Toxic Chemical Residue From Ohio Train Derailment Remains In Buildings
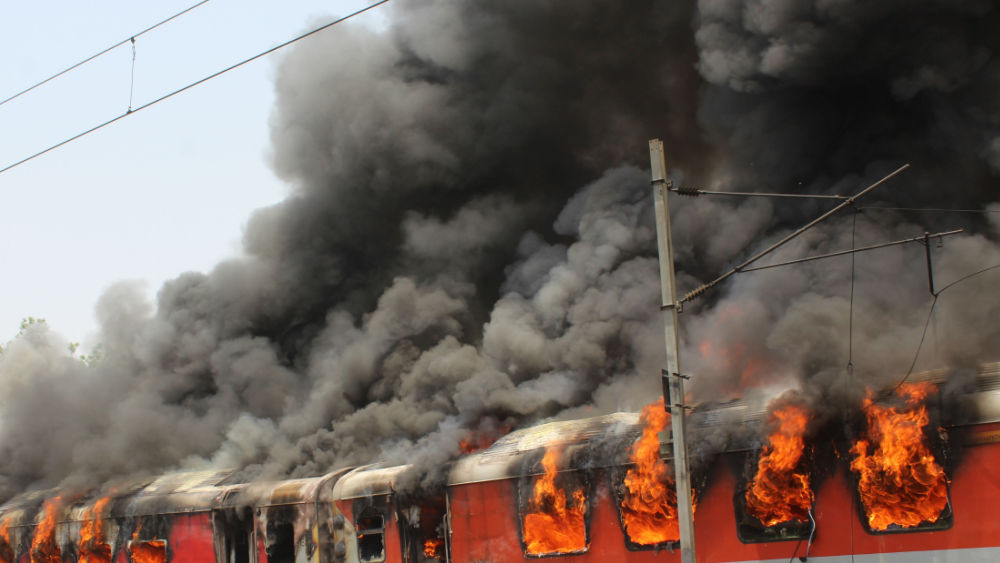

Table of Contents
Extent of Building Contamination
The extent of building contamination from the Ohio train derailment is a complex and evolving issue. The persistence of vinyl chloride and other toxic chemicals within building structures poses a significant challenge to remediation efforts.
Vinyl Chloride Persistence
Vinyl chloride, a known carcinogen, is particularly problematic due to its properties. It readily adheres to porous surfaces and can penetrate building materials, making complete removal incredibly difficult.
- Affected Building Materials: Vinyl chloride has been found in various building materials including wood, drywall, insulation, and carpeting. The porous nature of these materials allows for deep penetration, hindering decontamination efforts.
- Detection Methods: Identifying the presence of vinyl chloride requires sophisticated testing. Air sampling and surface wipes are commonly used methods to detect and quantify the levels of contamination within buildings. These methods must be employed thoroughly to accurately assess the extent of the problem.
Other Contaminated Compounds
Beyond vinyl chloride, other toxic chemicals released during the derailment are present in the environment and may have infiltrated buildings. These compounds add to the complexity of the contamination and pose additional health risks.
- Identified Chemicals and Health Risks: Initial reports indicate the presence of butyl acrylate, ethylhexyl acrylate, and ethylene glycol monobutyl ether, all with varying degrees of toxicity. Exposure to these chemicals can lead to respiratory problems, skin irritation, and other health complications.
- Synergistic Effects: The combined impact of multiple chemical exposures is a significant concern. The synergistic effects of these chemicals mean that the overall health risk may be greater than the sum of their individual impacts. More research is needed to understand these interactions fully.
Geographic Spread of Contamination
The spread of chemical residue extends beyond the immediate vicinity of the derailment site. Wind patterns and water runoff have played a significant role in distributing the contaminants over a wider area.
- Potential Spread: Modeling the spread of contamination based on wind direction and rainfall patterns suggests that a considerably larger area than initially anticipated may be affected. This underlines the need for widespread testing and remediation efforts.
- Affected Building Types: The contamination impacts various building types, including residential homes, commercial properties, and schools. This highlights the breadth of the environmental and public health threat posed by the derailment.
Challenges of Cleanup and Remediation
Effectively cleaning up and remediating the toxic chemical residue from buildings presents numerous challenges. The complex nature of the contamination, the costs involved, and the need for long-term monitoring significantly complicate the process.
Difficulties in Decontamination
Removing vinyl chloride and other toxic chemicals from building materials is technically challenging. The deep penetration of these substances into porous materials requires specialized and often expensive remediation techniques.
- Decontamination Processes: Methods used for decontamination vary depending on the material affected. This may include techniques like chemical washing, abrasive blasting, and even complete material replacement. The effectiveness of each method varies depending on the chemical and the building material.
- Limitations of Current Technologies: Current cleanup technologies may not be fully effective in removing all traces of these chemicals. Further research and development of innovative remediation technologies are needed to address this challenge.
Cost and Accessibility of Remediation
The financial burden of building cleanup and remediation is substantial, creating significant barriers for homeowners and businesses. Moreover, equitable access to remediation resources is a critical concern.
