Uncertainty Rises: Inflation And Unemployment Risks Increase
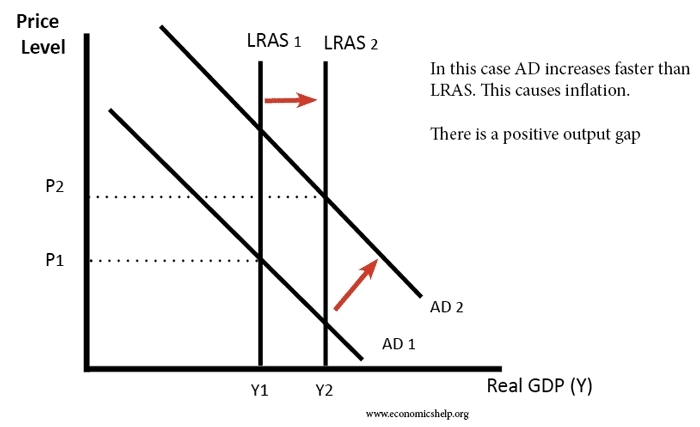
Table of Contents
Rising Inflation: A Deep Dive into the Causes and Consequences
Inflation, the persistent increase in the general price level of goods and services, is a significant concern. Several factors contribute to the current inflationary pressures, and understanding these is critical to addressing the issue.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Their Impact
Global supply chains, already strained before the pandemic, have been severely disrupted. Lockdowns, geopolitical instability, and increased demand have created bottlenecks, leading to shortages of crucial goods and a surge in transportation costs.
- Increased transportation costs: Fuel prices, shipping container shortages, and port congestion have significantly increased the cost of moving goods.
- Shortages of raw materials: Many industries face shortages of essential raw materials, leading to production delays and higher prices.
- Manufacturing bottlenecks: Factories are struggling to keep up with demand due to labor shortages, supply chain disruptions, and increased input costs. This particularly impacts industries like energy and manufacturing, driving up prices for consumers.
Demand-Pull Inflation and Consumer Spending
Another key driver of inflation is strong consumer demand. Government stimulus packages during the pandemic, coupled with pent-up demand from lockdowns, have led to increased consumer spending. This high demand, exceeding supply in many sectors, pushes prices upwards.
- Increased disposable income: Stimulus checks and other government support programs boosted disposable income for many households.
- Strong consumer confidence: Following the pandemic, consumer confidence rebounded quickly in many countries, fueling spending.
- Potential for wage-price spirals: As prices rise, workers demand higher wages to maintain their purchasing power, leading to further price increases, creating a potentially self-perpetuating cycle.
The Impact of Rising Inflation on Households and Businesses
Rising inflation erodes purchasing power, impacting households and businesses significantly. Households face reduced real wages, meaning their money buys less than before. Businesses face increased input costs, making it harder to maintain profit margins and potentially leading to job losses or business failures.
- Reduced real wages: Even with nominal wage increases, real wages (adjusted for inflation) may decline, reducing household purchasing power.
- Increased borrowing costs: Higher inflation typically leads to higher interest rates, increasing borrowing costs for both consumers and businesses.
- Potential for business failures: Businesses struggling with increased input costs and reduced demand may be forced to close, leading to job losses.
The Shadow of Unemployment: Analyzing the Current Job Market
While inflation is a pressing issue, the potential for increased unemployment looms large. The relationship between inflation and unemployment is complex, often depicted by the Phillips curve, suggesting an inverse relationship. However, the current situation presents unique challenges.
The Labor Market's Response to Inflation
Measures to combat inflation, such as raising interest rates, can lead to economic slowdowns, potentially resulting in job losses. Companies may respond to increased costs by reducing investment, implementing hiring freezes, or even resorting to layoffs.
- Increased interest rates: Higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive, reducing investment and potentially slowing economic growth.
- Reduced investment: Businesses may postpone investment plans in response to higher interest rates and economic uncertainty.
- Potential for recession: Aggressive measures to control inflation could trigger a recession, leading to widespread job losses.
Wage Growth and Its Relationship to Inflation
Wage growth is a key factor in the inflation-unemployment dynamic. While strong wage growth can boost consumer spending, it can also contribute to a wage-price spiral if not matched by productivity increases. Understanding current wage trends is critical to managing inflation.
- Real wage growth vs. nominal wage growth: It's crucial to differentiate between nominal wage increases (the actual increase in wages) and real wage growth (nominal wage growth adjusted for inflation).
