Targeting Chinese Students: A Financial Risk For US Universities?
Table of Contents
The Allure and the Risk: Why Chinese Students Became a Key Demographic
Historical Context: The rise of Chinese student enrollment in US universities and its impact on revenue.
The surge in Chinese student enrollment in US universities over the past two decades has been dramatic, contributing significantly to the revenue streams of many institutions. Several factors fueled this growth:
- Increased Wealth in China: Rising affluence allowed more Chinese families to afford the high costs of studying abroad.
- Perception of Superior US Education: American universities have long held a prestigious reputation globally, attracting ambitious students seeking high-quality education.
- Government Scholarships and Funding: Chinese government scholarships and funding programs further incentivized students to pursue higher education in the US.
This influx translated into substantial financial gains for universities. For example, in 2019, Chinese students contributed billions of dollars in tuition fees alone to US higher education institutions. This significant revenue stream made many universities heavily reliant on this demographic.
The Shifting Landscape: Geopolitical Factors and Their Impact
However, the landscape has shifted significantly. Geopolitical tensions between the US and China, stricter visa requirements, and evolving Chinese government policies have all impacted the flow of Chinese students to American universities.
- Political Tensions: Strained US-China relations have created uncertainty and apprehension among prospective Chinese students.
- Visa Restrictions: Increased scrutiny and stricter visa application processes have made it more challenging for Chinese students to secure visas.
- Changing Government Policies: China's growing emphasis on domestic education and the promotion of its own universities as world-class institutions have diverted some students from pursuing studies abroad.
These factors have led to a decrease in Chinese student enrollment, creating a significant financial challenge for universities that had become heavily dependent on this revenue stream.
Financial Dependence and Vulnerability: Analyzing the Risk
Tuition Revenue Dependency: The percentage of revenue reliant on Chinese students in various universities.
The level of dependence on Chinese students varies widely across universities. Some institutions have a significantly higher percentage of their revenue derived from Chinese student tuition fees compared to others.
- University A: May rely on Chinese students for 20% of its tuition revenue.
- University B: Might be heavily reliant, with 40% or more of its revenue stemming from this demographic.
This disparity creates varying degrees of vulnerability. Universities with a high percentage of revenue from Chinese students face a greater risk of financial instability if enrollment numbers decline. Case studies reveal that institutions heavily reliant on a single international student demographic experienced significant budget shortfalls following sharp declines in enrollment.
Fluctuations in Enrollment: The impact of unpredictable geopolitical events on university finances.
The unpredictable nature of geopolitical relations and government policies means that the number of Chinese students enrolling in US universities can fluctuate dramatically. This instability directly impacts university finances.
- Example 1: A sudden tightening of visa regulations can lead to a substantial drop in enrollment within a single academic year.
- Example 2: Escalating political tensions can deter prospective students and their families, resulting in significant revenue loss.
Analyzing historical data reveals a strong correlation between major geopolitical events and fluctuations in Chinese student enrollment, underscoring the need for robust risk management strategies.
Mitigation Strategies: Diversifying Revenue Streams and Reducing Risk
Attracting a More Diverse Student Body: Strategies for broadening the student base.
To mitigate the risks associated with relying heavily on Chinese students, universities must prioritize attracting a more diverse student body. This involves:
- Targeted Marketing: Developing comprehensive marketing campaigns targeting different international and domestic student populations.
- Scholarships and Financial Aid: Offering competitive financial aid packages to attract a broader range of students.
- Strengthening Outreach: Actively engaging with diverse communities through partnerships with educational institutions and community organizations.
Successful diversity initiatives in higher education demonstrate that a diverse student body leads to a more robust and resilient institution.
Strengthening Financial Management: Improving budgetary practices and diversifying funding sources.
Beyond diversifying the student body, universities need to enhance their financial management practices. This includes:
- Exploring Alternative Revenue Streams: Increasing reliance on research grants, endowments, and online education programs.
- Improving Budgeting and Forecasting: Developing sophisticated models that account for potential fluctuations in international student enrollment.
- Cost Control Measures: Implementing efficient operational strategies to minimize expenses.
Successful financial diversification strategies in universities illustrate that a multi-faceted approach to funding improves resilience against external shocks.
Long-Term Planning: Preparing for Future Uncertainties in International Student Enrollment
Scenario Planning: Developing strategies to manage various potential enrollment scenarios.
Universities need to engage in proactive scenario planning to anticipate various potential enrollment trends. This involves:
- Best-Case Scenario: Developing strategies assuming continued growth in international student enrollment.
- Worst-Case Scenario: Planning for significant declines in enrollment from specific regions.
- Moderate-Case Scenario: Developing strategies that assume moderate fluctuations in enrollment.
Universities implementing proactive scenario planning are better equipped to handle unforeseen circumstances.
Building a Resilient Financial Model: Reducing dependency on any single student demographic.
Building a resilient financial model is crucial for long-term stability. This requires:
- Diversification of Revenue Sources: Reducing reliance on tuition fees from any single student demographic.
- Strong Endowment Management: Effectively managing and growing university endowments to provide a stable source of funding.
- Strategic Partnerships: Developing partnerships with industry, government, and other organizations to secure additional funding.
Best practices in university financial management highlight the importance of proactive planning and diversification.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future of International Student Recruitment
This article highlighted the significant financial risks associated with over-reliance on Chinese students for revenue generation in US universities. The decline in Chinese student enrollment, driven by geopolitical factors and policy changes, underscores the need for proactive strategies to mitigate these risks. Key takeaways include the importance of diversifying recruitment strategies for international students, strengthening financial management practices, and engaging in proactive risk management.
