Threats To Clean Energy's Continued Expansion
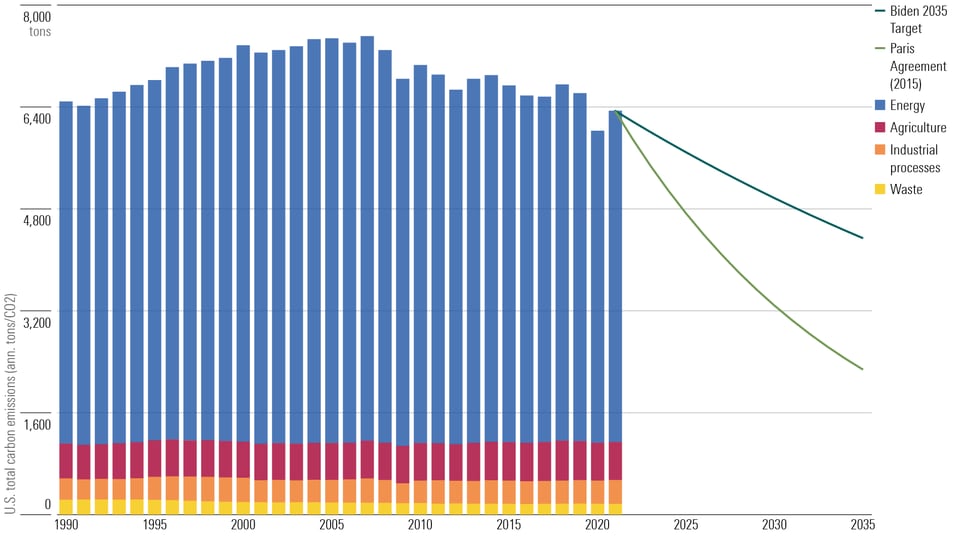
Table of Contents
Political and Regulatory Hurdles to Clean Energy Expansion
Navigating the complex landscape of politics and regulation is a major hurdle for clean energy expansion. Inconsistent policies and shifting priorities create an unstable environment that discourages long-term investments in renewable energy projects.
Policy Instability and Shifting Priorities
The clean energy sector thrives on long-term planning and substantial investment. However, changing government policies and regulations can significantly undermine these efforts.
- Examples of policy instability: Frequent changes in subsidies for renewable energy projects, fluctuating tax credits, and unpredictable permitting processes all contribute to uncertainty and risk.
- Political polarization: Deep political divides often lead to partisan battles over clean energy initiatives, resulting in delays, stalled projects, and even outright reversals of supportive policies.
- Regulatory rollbacks: The risk of future administrations rolling back existing environmental regulations or subsidies for renewable energy creates a chilling effect on investment. This regulatory uncertainty makes it difficult for businesses to plan for the long-term and commit significant capital.
These factors severely impact the confidence of investors and developers, making it harder to secure funding and initiate new clean energy projects. Consistent and supportive clean energy policy is fundamental for sustainable renewable energy subsidies and a stable investment climate.
Grid Infrastructure Limitations
Integrating intermittent renewable energy sources like solar and wind power into existing power grids presents significant challenges. Our current infrastructure is largely designed for centralized power generation from fossil fuels, and upgrading it to handle the decentralized and fluctuating nature of renewable energy is crucial.
- Grid modernization and upgrades: Massive investments are needed to modernize and expand electricity grids to accommodate the increased capacity and variable nature of renewable energy sources. Smart grid technologies are essential for efficient management of the fluctuating supply from solar and wind.
- Energy storage solutions: The intermittent nature of solar and wind power requires effective energy storage solutions to ensure a consistent energy supply. Developing and deploying large-scale energy storage technologies remains a major technical and economic challenge.
- Transmission capacity: Lack of sufficient transmission capacity can prevent renewable energy generated in remote areas from reaching population centers, hindering clean energy integration.
- Regional disparities in grid infrastructure: Significant variations in grid infrastructure quality and capacity across different regions create further challenges for widespread clean energy adoption.
