Uncertainty In The Economy: Higher Inflation And Unemployment Threaten Growth

Table of Contents
The Inflationary Spiral: Eroding Purchasing Power and Stifling Growth
Inflation, a sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time, is currently a major concern globally. The inflation rate, often measured using the Consumer Price Index (CPI), reflects the cost of living. High inflation erodes purchasing power, meaning consumers can buy less with the same amount of money. This reduction in real wages significantly impacts consumer spending, a crucial driver of economic growth. Businesses, facing increased input costs and reduced consumer demand, are less likely to invest, further hindering growth.
- Reduced consumer confidence: Rising prices lead to uncertainty about the future, causing consumers to postpone purchases.
- Increased borrowing costs: Higher inflation typically leads to increased interest rates, making it more expensive for businesses to borrow money for investment.
- Supply chain disruptions: Global supply chain bottlenecks continue to exacerbate inflationary pressures by limiting the availability of goods and services.
- Decreased real wages: When wages don't keep pace with inflation, consumers have less disposable income, dampening demand.
Unemployment's Rise: A Double-Edged Sword for Economic Recovery
Alongside high inflation, rising unemployment poses a significant threat to economic recovery. The unemployment rate, representing the percentage of the labor force actively seeking employment but unable to find it, is a key indicator of economic health. Job losses directly impact aggregate demand, as unemployed individuals have reduced spending power. This decrease in consumer spending further weakens economic activity, creating a vicious cycle. The types of unemployment – frictional (temporary unemployment between jobs), structural (mismatch between skills and available jobs), and cyclical (due to economic downturns) – all contribute to the overall picture.
- Reduced consumer spending: Job losses directly translate to decreased consumer spending, impacting businesses and overall economic activity.
- Increased government spending on social welfare programs: Higher unemployment necessitates increased government expenditure on unemployment benefits and other social safety nets, potentially straining public finances.
- Potential for social unrest: Widespread unemployment can lead to social unrest and instability, further destabilizing the economy.
- Skills mismatch in the labor market: Structural unemployment, arising from a skills gap, highlights the need for workforce retraining and education initiatives.
The Interplay of Inflation and Unemployment: The Phillips Curve Revisited
The relationship between inflation and unemployment is often examined through the lens of the Phillips Curve, which traditionally suggests an inverse relationship: lower unemployment is associated with higher inflation, and vice versa. However, the validity of this traditional relationship in the modern economy is increasingly debated. The current economic climate, with simultaneous high inflation and potentially rising unemployment, raises concerns about stagflation – a period of slow economic growth accompanied by high unemployment and inflation.
- Examination of historical data: Analyzing historical data is crucial to assess whether the traditional Phillips Curve relationship still holds true in the face of recent economic shocks.
- Discussion of potential policy responses: Understanding the interplay between inflation and unemployment informs the design of effective policy responses.
- Analysis of the impact of supply shocks: Supply-side shocks, such as those seen during the pandemic, can significantly disrupt the inflation-unemployment relationship.
Strategies for Navigating Economic Uncertainty: Mitigation and Adaptation
Addressing the intertwined challenges of inflation and unemployment requires a multi-pronged approach involving both fiscal and monetary policies. Fiscal policy, involving government spending and taxation, can stimulate demand through infrastructure projects and targeted support for vulnerable populations. Monetary policy, controlled by central banks, uses interest rate adjustments to influence inflation and credit availability. However, the effectiveness of these policies can vary depending on the specific economic context and the severity of the challenges.
Businesses and individuals also need to adopt strategies for navigating economic uncertainty. Risk management, financial planning, diversification, and effective budgeting are crucial for weathering economic storms.
- Government spending on infrastructure projects: Investment in infrastructure can create jobs and boost aggregate demand.
- Central bank actions to control inflation through interest rate adjustments: Raising interest rates can curb inflation but may also slow economic growth and increase unemployment.
- Strategies for businesses to improve efficiency and reduce costs: Improving productivity and streamlining operations can help businesses mitigate inflationary pressures.
- Financial planning advice for individuals to cope with rising living costs: Creating a realistic budget, building an emergency fund, and exploring ways to increase income are important steps for individuals.
Mitigating Economic Uncertainty: A Path Forward
The current economic climate presents significant challenges, with high inflation and rising unemployment threatening economic growth. The relationship between these factors is complex and requires careful analysis. While the traditional Phillips Curve may not fully explain the current situation, understanding the interplay between inflation and unemployment is crucial for designing effective policies and strategies. Government intervention through fiscal and monetary policies is essential, but individual and business adaptation is equally important.
Understanding economic uncertainty is crucial for navigating these turbulent times. Prepare for economic uncertainty by monitoring key economic indicators like inflation rates, unemployment figures, and interest rates. Proactive financial planning, diversification of investments, and a focus on improving efficiency are vital steps towards mitigating the impact of economic uncertainty on your personal and business well-being.

