School Desegregation Order Terminated: Expected Impact On Educational Equity
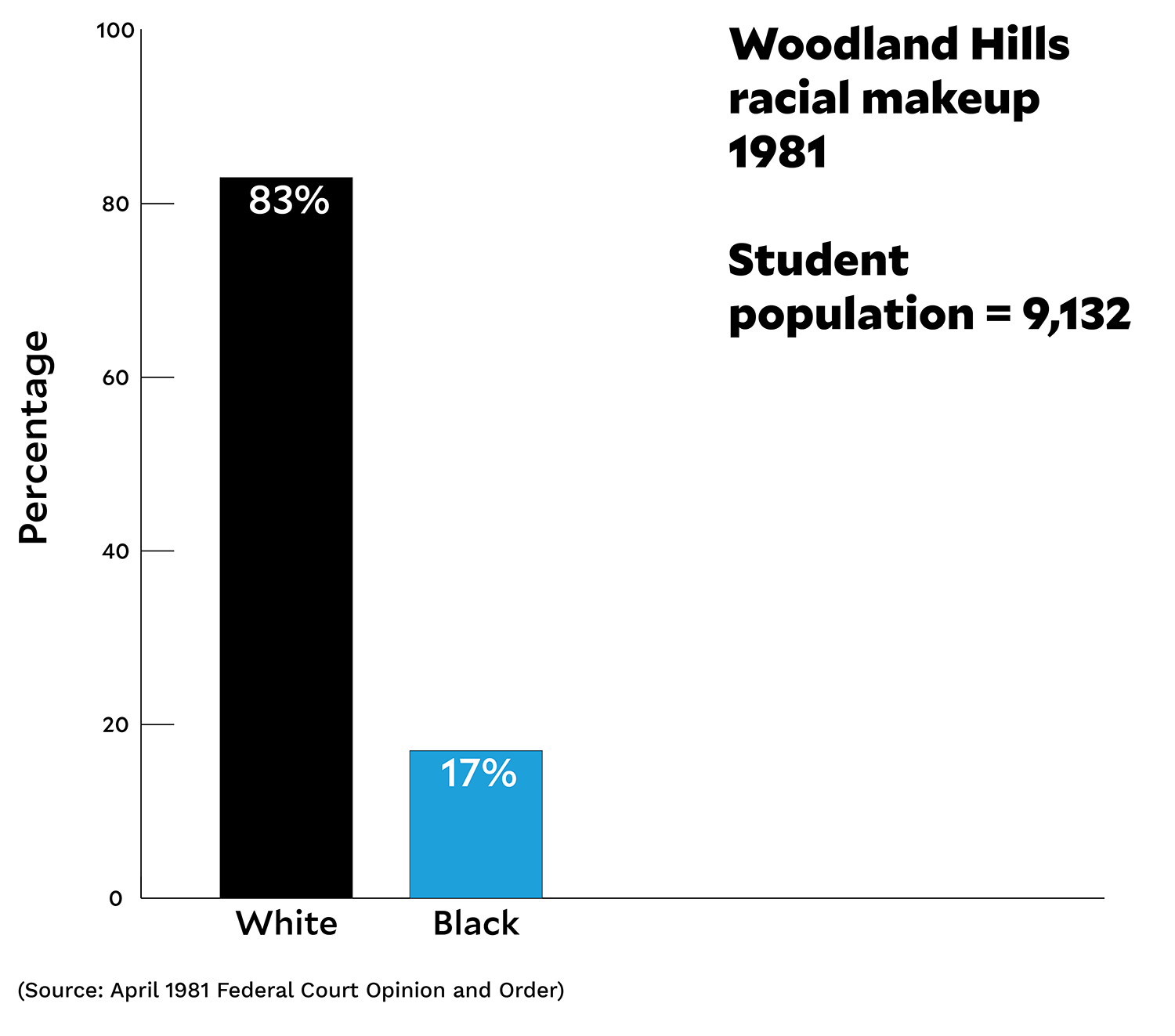
Table of Contents
Increased Racial Segregation in Schools
The termination of school desegregation orders raises serious concerns about a return to racially segregated schools. While overt, legally mandated segregation is gone, the subtle and complex mechanisms of de facto segregation—segregation in practice, even without explicit laws—remain potent. The termination of these orders removes a crucial legal mechanism for addressing and mitigating this de facto segregation.
- Increased concentration of minority students in certain schools: Without active desegregation efforts, schools in predominantly minority neighborhoods may become overwhelmingly populated by students from underrepresented groups, potentially exacerbating existing inequalities.
- Potential resurgence of de facto segregation due to housing patterns: Residential segregation often mirrors school segregation. If families self-segregate, the schools within those communities will likely reflect that demographic split, leading to racially isolated learning environments. This creates a vicious cycle of inequality, impacting access to quality education.