- Financial Burden: The cost of testing, decontamination, and potential rebuilding can be prohibitive for many residents, particularly those with limited financial resources. Government assistance and financial aid programs are crucial.
- Equity Issues: Ensuring that remediation resources are accessible to all affected residents, regardless of their socioeconomic status, is paramount. Disparities in access to resources must be addressed proactively.
Long-Term Monitoring and Assessment
Ongoing monitoring and assessment are crucial to track the long-term impact of the contamination and evaluate the effectiveness of remediation efforts. This requires a comprehensive and sustained commitment to public health and environmental protection.
- Long-Term Health Studies: Long-term health studies are essential to assess the health effects on residents exposed to the toxic chemicals. These studies should be carefully designed and implemented to identify and address any long-term health consequences.
- Environmental Monitoring: Continuous environmental monitoring is needed to track the dispersion of chemicals and to evaluate the effectiveness of cleanup efforts. This will help to inform future remediation strategies.
Health Risks and Long-Term Effects
Exposure to vinyl chloride and other toxic chemicals released during the derailment poses significant acute and chronic health risks. The psychological impact on affected communities is equally important.
Acute and Chronic Health Impacts
Exposure to vinyl chloride and other chemicals can lead to a range of health problems. Acute effects may appear immediately, while chronic effects may develop over time.
- Potential Health Problems: These can include respiratory problems, liver damage, nervous system disorders, and an increased risk of cancer. The specific health impacts vary depending on the chemical and the level of exposure.
- Vulnerable Populations: Children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing health conditions are particularly vulnerable to the adverse effects of chemical exposure. Special attention should be given to protecting these groups.
Psychological Impacts
The train derailment and the subsequent threat of contamination have caused significant psychological distress among residents. Stress, anxiety, and uncertainty are prevalent in the affected community.
- Mental Health Impacts: The prolonged uncertainty about the extent of contamination and the potential long-term health effects are significantly impacting mental health. Access to mental health services and support is essential.
- Community Support: Strong community support networks and access to mental health professionals are crucial for helping residents cope with the stress and anxiety resulting from this environmental disaster.
Legal and Regulatory Responses
The legal and regulatory responses to the Ohio train derailment are crucial to addressing the crisis and preventing future incidents. Accountability and stricter regulations are paramount.
