School Desegregation Order Terminated: Analysis And Potential Fallout
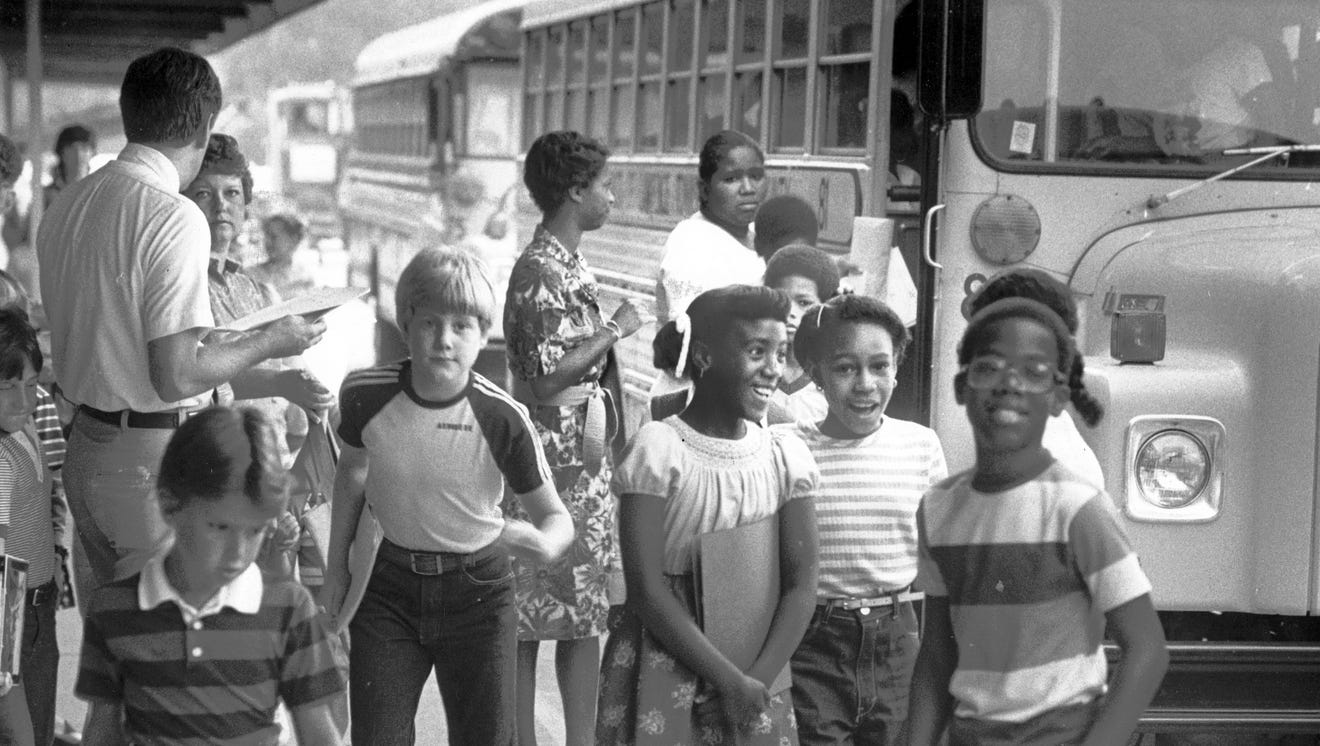
Table of Contents
H2: Historical Context of the Desegregation Order
Understanding the termination requires examining the historical context. The landmark 1954 Brown v. Board of Education Supreme Court decision declared state laws establishing separate public schools for black and white students unconstitutional. This ruling, however, didn't automatically lead to integrated schools. Resistance was widespread, and the implementation of desegregation faced significant legal and social challenges for decades. Many school districts resisted court-ordered busing and other integration efforts.
- Key milestones in the fight for school desegregation: The Civil Rights Act of 1964, the Voting Rights Act of 1965, and subsequent court cases played crucial roles in pushing for desegregation, albeit slowly and unevenly.
