The Challenge Of Rare Earth Minerals: Tesla's Optimus Robot And China's Influence
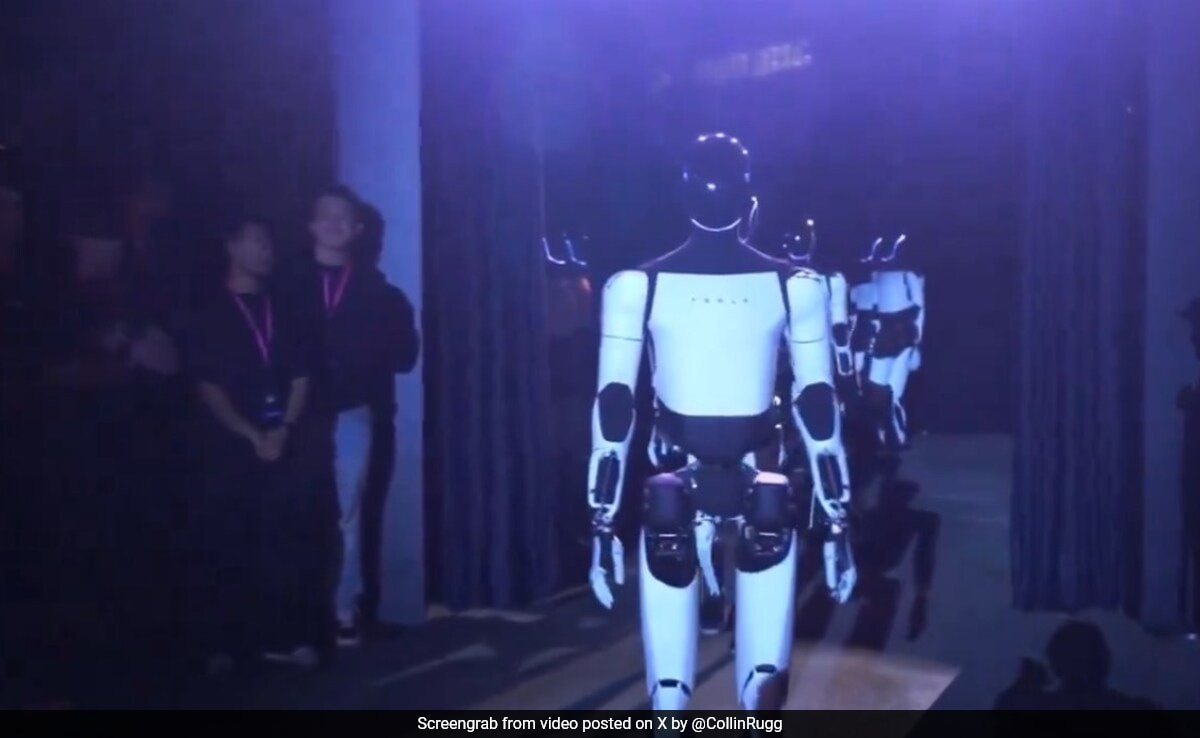

Table of Contents
The Crucial Role of Rare Earth Minerals in Robotics and Advanced Technologies
Rare earth elements (REEs), a group of 17 chemically similar metals, are indispensable to modern technology, particularly in robotics and advanced manufacturing. Their unique magnetic, electrical, and catalytic properties make them essential components in numerous high-tech applications. Tesla's Optimus robot, for example, relies heavily on REEs for its functionality.
- Neodymium magnets: These powerful magnets, primarily composed of neodymium, are crucial for the motors driving Optimus's locomotion and manipulation capabilities. Their strength and efficiency are unparalleled, making them irreplaceable in many robotic applications.
- Dysprosium: This REE is critical for enhancing the performance of neodymium magnets, increasing their resistance to demagnetization at high temperatures. This is vital for ensuring the robot's motors maintain their power and efficiency under demanding conditions.
- Other REEs: Elements like cerium, lanthanum, and praseodymium are used in various electronic components within Optimus, including sensors, control systems, and lighting.
Without sufficient access to a diverse and reliable supply of REEs, the performance and even the feasibility of robots like Optimus would be severely limited. The precision movements, powerful motors, and advanced sensors are all dependent on the unique properties of these minerals.
China's Dominance in the Rare Earth Supply Chain: A Geopolitical Tightrope
China currently controls a vast majority of the global rare earth mineral supply chain, dominating mining, processing, and refining. This dominance has significant implications for global supply chains and pricing, creating a significant geopolitical risk.
