Successfully Transferred: Ensuring A Smooth Data Migration Process
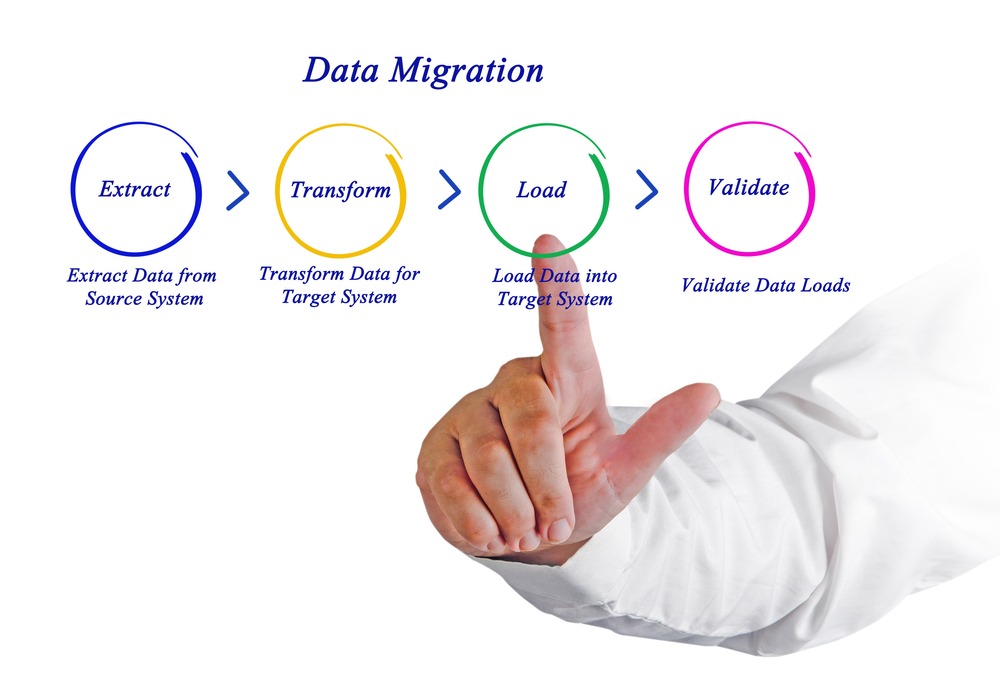
Table of Contents
Planning Your Data Migration Strategy – The Foundation for Success
Meticulous planning is the cornerstone of a successful data migration. Without a robust strategy, you risk encountering unforeseen problems and jeopardizing the integrity of your data. This section details the essential steps to lay a strong foundation for your project.
Defining Objectives and Scope
Clearly outlining your goals and the scope of your data migration is paramount. This involves defining what constitutes a successful migration for your organization.
- Define success metrics: What specific outcomes will indicate a successful data migration? (e.g., 99.9% data accuracy, zero downtime, improved application performance)
- Identify data sources and targets: Pinpoint the exact locations of your source data and the destination system. Understand the structure and format of the data in both locations.
- Determine data volume: Accurately estimate the size of your data set to determine the resources and time required for the migration.
Example: "Successfully migrating customer relationship management (CRM) data to a new cloud-based platform, achieving 99.9% data accuracy and less than 1 hour of downtime."
Choosing the Right Migration Method
Several methods exist for data migration, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Selecting the optimal method depends on factors like your downtime tolerance, data volume, complexity, and budget.
- Direct Migration: A fast but risky method, involving a direct transfer of data from the source to the target system. Suitable for smaller datasets with minimal downtime tolerance.
- Phased Migration: A more controlled approach, migrating data in stages. Minimizes downtime but extends the project timeline. Ideal for large and complex datasets.
- Parallel Migration: Running both the old and new systems simultaneously until the new system is fully tested and validated. Reduces risk but requires more resources.
- Database Cloning: Creating a complete copy of the database before migrating it to the target system. Facilitates testing and rollback options.
Example: "Phased migration minimizes downtime but requires longer project timelines, making it suitable for our large e-commerce database."
Building a Robust Testing and Validation Plan
Thorough testing is critical to identify and rectify potential issues before the actual migration. A well-defined testing plan minimizes the risk of errors and ensures data integrity.
- Develop test cases: Create comprehensive test cases covering various scenarios and data types.
- Perform data validation: Verify the accuracy and completeness of the migrated data by comparing it to the source data.
- Conduct user acceptance testing (UAT): Allow end-users to test the migrated data and systems to ensure usability and functionality.