Universities must develop comprehensive strategies for attracting a diverse student body and building a more resilient financial model. By managing the risks of international student recruitment effectively and diversifying their revenue streams, US universities can build a financially secure future, ensuring their continued success and sustainability in the evolving landscape of higher education. This includes focusing on managing the risks of international student recruitment by diversifying their student body and securing alternative revenue streams. Building a financially secure future for your university in the context of international students requires a proactive and multifaceted approach.

Featured Posts
-
 American Response To Global Social Media Censorship Official Bans
May 31, 2025
American Response To Global Social Media Censorship Official Bans
May 31, 2025 -
 New Covid 19 Variant Is It Fueling The Recent Surge In Cases
May 31, 2025
New Covid 19 Variant Is It Fueling The Recent Surge In Cases
May 31, 2025 -
 Northeast Ohio Weather Expecting Showers And Thunderstorms
May 31, 2025
Northeast Ohio Weather Expecting Showers And Thunderstorms
May 31, 2025 -
 Former Nypd Commissioner Bernard Kerik Hospitalized Full Recovery Expected
May 31, 2025
Former Nypd Commissioner Bernard Kerik Hospitalized Full Recovery Expected
May 31, 2025 -
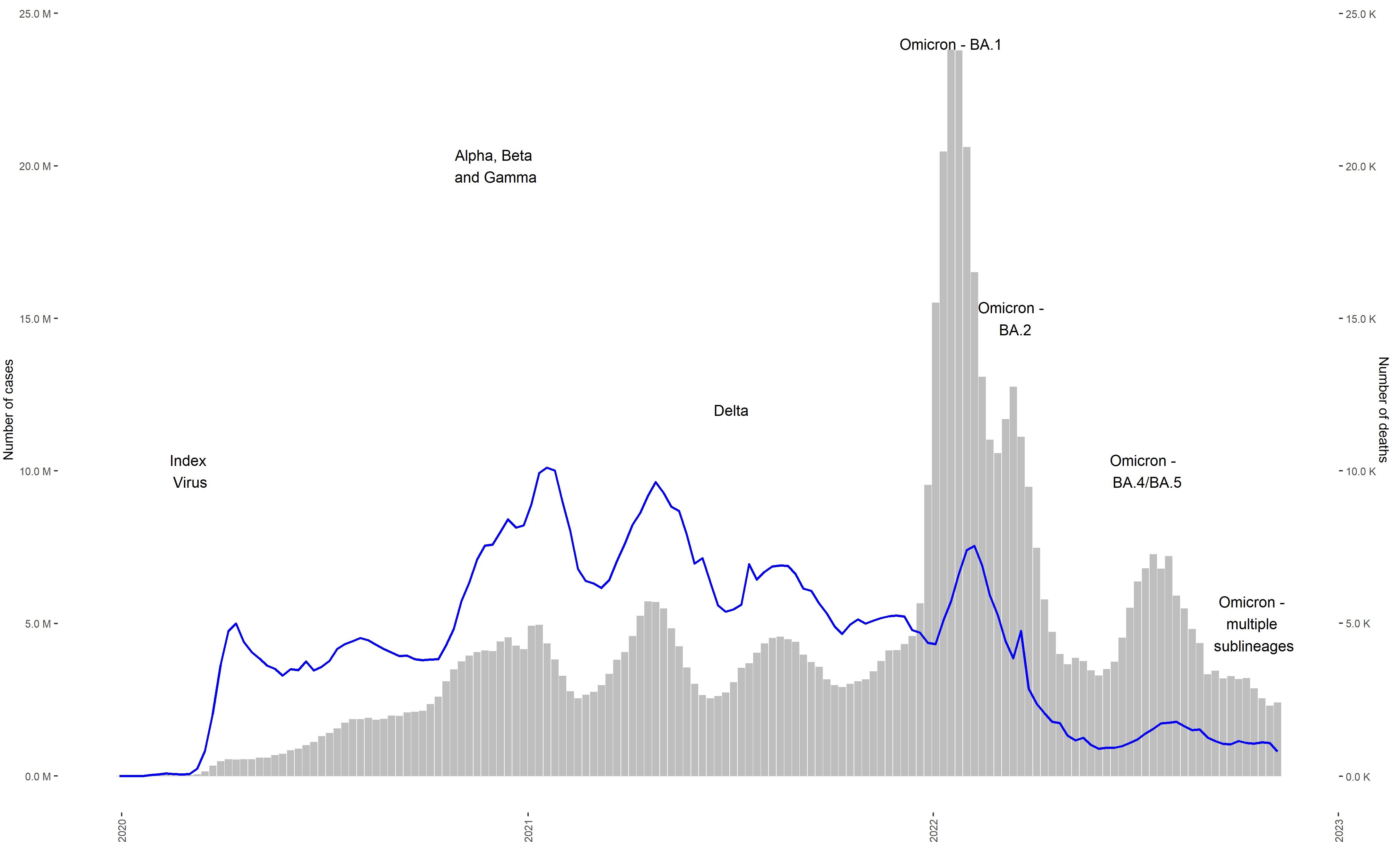 New Covid 19 Variant A Global Health Concern
May 31, 2025
New Covid 19 Variant A Global Health Concern
May 31, 2025