- Production Dominance: China controls over 70% of global REE production, holding a virtual monopoly on the processing and refining of these critical materials.
- Environmental Concerns: China's mining practices have raised significant environmental concerns, including land degradation and water pollution, highlighting the need for more sustainable extraction methods globally.
- Geopolitical Leverage: China's control over REEs gives it considerable geopolitical leverage, potentially influencing global trade relations and creating vulnerabilities for countries heavily reliant on its supply.
This heavy reliance on a single source for such crucial materials presents substantial risks. Disruptions to the supply chain, whether due to geopolitical tensions, environmental regulations, or natural disasters, could have devastating consequences for industries reliant on REEs, including the robotics sector and the production of Optimus.
Strategies for Mitigating the Rare Earth Mineral Dependency: Diversification and Innovation
Reducing reliance on China for rare earth minerals requires a multifaceted approach focusing on diversification and innovation. This involves several key strategies:
- Investment in Exploration and Mining: Increased investment in exploration and mining activities in other countries with REE deposits is essential to diversify the supply chain. This requires significant financial commitment and collaboration between governments and private companies.
- Recycling Technologies: Developing efficient and cost-effective recycling technologies for REEs from end-of-life products, such as discarded electronics and electric vehicles, is crucial for both environmental sustainability and resource security.
- Alternative Materials and Designs: Research and development into alternative materials and designs that reduce or eliminate the need for REEs in advanced technologies should be prioritized. This could involve exploring substitute materials or redesigning components to minimize REE dependence.
Governments and companies are already taking steps towards diversification, including increased exploration efforts in countries like Australia, the United States, and Canada, and investments in recycling technologies. However, significant progress is still needed to create a truly diversified and resilient supply chain.
The Future of Optimus and the Global REE Market: A Balancing Act
The long-term success of Tesla's Optimus robot and its future scalability are directly tied to the resolution of the REE challenge. Several scenarios are possible:
- Production Costs and Scalability: Continued reliance on China could lead to volatile production costs and limit the scalability of Optimus, impacting Tesla's overall business strategy.
- Secure REE Supplies: Securing stable and reliable REE supplies is paramount for Tesla's long-term success. This requires strategic partnerships, investment in alternative sourcing, and engagement with policymakers to address the geopolitical challenges.
- Collaboration and Innovation: Collaboration between Tesla, other tech companies, governments, and research institutions is vital to foster innovation in REE sourcing, recycling, and the development of alternative materials.
The future of robotics and advanced technologies will depend on our collective ability to navigate this complex geopolitical and environmental landscape.
Conclusion: Addressing the Challenge of Rare Earth Minerals for a Sustainable Future
The limited availability and geopolitical concentration of rare earth minerals present a significant challenge to the future of advanced technologies like Tesla's Optimus robot. China's dominance in the supply chain creates a vulnerability that demands urgent attention. Diversifying rare earth mineral sources, investing in sustainable mining practices, and fostering innovation in alternative materials are critical for ensuring a stable and secure supply chain. We urge readers, governments, and businesses to actively participate in finding solutions to the challenge of rare earth minerals, supporting research, promoting responsible sourcing, and advocating for policies that encourage global cooperation. The future of technologies like Tesla's Optimus robot, and indeed many other crucial advancements, depends on our collective ability to overcome the challenge of rare earth minerals and build a more sustainable and resilient future.

Featured Posts
-
 Market Analysis Whats Driving The Niftys Bullish Trend In India
Apr 24, 2025
Market Analysis Whats Driving The Niftys Bullish Trend In India
Apr 24, 2025 -
 How Elite Universities Are Responding To Funding Threats From The Trump Administration
Apr 24, 2025
How Elite Universities Are Responding To Funding Threats From The Trump Administration
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Zuckerbergs Next Chapter Navigating A Trump Presidency
Apr 24, 2025
Zuckerbergs Next Chapter Navigating A Trump Presidency
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Canadas Economic Outlook The Importance Of Fiscal Responsibility Under Liberal Leadership
Apr 24, 2025
Canadas Economic Outlook The Importance Of Fiscal Responsibility Under Liberal Leadership
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Nba All Star Game Draymond Green Moses Moody And Buddy Hield Participate
Apr 24, 2025
Nba All Star Game Draymond Green Moses Moody And Buddy Hield Participate
Apr 24, 2025