Economic and Financial Barriers to Clean Energy Expansion
Despite the growing awareness of climate change, economic realities continue to play a significant role in the clean energy transition.
High Initial Costs and Financing Challenges
The upfront capital expenditure for renewable energy projects is often substantial compared to fossil fuel-based alternatives, creating a barrier to entry for many developers. Securing sufficient funding is another significant hurdle.
- Cost comparison with fossil fuels: While the long-term operational costs of renewable energy are often lower, the initial investment is typically higher. This initial cost disparity makes it challenging to compete directly with established fossil fuel industries.
- Availability of financing options: While green bonds and other specialized financing mechanisms are emerging, access to affordable and readily available financing remains limited, particularly for smaller-scale renewable energy projects.
- Government incentives and private investment: Government incentives, such as tax credits and subsidies, play a vital role in attracting private investment, but their availability and consistency are often uncertain.
- Risk perception by investors: The long-term nature of renewable energy projects and the inherent uncertainties related to technology, policy, and market demand can make them seem riskier to some investors than more established energy sources.
Competition from Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels continue to benefit from substantial government subsidies and established infrastructure, providing an unfair competitive advantage over cleaner energy sources.
- Fossil fuel subsidies: Direct and indirect subsidies for fossil fuels distort the energy market, making it artificially cheaper to use fossil fuels than renewable alternatives.
- Lobbying efforts by fossil fuel industries: Powerful lobbying efforts by established fossil fuel industries significantly influence policy decisions, hindering the adoption of policies favorable to clean energy expansion.
- Influence of established energy infrastructure: The existing energy infrastructure, built around fossil fuels, creates a significant inertia that makes transitioning to clean energy more challenging and expensive.
- Challenge of transitioning away from fossil fuel dependence: The global economy's dependence on fossil fuels is deeply ingrained and requires a concerted effort and significant policy changes to overcome. Implementing effective carbon pricing mechanisms is crucial for leveling the playing field.
Technological and Resource Constraints to Clean Energy Expansion
Technological advancements and resource availability are critical to the success of clean energy expansion.
Technological Advancements and Scalability
Continued technological innovation is essential to improve the efficiency, reduce the cost, and increase the scalability of clean energy technologies.
- Advancements in battery technology: Improving the energy density, lifespan, and cost-effectiveness of batteries is crucial for enabling wider adoption of renewable energy sources and facilitating effective energy storage solutions.
- Improvements in solar panel efficiency: Ongoing research into higher efficiency solar panels and lower manufacturing costs is vital for reducing the cost of solar energy.
- Innovations in wind turbine design: Designing more efficient and robust wind turbines that can generate energy in diverse wind conditions is essential for expanding wind power capacity.
- Breakthroughs in energy storage: Developing innovative and cost-effective energy storage technologies is crucial for addressing the intermittency challenges associated with solar and wind power.
- Need for research and development: Continued and substantial investment in research and development is vital for driving technological innovation in all aspects of clean energy.
Resource Availability and Supply Chain Issues
The production of clean energy technologies relies on specific raw materials, creating potential bottlenecks due to resource scarcity and supply chain vulnerabilities.
- Sourcing of rare earth minerals: Many clean energy technologies, including wind turbines and electric vehicles, rely on rare earth minerals, the extraction of which raises significant environmental and geopolitical concerns.
- Environmental impact of mining: The mining and processing of these resources can have a detrimental environmental impact unless sustainable practices are employed.
- Geopolitical risks associated with resource dependence: Over-reliance on specific countries for critical raw materials creates geopolitical vulnerabilities and supply chain risks.
- Importance of responsible sourcing and recycling: Promoting responsible sourcing practices and developing efficient recycling mechanisms is crucial for minimizing the environmental footprint of clean energy technologies and ensuring long-term supply chain resilience.