- The legal basis for the original order: The specific desegregation order in question stemmed from a federal court case, likely involving allegations of persistent segregation despite Brown v. Board of Education. These orders often included specific mandates for student assignment, busing, and resource allocation to achieve racial balance.
- Initial successes and challenges in implementing desegregation: While some areas saw significant progress, many others faced intense resistance, leading to protracted legal battles and ongoing struggles with achieving meaningful integration. White flight to suburban schools and the creation of de facto segregation through housing patterns further complicated the process.
H2: Reasons for the Termination of the Desegregation Order
The termination of the desegregation order was likely justified by proponents using several arguments.
- Claims of successful integration and achieving the order's goals: Arguments for termination often center on the claim that the school district has achieved a sufficient level of racial integration, rendering the order obsolete. This often involves citing current student demographics and arguing that the original goals of the order have been met.
- Arguments about local control over schools: Proponents often emphasize the importance of local control over education, suggesting that the desegregation order infringes upon the autonomy of school districts and undermines local decision-making processes. This argument often resonates with those who feel that federal intervention in education is excessive.
- Potential legal challenges to the order's continued enforcement: Over time, legal challenges to the continued enforcement of decades-old desegregation orders can emerge. Changes in demographics, legal precedents, or shifting interpretations of the law might create grounds for arguing that the order is no longer legally sound or necessary.
H2: Potential Negative Consequences of the Termination
Ending the desegregation order carries significant risks, potentially reversing decades of progress.
- Increased racial segregation in schools: The most immediate concern is a return to racially segregated schools. Without the order's mandates, school districts might revert to patterns of segregation, creating schools that are predominantly white or predominantly minority.
- Disparities in educational resources and opportunities: Racial segregation often correlates with disparities in school funding, teacher quality, and access to educational resources. The termination could exacerbate these existing inequalities.
- Negative effects on academic achievement for minority students: Research consistently shows that students in racially diverse schools tend to perform better academically. Increased segregation could negatively impact the academic achievement of minority students.
- Potential rise in racial tension within school communities: A return to segregated schools could heighten racial tensions and create a less inclusive and welcoming environment for all students.
H2: Potential Positive Consequences (if any)
While the potential negative consequences are significant, proponents of termination may point to some potential benefits. However, these claims often require critical evaluation.
- Arguments for greater local autonomy: Increased local control could theoretically allow school districts to tailor their educational programs to better meet the specific needs of their communities. However, this must be weighed against the risk of perpetuating inequalities.
- Claims of improved school choice and diversity through other means: Proponents might suggest that school choice programs or other initiatives can achieve racial diversity more effectively than court-ordered desegregation. However, the effectiveness of these alternatives in achieving meaningful integration is often debated.
- Counterarguments addressing the potential limitations of these claims: It's crucial to acknowledge that school choice programs can often exacerbate segregation if not carefully designed and implemented. Furthermore, relying solely on these alternative approaches without addressing underlying systemic inequalities is unlikely to lead to truly equitable outcomes.
H2: The Ongoing Debate and Future of School Desegregation
The termination of this desegregation order fuels an ongoing debate about the future of racial integration in education.
- Ongoing lawsuits and legal challenges: The termination is likely to face legal challenges, leading to ongoing lawsuits and appeals.
- Policy recommendations for promoting school integration: Experts will advocate for policies aimed at promoting school integration, such as equitable funding formulas, addressing housing segregation, and promoting diverse school enrollment patterns.
- The role of federal and state governments in ensuring equitable education: The federal and state governments have a crucial role to play in ensuring that all students have access to equitable educational opportunities, regardless of race. This includes providing adequate resources and enforcing anti-discrimination laws.
- The importance of community engagement and dialogue: Open community dialogue and engagement are critical to address concerns about school desegregation and to develop strategies for promoting inclusive and equitable schools for all children.
