Trump's Tariff Revenue: A Realistic Replacement For Income Taxes?
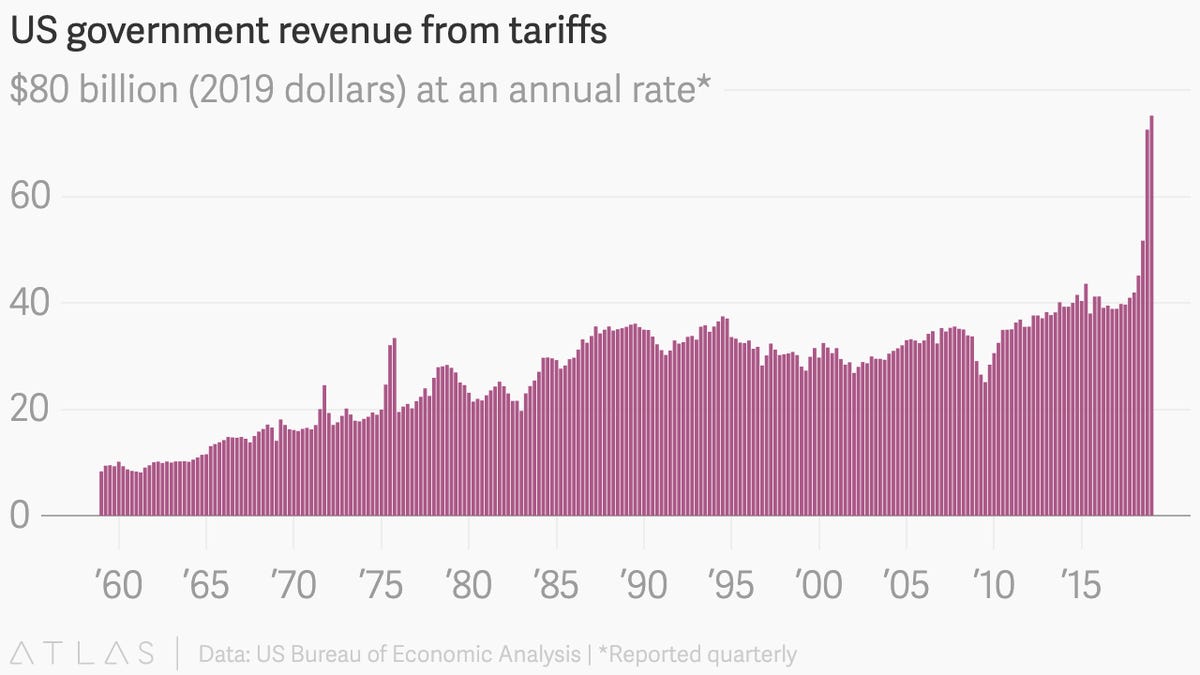
Table of Contents
The Scale of Income Tax Revenue vs. Tariff Revenue
The sheer difference in scale between US income tax revenue and tariff revenue under the Trump administration makes the idea of replacement untenable.
Magnitude of US Income Tax Revenue
The US government collects hundreds of billions of dollars annually through individual and corporate income taxes. For example, in 2022, individual income tax revenue exceeded $2 trillion. This forms the backbone of federal government funding for crucial social programs, infrastructure projects, and national defense.
Tariff Revenue under the Trump Administration
While the Trump administration's tariffs generated significant revenue, it pales in comparison to income tax revenue. The revenue generated from tariffs varied year to year and was dependent on the specific tariffs imposed and the global trade environment. Although precise figures fluctuate, it's clear that the revenue generated from tariffs was far less than the income tax revenue. For instance, specific tariffs on steel and aluminum, while generating some revenue, had limited impact on overall government coffers.
- Direct Comparison: The massive discrepancy between income tax and tariff revenue highlights the impossibility of a complete replacement.
- Limitations of Tariffs: Tariffs are inherently limited in their revenue-generating capacity, largely dependent on the volume of imported goods.
- Volatility: Tariff revenue is highly volatile, fluctuating with changes in global trade patterns, economic downturns, and retaliatory tariffs from other nations.
Economic Consequences of a Tariff-Based Tax System
Shifting to a tariff-based tax system would trigger significant negative economic consequences, both domestically and internationally.