Conclusion
The transition to a sustainable energy future hinges on overcoming significant threats to clean energy expansion. Political instability, inadequate grid infrastructure, high initial costs, competition from fossil fuels, technological limitations, and resource constraints all pose challenges to achieving widespread clean energy adoption. Addressing these obstacles requires a collaborative effort from governments, industries, and individuals. We need supportive and consistent clean energy policies, innovative technologies, responsible resource management, and substantial investment in renewable energy development and grid modernization. Learn more about the obstacles to clean energy expansion and actively support policies and initiatives that promote the transition to a cleaner energy future. The future of sustainable energy growth, clean energy development, and renewable energy expansion depends on our collective action today.

Featured Posts
-
 Minnesota Twins Baseball 10 Games On Kcrg Tv 9
May 20, 2025
Minnesota Twins Baseball 10 Games On Kcrg Tv 9
May 20, 2025 -
 Everything You Need To Know About Lou Gala Of The Decameron
May 20, 2025
Everything You Need To Know About Lou Gala Of The Decameron
May 20, 2025 -
 Mia Deyteri Eykairia I Martha Antimetopizei Ta Tampoy Toy Gamoy
May 20, 2025
Mia Deyteri Eykairia I Martha Antimetopizei Ta Tampoy Toy Gamoy
May 20, 2025 -
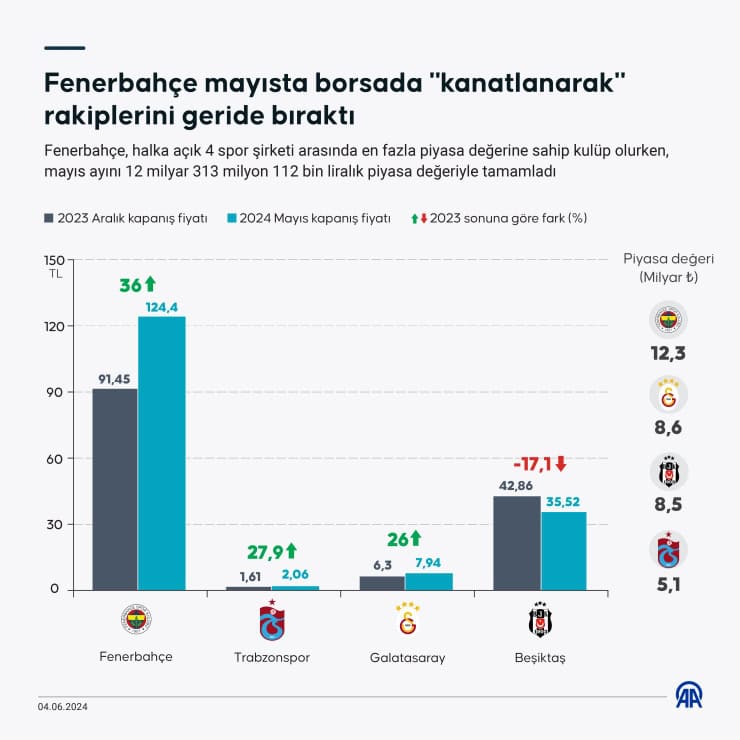 Mourinho Nun Etkisi Fenerbahce Oyuncusunun Ajax Transferi
May 20, 2025
Mourinho Nun Etkisi Fenerbahce Oyuncusunun Ajax Transferi
May 20, 2025 -
 Nyt Mini Crossword May 13 2025 Complete Answers And Gameplay Guide
May 20, 2025
Nyt Mini Crossword May 13 2025 Complete Answers And Gameplay Guide
May 20, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Scott Savilles Cycling Journey From Ragbrai To Daily Commutes
May 20, 2025
Scott Savilles Cycling Journey From Ragbrai To Daily Commutes
May 20, 2025 -
 Mild Temperatures And Little Rain Chance Perfect For Outdoor Activities
May 20, 2025
Mild Temperatures And Little Rain Chance Perfect For Outdoor Activities
May 20, 2025 -
 Washington County Breeder Faces Action After 49 Dogs Removed
May 20, 2025
Washington County Breeder Faces Action After 49 Dogs Removed
May 20, 2025 -
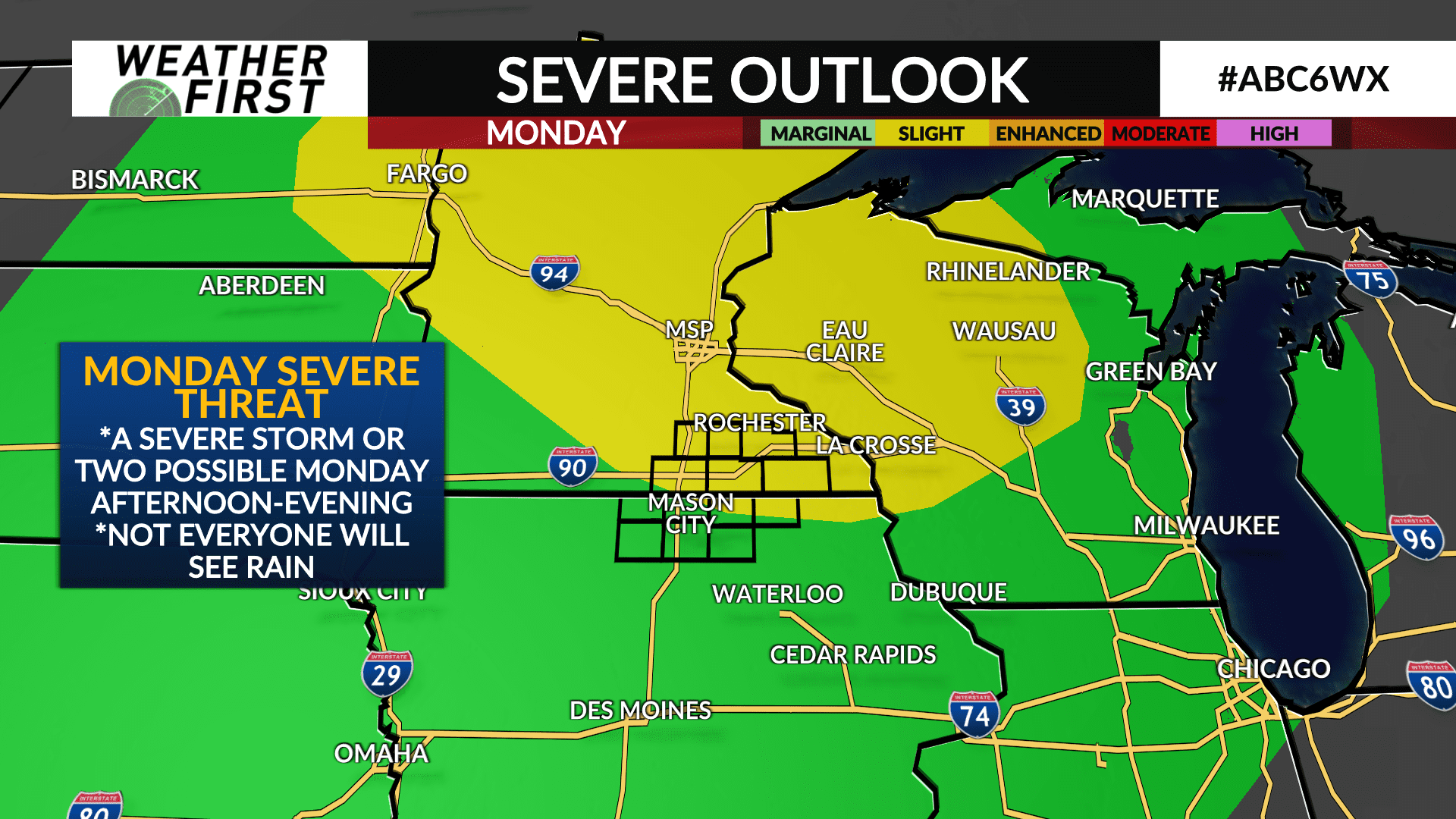 Increased Storm Chance Overnight Severe Weather Possible Monday
May 20, 2025
Increased Storm Chance Overnight Severe Weather Possible Monday
May 20, 2025 -
 Expect Mild Temperatures And Little Rain Chance This Week
May 20, 2025
Expect Mild Temperatures And Little Rain Chance This Week
May 20, 2025