- Limited access to high-quality resources in previously integrated schools: Schools that were once integrated and benefited from a diverse student body might now face a decline in resources if the student population shifts significantly. This could lead to a disparity in educational quality based on race and socioeconomic status.
Existing data reveals stark racial disparities in education. Studies consistently show achievement gaps between white students and students of color, often linked to factors such as school funding, teacher quality, and access to advanced courses. The termination of desegregation orders threatens to widen these existing educational disparities and create new racial imbalances within the school system.
Impact on Academic Achievement
The potential for increased school segregation directly impacts academic performance. Schools with predominantly minority populations often face challenges in securing adequate funding, attracting and retaining qualified teachers, and providing access to enriching extracurricular activities. This translates into:
- Reduced academic achievement for minority students in under-resourced schools: A lack of resources, coupled with a less diverse learning environment, can negatively affect the academic progress of minority students.
- Wider achievement gaps between different racial and socioeconomic groups: Re-segregation risks exacerbating existing achievement gaps, potentially widening the disparity between students from different backgrounds.
- Limited access to advanced courses and extracurricular activities: Under-resourced schools might lack the capacity to offer advanced placement courses, specialized programs, and a broad range of extracurricular opportunities, limiting students' educational and personal growth.
The consequences are far-reaching, potentially limiting the future opportunities for students from under-resourced communities. Addressing the potential negative impacts on educational outcomes is crucial for promoting equitable access to a quality education.
Effects on School Funding and Resource Allocation
The termination of desegregation orders may significantly impact school funding and resource allocation. Funding models often rely on local property taxes, which can lead to significant disparities between wealthy and impoverished communities. This means:
- Potential decrease in funding for schools with predominantly minority populations: Schools in lower-income areas, which often have larger minority populations, may receive less funding, perpetuating existing inequalities.
- Unequal access to qualified teachers, advanced technology, and other essential resources: Funding disparities translate directly into unequal access to quality teachers, modern technology, updated facilities, and other crucial resources that contribute to successful learning.
- Disparities in school infrastructure and facilities: This can range from outdated textbooks and equipment to dilapidated buildings, negatively impacting the learning environment and student well-being.
These funding disparities contribute to educational inequality, creating a system where some students have significantly better opportunities than others simply based on their zip code. Addressing this requires a systematic approach to ensure equitable resource allocation across all schools.
The Role of Community Involvement and Advocacy
Despite the potential negative consequences of school desegregation order termination, community involvement and advocacy play a vital role in mitigating its effects and promoting educational equity.
- Community-led initiatives to promote school integration: Local communities can spearhead initiatives to foster integration, such as advocating for open enrollment policies, promoting inter-school collaborations, and organizing community-based learning programs.
- Advocacy efforts to ensure equitable resource allocation: Community members can advocate for policy changes that ensure equitable funding and resource distribution across all schools, regardless of the racial composition of the student body.
- The importance of parental involvement in shaping school policies: Active parental involvement in school governance and decision-making processes is crucial to ensuring that the needs of all students are met and that schools remain accountable to their communities.
Through active community engagement and robust educational advocacy, communities can work to overcome the challenges posed by the termination of desegregation orders and build a more equitable educational system for all children. Exploring various school choice options and their implications for integration is also crucial.
The Future of Educational Equity After School Desegregation Order Termination
The potential consequences of School Desegregation Order Termination on educational equity are significant. The threat of increased racial segregation, widening achievement gaps, and unequal resource allocation necessitates proactive measures. We must actively fight for educational equity and advocate for policies that ensure equitable access to quality education for all students, regardless of race or socioeconomic background. The termination of these orders does not signal the end of the fight for equitable education; rather, it underscores the ongoing need for vigilance and action. We must continue to advocate for school desegregation and ensure that all students have the opportunity to thrive in a fair and just educational system. Let's work together to ensure equitable access to education for every child.

Featured Posts
-
 Ghanas Mental Healthcare System 80 Psychiatrists For 30 Million People
May 03, 2025
Ghanas Mental Healthcare System 80 Psychiatrists For 30 Million People
May 03, 2025 -
 Doctor Who Star Responds To Criticism Show Is Reflecting The Times
May 03, 2025
Doctor Who Star Responds To Criticism Show Is Reflecting The Times
May 03, 2025 -
 Secure Your Free Cowboy Bebop Fortnite Rewards
May 03, 2025
Secure Your Free Cowboy Bebop Fortnite Rewards
May 03, 2025 -
 Loyle Carners New Album And Glastonbury Performance A Fathers Perspective
May 03, 2025
Loyle Carners New Album And Glastonbury Performance A Fathers Perspective
May 03, 2025 -
 Scottish Parliament Election Farages Reform Uks Stance Explained
May 03, 2025
Scottish Parliament Election Farages Reform Uks Stance Explained
May 03, 2025