Conclusion:
The termination of this school desegregation order represents a significant development with potentially far-reaching consequences. While proponents argue for local control and the achievement of integration goals, the potential for increased racial segregation and educational disparities remains a significant concern. The ongoing debate underscores the continued need for vigilance and proactive measures to ensure equitable access to quality education for all students. Further research and analysis of the effects of this termination are crucial. We must continue to monitor the impact of this decision on school desegregation and advocate for policies that promote inclusivity and educational justice for all children. The fight for school desegregation continues, demanding our attention and action.
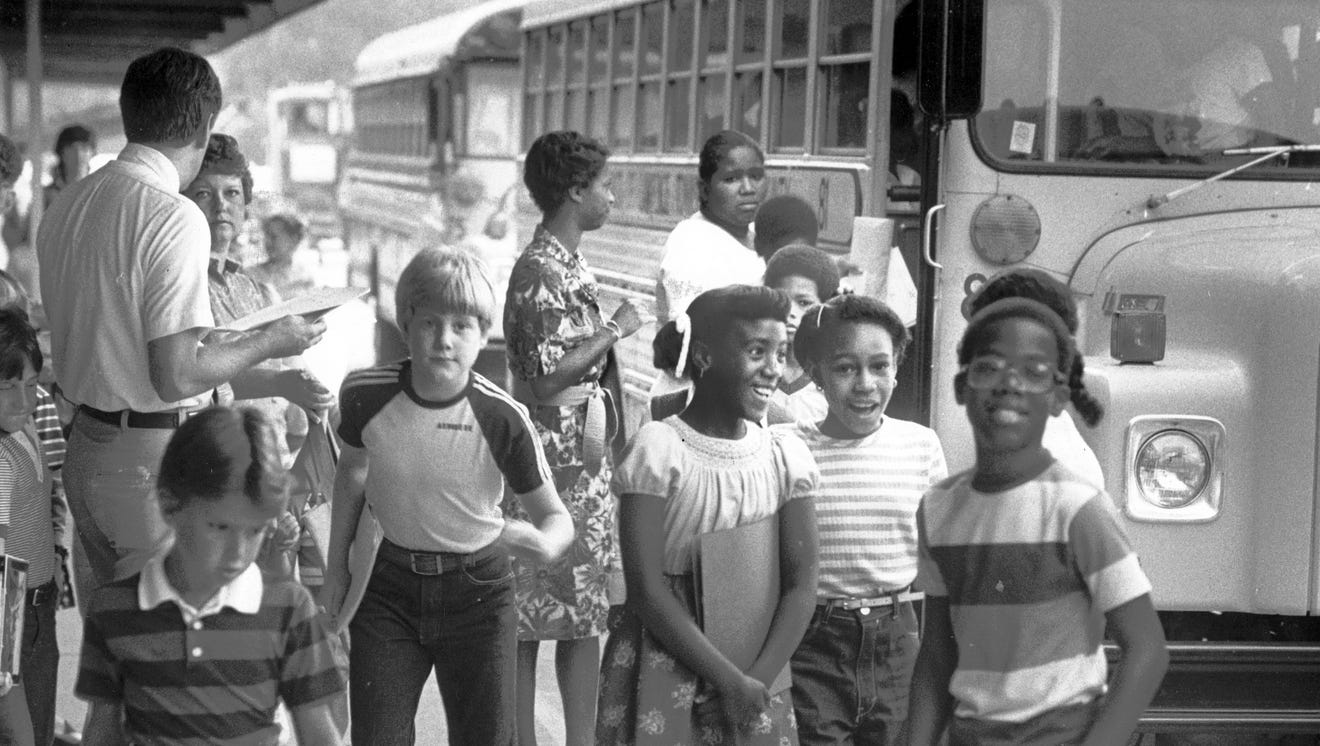
Featured Posts
-
 Is Havertz The Right Fit For Arsenal Souness Doubts It
May 02, 2025
Is Havertz The Right Fit For Arsenal Souness Doubts It
May 02, 2025 -
 Pancake Day Traditions A Look At The History Of Shrove Tuesday
May 02, 2025
Pancake Day Traditions A Look At The History Of Shrove Tuesday
May 02, 2025 -
 Stanways Emotional Tribute Following Fatal Pitch Accident In Kendal