Impact on Trade and Global Relations
Relying primarily on tariffs for government revenue would severely damage international trade relationships and destabilize the global economy. Other countries would likely retaliate with their own tariffs, leading to trade wars and harming businesses on both sides.
Effects on Domestic Businesses and Consumers
A tariff-based system would place a significant burden on domestic businesses, especially those reliant on imported goods. Increased input costs would lead to higher prices for consumers, potentially fueling inflation and decreasing consumer spending.
- Retaliatory Tariffs: Other countries are likely to impose retaliatory tariffs, leading to a significant reduction in exports for certain US industries.
- Industry Impacts: Industries heavily reliant on imports, such as manufacturing and agriculture, would be disproportionately affected.
- Inflationary Pressures: Higher prices on imported goods and raw materials would lead to higher consumer prices, causing inflation.
The Distributional Effects of a Tariff-Based Tax System
A tariff-based tax system is inherently regressive, disproportionately impacting lower-income individuals.
Regressive Nature of Tariffs
Tariffs raise the prices of imported goods, impacting all consumers. However, lower-income households spend a larger proportion of their income on these goods, thus bearing a heavier burden. This contrasts sharply with the progressive nature of the income tax system, where higher earners pay a larger percentage of their income in taxes.
Comparison with Progressive Income Tax System
The current income tax system is designed to be progressive, meaning higher earners contribute a larger share to government revenue. A tariff-based system would reverse this, creating an unfair and unequal distribution of the tax burden.
- Impact on Low-Income Households: Essential goods like food and clothing, often sourced internationally, would become more expensive, impacting lower-income families the most.
- Social and Economic Implications: A regressive tax system could exacerbate income inequality and lead to social unrest.
- Equitable Alternatives: Progressive income taxes, corporate taxes, and other tax mechanisms offer more equitable ways to fund government operations.
Practical Challenges of Replacing Income Taxes with Tariffs
Implementing a tariff-based tax system would present numerous practical challenges.
Administrative Complexity
Administering a tariff system to replace income tax would be incredibly complex. It would require a vast expansion of customs enforcement and a highly intricate system for tracking imports and exports, as well as constant adjustments to tariff rates based on market dynamics.
Predictability and Stability
Tariff revenue is inherently unpredictable and unstable. Unlike the relatively stable income tax revenue stream, tariff revenue is highly susceptible to changes in global trade patterns, economic fluctuations, and international political relationships.
- Constant Adjustments: Tariff rates would need constant adjustments based on global trade conditions, making long-term budget planning extremely difficult.
- Enforcement Difficulties: Tariff evasion and smuggling would be major challenges, requiring significant resources for enforcement.
- Political Manipulation: Tariff rates could be easily manipulated for political purposes, undermining the fairness and stability of the system.
Conclusion: Trump's Tariffs and the Unrealistic Goal of Income Tax Replacement
Replacing the US income tax system with revenue generated from tariffs is demonstrably unrealistic. The scale of income tax revenue dwarfs that of tariff revenue. Furthermore, a complete shift to tariffs would have devastating economic consequences, impacting trade relations, domestic businesses, and consumers. The inherent regressive nature of tariffs, coupled with the considerable administrative and predictability challenges, makes such a proposal impractical and economically unsound. Understanding the limitations of tariff revenue as a replacement for income taxes is crucial for informed policy discussions. Learn more about the complexities of tax policy and the limitations of relying on tariffs as a primary revenue source [link to relevant resource].

Featured Posts
-
 Three Injured In Yate House Explosion Gas Leak Suspected
Apr 30, 2025
Three Injured In Yate House Explosion Gas Leak Suspected
Apr 30, 2025 -
 The Our Yorkshire Farm Show Reuben Owens Negative Experience
Apr 30, 2025
The Our Yorkshire Farm Show Reuben Owens Negative Experience
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Diddy Zaak Aanklacht Ingetrokken Tegen Beyonce En Jay Z
Apr 30, 2025
Diddy Zaak Aanklacht Ingetrokken Tegen Beyonce En Jay Z
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Are Zoe Kravitz And Noah Centineo Dating Unpacking The Rumors
Apr 30, 2025
Are Zoe Kravitz And Noah Centineo Dating Unpacking The Rumors
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Nypd Probes Allegations Of Harassment Against Woman By Pro Israel Group
Apr 30, 2025
Nypd Probes Allegations Of Harassment Against Woman By Pro Israel Group
Apr 30, 2025