Featured Posts
-
 Emma Raducanus Strong Showing Propels Her To Miami Last 16
May 30, 2025
Emma Raducanus Strong Showing Propels Her To Miami Last 16
May 30, 2025 -
 New Bts Trailer Teases Major Reunion What Can Armys Expect
May 30, 2025
New Bts Trailer Teases Major Reunion What Can Armys Expect
May 30, 2025 -
 Lw Ansf Alqwmu Drws Mn Almady Lbnae Mstqbl Afdl Fy Dhkra Alastqlal
May 30, 2025
Lw Ansf Alqwmu Drws Mn Almady Lbnae Mstqbl Afdl Fy Dhkra Alastqlal
May 30, 2025 -
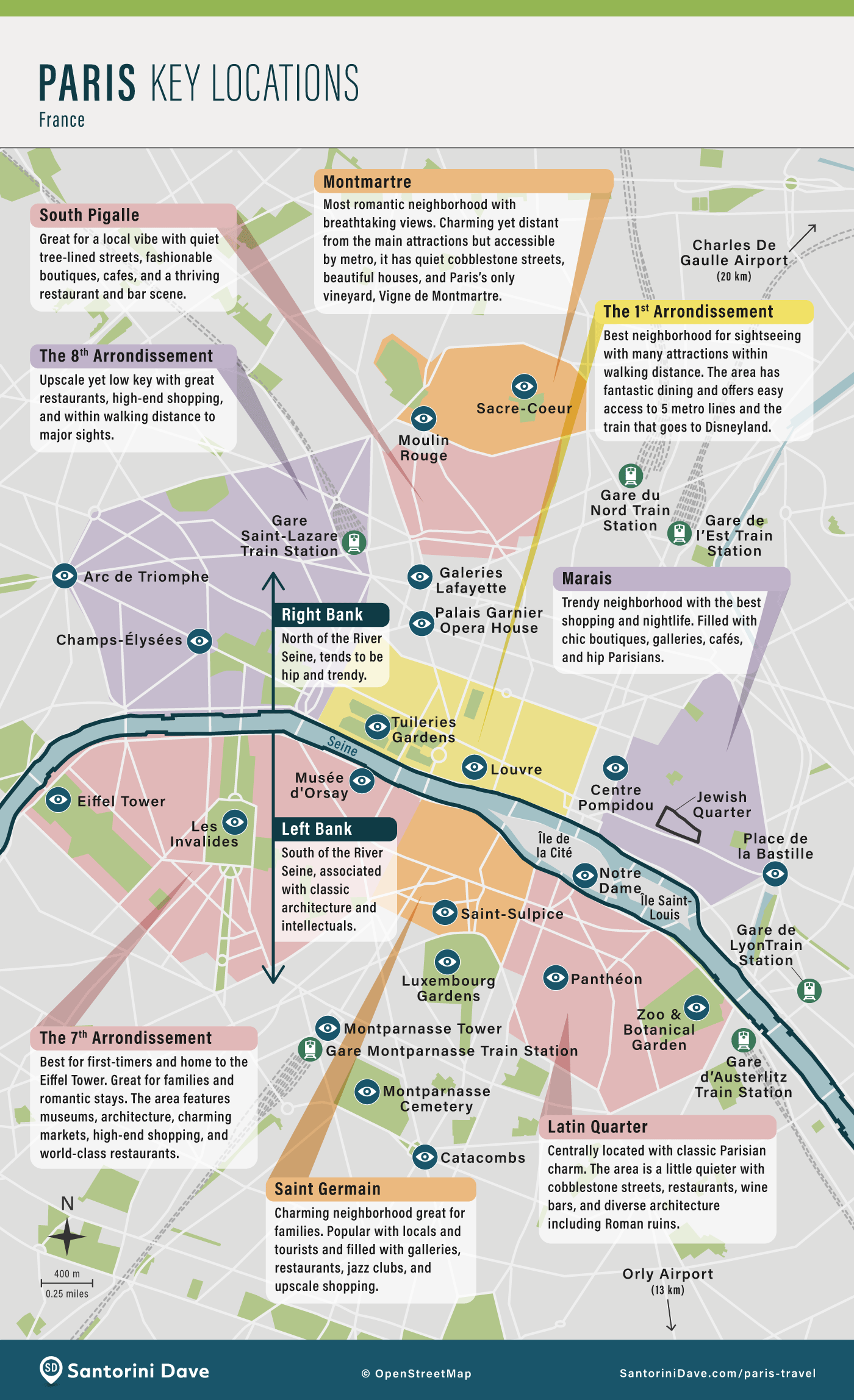 Where To Stay In Paris A Neighborhood Guide For Every Traveler
May 30, 2025
Where To Stay In Paris A Neighborhood Guide For Every Traveler
May 30, 2025 -
 13 Hya Flstynya Mhddt Balastylae Mqawmt Aljdar Walastytan
May 30, 2025
13 Hya Flstynya Mhddt Balastylae Mqawmt Aljdar Walastytan
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Summer Arts And Entertainment A Locals Guide To The Best Events
May 31, 2025
Summer Arts And Entertainment A Locals Guide To The Best Events
May 31, 2025 -
 Girons Victory Ends Berrettinis Madrid Campaign
May 31, 2025
Girons Victory Ends Berrettinis Madrid Campaign
May 31, 2025 -
 The Comprehensive Summer Arts And Entertainment Guide For Location If Applicable
May 31, 2025
The Comprehensive Summer Arts And Entertainment Guide For Location If Applicable
May 31, 2025 -
 Madrid Masters 1000 Berrettinis Exit Confirmed
May 31, 2025
Madrid Masters 1000 Berrettinis Exit Confirmed
May 31, 2025 -
 Elon Musk Resigns From Trump Administration Reasons And Implications
May 31, 2025
Elon Musk Resigns From Trump Administration Reasons And Implications
May 31, 2025