- Impact of unionization: Strong unions can negotiate for higher wages, potentially contributing to inflationary pressures.
- Minimum wage debates: Increases in minimum wage can put upward pressure on wages across the board, affecting inflation.
The Impact of Unemployment on Social Welfare and Economic Stability
High unemployment rates have significant social and economic consequences. Increased poverty, social unrest, and reduced consumer spending all contribute to instability.
- Increased social welfare costs: Higher unemployment leads to increased demand for social welfare programs, placing a strain on government budgets.
- Reduced tax revenue: Job losses translate to reduced tax revenue, further limiting government resources.
- Decreased economic growth: High unemployment weakens the economy by reducing consumer spending and overall economic activity.
Mitigating the Risks: Policy Responses and Potential Solutions
Addressing the simultaneous risks of inflation and unemployment requires a carefully calibrated approach involving both monetary and fiscal policies.
Monetary Policy and Central Bank Interventions
Central banks play a crucial role in controlling inflation through monetary policy tools. However, these tools can have significant impacts on employment.
- Quantitative tightening: Central banks may reduce the money supply by selling government bonds, potentially slowing economic growth and increasing unemployment.
- Interest rate adjustments: Raising interest rates makes borrowing more expensive, potentially slowing inflation but also risking a recession and job losses.
- Inflation targeting: Many central banks aim to keep inflation within a specific target range, balancing the need to control inflation with the need to maintain economic growth and employment.
Fiscal Policy and Government Spending
Governments can use fiscal policy to address unemployment, such as job creation programs and targeted unemployment benefits. However, excessive government spending can exacerbate inflation.
- Investment in infrastructure: Government investment in infrastructure projects can stimulate economic growth and create jobs.
- Targeted unemployment benefits: Providing unemployment benefits can help individuals maintain their living standards during periods of job loss.
- Tax policies: Tax policies can be used to incentivize investment, stimulate demand, or redistribute income.
Conclusion: Navigating the Uncertainties of Inflation and Unemployment
The intertwined risks of inflation and unemployment present significant challenges for policymakers and individuals alike. The current economic climate highlights the complexity of balancing the need to control inflation with the need to maintain full employment. Understanding the causes and consequences of both inflation and unemployment is crucial to developing effective solutions. Staying informed about the evolving economic landscape and engaging in discussions about appropriate policy responses is vital. The future economic trajectory will depend on a well-coordinated and timely response to these significant inflation and unemployment risks increase. Continue to seek out reliable sources of economic information to stay informed and advocate for policies that address these crucial issues effectively.

Featured Posts
-
 Rising Temperatures Rising Deaths 311 Fatalities In Englands Heatwave
May 30, 2025
Rising Temperatures Rising Deaths 311 Fatalities In Englands Heatwave
May 30, 2025 -
 Ira Khans Shocking Revelation After Meeting Andre Agassi
May 30, 2025
Ira Khans Shocking Revelation After Meeting Andre Agassi
May 30, 2025 -
 Paddy Pimbletts Heavyweight Pick Jones Or Aspinall
May 30, 2025
Paddy Pimbletts Heavyweight Pick Jones Or Aspinall
May 30, 2025 -
 Pengalaman Berkendara Premium Tiga Jet Ski Kawasaki Resmi Diluncurkan
May 30, 2025
Pengalaman Berkendara Premium Tiga Jet Ski Kawasaki Resmi Diluncurkan
May 30, 2025 -
 Agassi Mai Nervos Ca Un Tigan Cu Ipoteca Dezvaluiri Despre Viata Sa
May 30, 2025
Agassi Mai Nervos Ca Un Tigan Cu Ipoteca Dezvaluiri Despre Viata Sa
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Zverev Battles Past Shelton And Cerundolo In Munich
May 31, 2025
Zverev Battles Past Shelton And Cerundolo In Munich
May 31, 2025 -
 Thompsons Monte Carlo Performance A Comprehensive Review
May 31, 2025
Thompsons Monte Carlo Performance A Comprehensive Review
May 31, 2025 -
 Zverevs Comeback Victory Sends Him To Munich Semifinals
May 31, 2025
Zverevs Comeback Victory Sends Him To Munich Semifinals
May 31, 2025 -
 Analyzing Thompsons Loss In Monte Carlo
May 31, 2025
Analyzing Thompsons Loss In Monte Carlo
May 31, 2025 -
 Ben Sheltons Munich Semifinal Berth Darderi Defeat
May 31, 2025
Ben Sheltons Munich Semifinal Berth Darderi Defeat
May 31, 2025
