes on Bitcoin mining is constantly evolving and requires careful monitoring.
-
Bitcoin price fluctuations: The price of Bitcoin directly impacts mining profitability. When the price rises, mining becomes more lucrative, attracting new miners and encouraging existing miners to increase their operations. Conversely, a price decline can lead to miners switching off their equipment, resulting in a lower hashrate.
-
Energy costs and their regional variations: Energy costs are a major factor determining the profitability of Bitcoin mining. Regions with lower energy prices naturally attract more mining operations. The ongoing search for cost-effective energy sources is a critical aspect of the Bitcoin mining landscape.
Analyzing the impact of the hashrate increase on mining profitability
The increased hashrate, while contributing to network security, also intensifies competition among miners. This heightened competition directly affects profitability.
-
Increased competition and its effect on individual miner rewards: With more miners competing for block rewards, the share of the reward each miner receives diminishes. This necessitates higher efficiency and lower operational costs to maintain profitability.
-
The importance of mining efficiency and energy costs in determining profitability: Mining efficiency, measured by hash rate per watt of energy consumed, is paramount. Miners constantly seek more efficient equipment and strategies to minimize energy costs, maximizing their profit margins.
-
Strategies miners employ to maintain profitability in a competitive environment (e.g., ASIC upgrades, pool participation): Miners adopt various strategies to remain competitive, including upgrading to the latest ASICs, joining mining pools to share resources and reduce risk, and optimizing their operations to reduce energy consumption.
Implications of the Increased Bitcoin Mining Difficulty and Hashrate
The ongoing increase in Bitcoin mining difficulty and hashrate has significant implications for the Bitcoin network and its users.
-
Enhanced network security and resilience against 51% attacks: A higher hashrate makes it exponentially more difficult for malicious actors to launch a 51% attack, a scenario where a single entity controls over half of the network's hashing power. This significantly strengthens Bitcoin's security and decentralization.
-
Potential impact on transaction fees: Increased competition among miners can lead to fluctuations in transaction fees. High hashrates can sometimes lead to lower fees as miners compete for transactions to include in blocks, but this is not always guaranteed.
-
Decentralization implications – is the increased hashrate concentrating in fewer hands?: The concentration of hashing power among large mining operations raises concerns about the network's decentralization. This is a complex issue requiring ongoing monitoring and analysis.
-
The long-term sustainability of Bitcoin mining: The environmental impact of Bitcoin mining, particularly its energy consumption, remains a subject of debate. The ongoing development of more energy-efficient mining technologies and the adoption of renewable energy sources will be crucial for the long-term sustainability of Bitcoin mining.
Conclusion
This article explored the recent surge in Bitcoin mining difficulty and hashrate, identifying key contributing factors such as advancements in ASIC technology, institutional investment, and Bitcoin price fluctuations. We've also analyzed the interplay between these two metrics and their implications for the security and sustainability of the Bitcoin network. Understanding the dynamics of Bitcoin mining difficulty and hashrate reveals vital insights into the health and evolution of the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Call to Action: Understanding the dynamics of Bitcoin mining difficulty and hashrate is crucial for anyone involved in or interested in the cryptocurrency space. Stay informed about these vital metrics to make informed decisions about your involvement in the Bitcoin ecosystem. Continue learning about the intricacies of Bitcoin mining difficulty and hashrate to better navigate this ever-evolving landscape.

Featured Posts
-
 Melanie Griffith And Dakota Johnson At The Materialists Film Screening
May 09, 2025
Melanie Griffith And Dakota Johnson At The Materialists Film Screening
May 09, 2025 -
 Harry Styles On Snl Impression His Devastated Response
May 09, 2025
Harry Styles On Snl Impression His Devastated Response
May 09, 2025 -
 R3
May 09, 2025
R3
May 09, 2025 -
 Dakota Johnson With Family At Materialist Premiere Photos
May 09, 2025
Dakota Johnson With Family At Materialist Premiere Photos
May 09, 2025 -
 V Mware Pricing To Explode At And T Highlights Broadcoms 1050 Proposed Hike
May 09, 2025
V Mware Pricing To Explode At And T Highlights Broadcoms 1050 Proposed Hike
May 09, 2025