- Legal Challenges: Determining liability and securing compensation for affected residents presents significant legal challenges. Legal action is vital to hold those responsible accountable for the damages incurred.
- Stricter Regulations: The incident highlights the urgent need for stricter regulations on the transportation of hazardous materials, improved safety measures for rail infrastructure, and enhanced emergency response protocols.
Conclusion
The lingering presence of toxic chemical residue from the Ohio train derailment in buildings presents a significant and ongoing threat to public health and the environment. Addressing this crisis requires immediate and comprehensive action, including thorough building decontamination, long-term health monitoring, and robust regulatory reforms. Failure to take decisive action will prolong the suffering of those affected and risk future similar catastrophes. We must continue to demand accountability and transparency to ensure the complete and effective removal of toxic chemical residue from affected buildings and the surrounding area. Ignoring this issue is not an option. We need to continue to monitor the situation and pressure authorities to guarantee complete and effective remediation of the toxic chemical residue from the Ohio train derailment.

Featured Posts
-
 Get To Know Paulina Gretzky Dustin Johnsons Wife Her Career And Kids
May 20, 2025
Get To Know Paulina Gretzky Dustin Johnsons Wife Her Career And Kids
May 20, 2025 -
 Why Buy This Ai Quantum Computing Stock During A Dip
May 20, 2025
Why Buy This Ai Quantum Computing Stock During A Dip
May 20, 2025 -
 Analyzing Snls 50th Season Finale Ratings And Impact
May 20, 2025
Analyzing Snls 50th Season Finale Ratings And Impact
May 20, 2025 -
 Analyzing The Risks Of The Philippines Typhon Missile System Deployment
May 20, 2025
Analyzing The Risks Of The Philippines Typhon Missile System Deployment
May 20, 2025 -
 Restaurants Biarritz Nouveaux Chefs Et Adresses A Decouvrir
May 20, 2025
Restaurants Biarritz Nouveaux Chefs Et Adresses A Decouvrir
May 20, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Gladbach Defeat Boosts Mainzs Top Four Chances
May 20, 2025
Gladbach Defeat Boosts Mainzs Top Four Chances
May 20, 2025 -
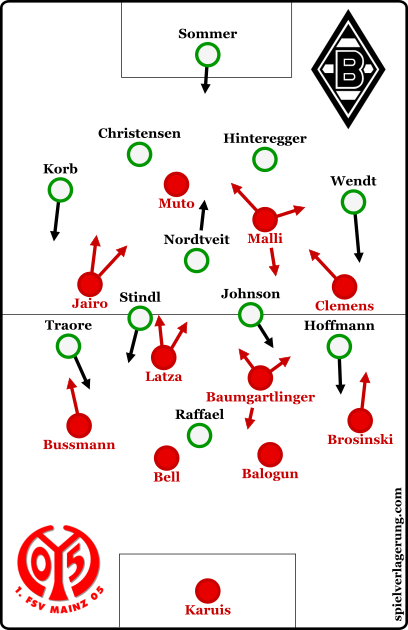 Mainz Extends Top Four Hopes Following Gladbach Win
May 20, 2025
Mainz Extends Top Four Hopes Following Gladbach Win
May 20, 2025 -
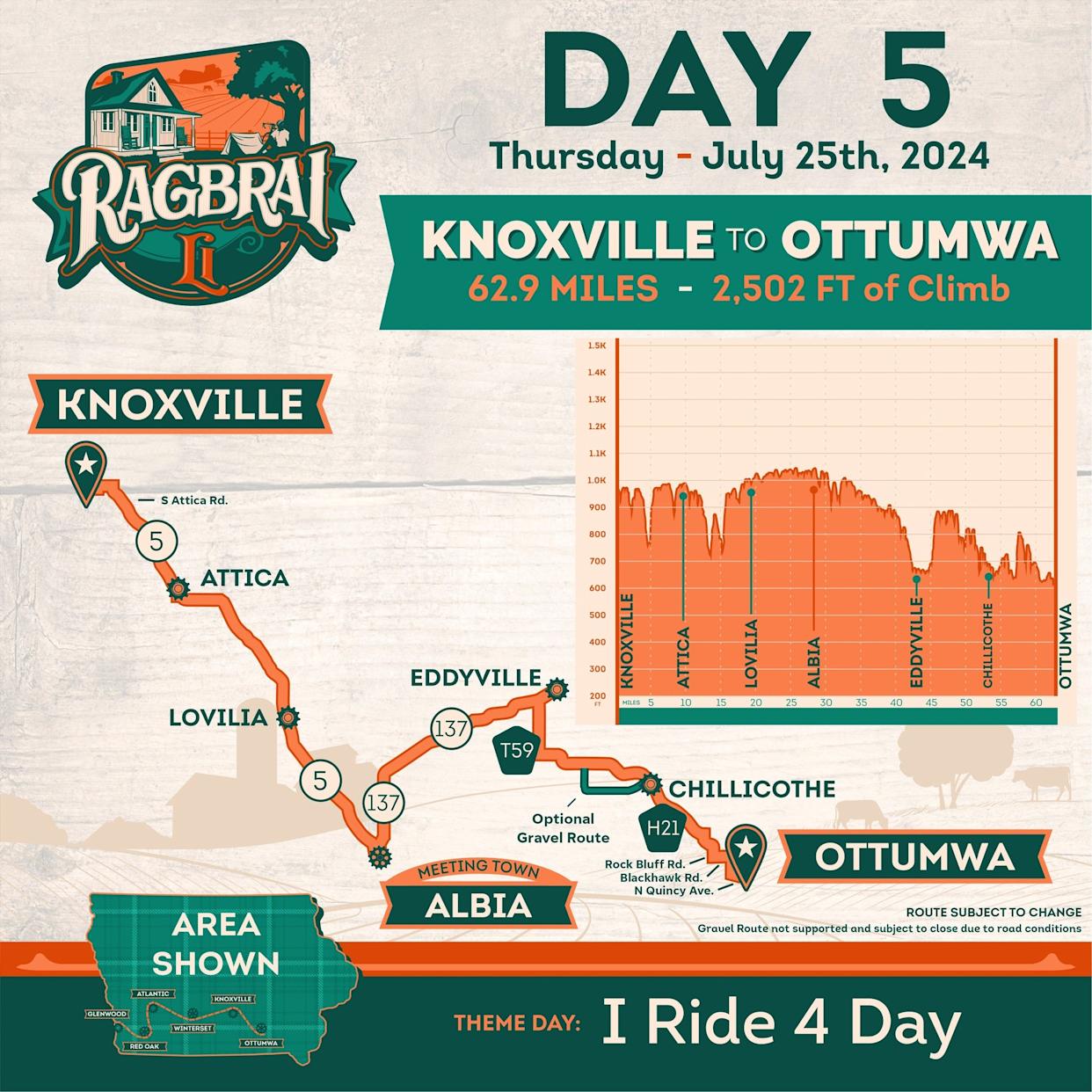 From Ragbrai To Daily Rides Scott Savilles Passion For Biking
May 20, 2025
From Ragbrai To Daily Rides Scott Savilles Passion For Biking
May 20, 2025 -
 Scott Savilles Cycling Journey From Ragbrai To Daily Commutes
May 20, 2025
Scott Savilles Cycling Journey From Ragbrai To Daily Commutes
May 20, 2025 -
 Mild Temperatures And Little Rain Chance Perfect For Outdoor Activities
May 20, 2025
Mild Temperatures And Little Rain Chance Perfect For Outdoor Activities
May 20, 2025
