The Rising Cost Of Borrowing: Federal Debt And Mortgages
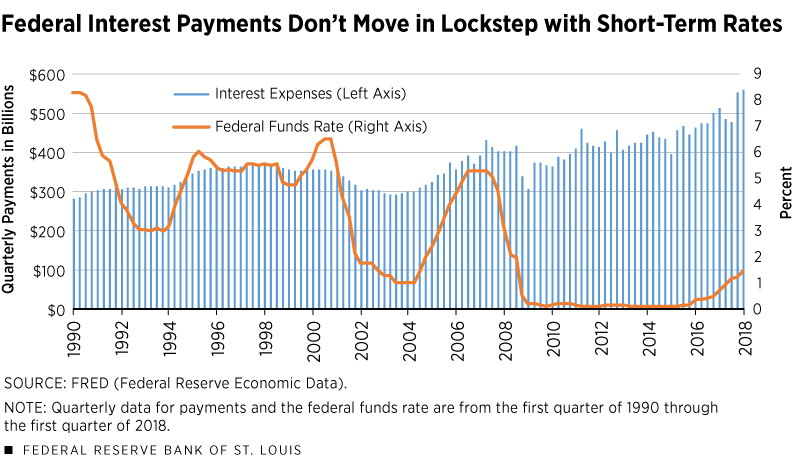
Table of Contents
The Impact of Federal Debt on Interest Rates
The rising cost of borrowing is significantly influenced by the level of federal debt. Understanding this relationship requires examining the role of the Federal Reserve and the dynamics of the bond market.
Understanding the Federal Reserve's Role
The Federal Reserve (the Fed) plays a crucial role in managing interest rates to maintain economic stability. Its primary tools include adjusting the federal funds rate – the target rate banks charge each other for overnight loans. By influencing this rate, the Fed indirectly affects other interest rates throughout the economy.
- Increased Federal Debt and Inflation: When the government borrows heavily, it can increase the money supply, potentially leading to inflation. To combat inflation, the Fed often raises interest rates, making borrowing more expensive.
- Quantitative Easing (QE) and Quantitative Tightening (QT): QE involves the Fed injecting money into the economy by purchasing government bonds, aiming to lower long-term interest rates. Conversely, QT involves the opposite – reducing the money supply by selling bonds, pushing interest rates higher. These policies directly reflect the impact of federal debt management on interest rates.
The Bond Market and Interest Rate Fluctuations
Government bonds are a significant component of the bond market. When the government increases borrowing to finance its debt, it issues more bonds. This increased supply can, in some circumstances, drive up demand for bonds, potentially increasing their yields (returns). These higher yields impact other borrowing costs, as lenders adjust their rates to compete with government bond returns.
- Increased Government Borrowing and Bond Yields: Higher government borrowing can lead to higher yields on government bonds, influencing the overall cost of borrowing across the board.
- Yield Curves and Economic Forecasting: The yield curve, which compares the yields of bonds with different maturities, is a key indicator used by economists to predict future economic activity. A flattening or inverted yield curve often precedes economic slowdowns.
The Rising Cost of Mortgages
The rising cost of borrowing directly impacts mortgage rates, making homeownership less attainable for many.
Mortgage Rates and Federal Debt
The link between rising federal debt and increasing mortgage rates is clear: when the Fed raises interest rates to control inflation fueled by increased government borrowing, mortgage rates inevitably follow suit. This increase makes borrowing for a home more expensive.
- Transmission of Interest Rate Hikes: Higher federal funds rates translate into higher rates for banks, which then pass those costs onto consumers through higher mortgage rates.
- Fixed-Rate vs. Adjustable-Rate Mortgages: While fixed-rate mortgages provide rate certainty for the loan's duration, adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs) are directly vulnerable to fluctuations in interest rates, potentially leading to significant increases in monthly payments.
The Impact on Home Affordability
Higher mortgage rates significantly reduce home affordability, impacting potential homebuyers and the overall housing market.
- Reduced Purchasing Power: Increased borrowing costs mean that buyers can afford less expensive homes, potentially leading to a decrease in demand.
- Shrinking Home Affordability: Affordability indexes, which measure the relationship between home prices and income, often decline sharply during periods of rising interest rates. This makes homeownership increasingly challenging.
- Potential Market Slowdown: The combined effect of higher prices and higher interest rates can lead to a slowdown in the housing market, with fewer transactions and potentially lower home prices.
Other Borrowing Costs Affected by Federal Debt
The impact of rising federal debt extends beyond mortgages, affecting various other forms of borrowing.
Auto Loans and Personal Loans
Increased interest rates resulting from higher federal debt affect auto loans and personal loans, making them more expensive for consumers.
- Impact on Consumer Spending: Higher borrowing costs for autos and personal items can reduce consumer spending, impacting economic growth.
- Reduced Consumer Confidence: The rising cost of borrowing can lead to decreased consumer confidence, affecting spending patterns and economic activity.
Business Loans and Economic Growth
Higher borrowing costs also impact businesses, affecting investment and economic expansion.
- Reduced Business Investment: Businesses may postpone or cancel expansion plans due to the increased cost of borrowing, impacting job creation and economic growth.
- Implications for Economic Health: Reduced business investment can lead to slower economic growth and potentially increased unemployment.
Conclusion
The rising cost of borrowing, significantly driven by increased federal debt, has far-reaching consequences. The connection between federal debt, interest rates, and the increased cost of borrowing across sectors like mortgages, auto loans, and business loans is undeniable. Higher mortgage interest rates reduce home affordability, while increased borrowing costs for businesses can stifle economic growth. Understanding the rising cost of borrowing and its link to federal debt is crucial for making informed financial decisions. Stay updated on economic news and plan your financial future accordingly, considering the implications of federal debt on mortgage interest rates and other borrowing costs.

Featured Posts
-
 Pahalgam Terror Attack Arrested You Tuber Jyoti Malhotras Connection To Pakistan Investigated
May 19, 2025
Pahalgam Terror Attack Arrested You Tuber Jyoti Malhotras Connection To Pakistan Investigated
May 19, 2025 -
 Stefanos Stefanu Kibris Sorununda Yeni Bir Girisim
May 19, 2025
Stefanos Stefanu Kibris Sorununda Yeni Bir Girisim
May 19, 2025 -
 Suncoast Searchlight Mental Health Crisis Exposes Resource Gaps
May 19, 2025
Suncoast Searchlight Mental Health Crisis Exposes Resource Gaps
May 19, 2025 -
 Austin Becomes A Testing Ground For Waymo And Ubers Self Driving Cars
May 19, 2025
Austin Becomes A Testing Ground For Waymo And Ubers Self Driving Cars
May 19, 2025 -
 Billy Ray Cyrus Ny Start Etter Skilsmisse Og Toffe Ar Med Elizabeth Hurley
May 19, 2025
Billy Ray Cyrus Ny Start Etter Skilsmisse Og Toffe Ar Med Elizabeth Hurley
May 19, 2025