Example: "Successfully validating the migrated data against the source data to ensure accuracy identified and resolved a crucial data mapping error."
Executing Your Data Migration – A Step-by-Step Approach
Effective execution of your migration plan is crucial for a successful outcome. This section details the practical steps involved in transferring your data.
Data Preparation and Cleansing
Before migration, data cleansing and preparation are vital steps that ensure data integrity and accuracy.
- Identify and correct data inconsistencies: Address errors, typos, and inconsistencies in your data.
- Handle missing values: Decide how to deal with missing data points (e.g., imputation, deletion).
- Remove duplicates: Eliminate redundant data entries to maintain data quality.
Example: "Successfully cleaning the data resulted in a 15% reduction in errors during the migration, improving overall data quality."
Data Transformation and Mapping
Data transformation involves converting data from the source format to the target system's requirements.
- Data type conversion: Convert data types (e.g., from text to numeric).
- Data format conversion: Change data formats (e.g., from CSV to JSON).
- Data normalization: Organize data to reduce redundancy and improve data integrity.
Example: "Successfully mapping source data fields to target data fields ensures data integrity and seamless integration with the new system."
Data Transfer and Loading
This phase involves the actual transfer and loading of data into the target system.
- Choosing the right tools: Select appropriate tools for data transfer (e.g., ETL tools, scripting languages).
- Monitoring the transfer process: Track the progress and identify any potential issues.
- Handling potential errors: Develop strategies to address and resolve errors during the transfer process.
Example: "Successfully transferring the data using a high-speed network connection and a robust ETL tool ensured minimal downtime and efficient data loading."
Post-Migration Activities – Ensuring Long-Term Success
Post-migration activities are equally crucial for ensuring the long-term success of your data migration project.
Data Validation and Verification
Post-migration validation confirms the accuracy and completeness of the migrated data.
- Compare migrated data with source data: Perform a thorough comparison to identify any discrepancies.
- Identify and resolve discrepancies: Address any identified errors or inconsistencies.
Example: "Successfully verifying the migrated data ensures the accuracy of reporting and analysis, providing reliable insights for business decisions."
System Monitoring and Maintenance
Ongoing monitoring and maintenance are essential for optimal system performance.
- Monitor system performance: Track key metrics to identify potential issues.
- Identify and address issues proactively: Resolve issues promptly to prevent disruptions.
- Implement regular backups: Ensure data protection and recovery capabilities.
Example: "Successfully monitoring the system after the migration identified and resolved a minor performance bottleneck, ensuring optimal system performance."
User Training and Support
Provide adequate training and support to users to ensure smooth adoption of the new system.
- Conduct training sessions: Offer comprehensive training to familiarize users with the new system.
- Provide documentation: Create user-friendly documentation and guides.
- Offer ongoing support: Provide ongoing support to address user queries and issues.
Example: "Successfully training users resulted in a high level of user satisfaction and system adoption, maximizing the benefits of the data migration."
Conclusion
Successfully completing a data migration requires careful planning, thorough execution, and ongoing monitoring. By following the strategies outlined in this guide, you can significantly increase your chances of a smooth and successful data migration. Remember, a well-planned and executed data migration is crucial for business continuity and operational efficiency. Don't hesitate to invest the time and resources necessary to ensure your data is "successfully transferred" to its new destination. Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you with your next data migration project.

Featured Posts
-
 2025 Bitcoin Conference In Seoul Industry Leaders Assemble
May 08, 2025
2025 Bitcoin Conference In Seoul Industry Leaders Assemble
May 08, 2025 -
 Quick News F4 Elden Ring Possum And Superman Updates
May 08, 2025
Quick News F4 Elden Ring Possum And Superman Updates
May 08, 2025 -
 Grbovic Psg O Prelaznoj Vladi Svi Predlozi Na Stolu
May 08, 2025
Grbovic Psg O Prelaznoj Vladi Svi Predlozi Na Stolu
May 08, 2025 -
 Lahwr Ky Ahtsab Edaltwn Ka Mstqbl 5 Edaltwn Ke Khatme Ke Bed
May 08, 2025
Lahwr Ky Ahtsab Edaltwn Ka Mstqbl 5 Edaltwn Ke Khatme Ke Bed
May 08, 2025 -
 Lotto 6aus49 Gewinnzahlen And Quoten Mittwoch 9 4 2025
May 08, 2025
Lotto 6aus49 Gewinnzahlen And Quoten Mittwoch 9 4 2025
May 08, 2025