May 02, 2025
Stanways Emotional Tribute Following Fatal Pitch Accident In Kendal
May 02, 2025 -
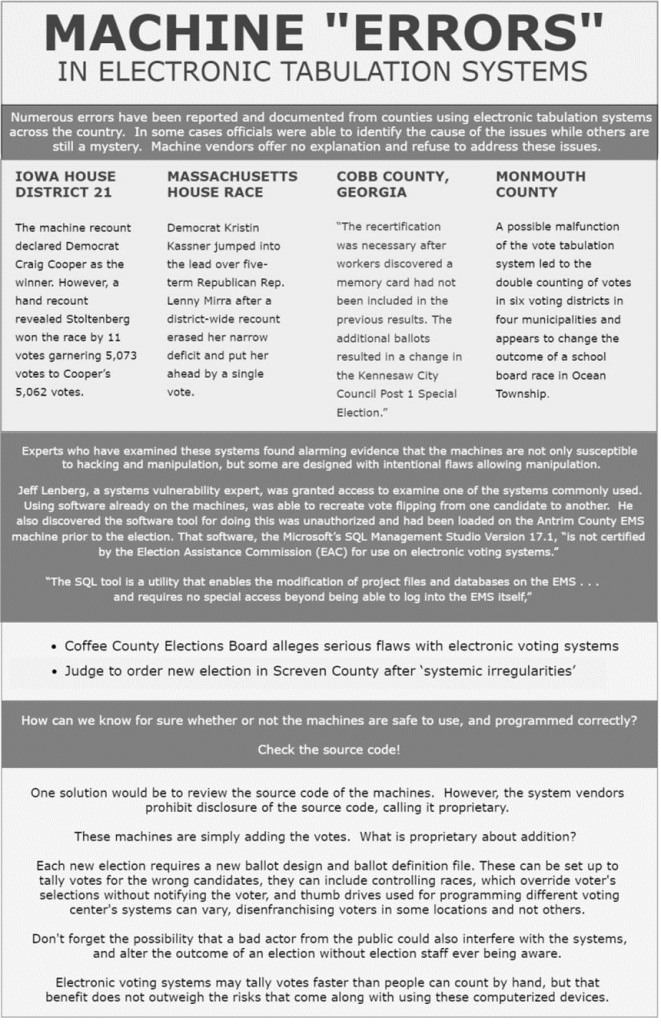 Improving Election Integrity With A Robust Poll Data System
May 02, 2025
Improving Election Integrity With A Robust Poll Data System
May 02, 2025 -
 Mbahthat Sewdyt Adhrbyjanyt Ltezyz Alteawn Fy Mjal Altjart
May 02, 2025
Mbahthat Sewdyt Adhrbyjanyt Ltezyz Alteawn Fy Mjal Altjart
May 02, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Can Reform Uk Deliver For Farmers A Critical Analysis
May 03, 2025
Can Reform Uk Deliver For Farmers A Critical Analysis
May 03, 2025 -
 Wrqt Syasat Aqtsadyt Mn Amant Alastthmar Baljbht Alwtnyt
May 03, 2025
Wrqt Syasat Aqtsadyt Mn Amant Alastthmar Baljbht Alwtnyt
May 03, 2025 -
 Amant Alastthmar Baljbht Alwtnyt Wrqt Syasat Aqtsadyt Jdydt
May 03, 2025
Amant Alastthmar Baljbht Alwtnyt Wrqt Syasat Aqtsadyt Jdydt
May 03, 2025 -
 Ampliacion De Flota Vehicular En El Sistema Penitenciario 7 Unidades
May 03, 2025
Ampliacion De Flota Vehicular En El Sistema Penitenciario 7 Unidades
May 03, 2025 -
 7 Nuevos Vehiculos Para Mejorar La Seguridad Penitenciaria
May 03, 2025
7 Nuevos Vehiculos Para Mejorar La Seguridad Penitenciaria
May 03, 2025
