Rising Measles Cases In Texas: Investigating The Source Of New Infections
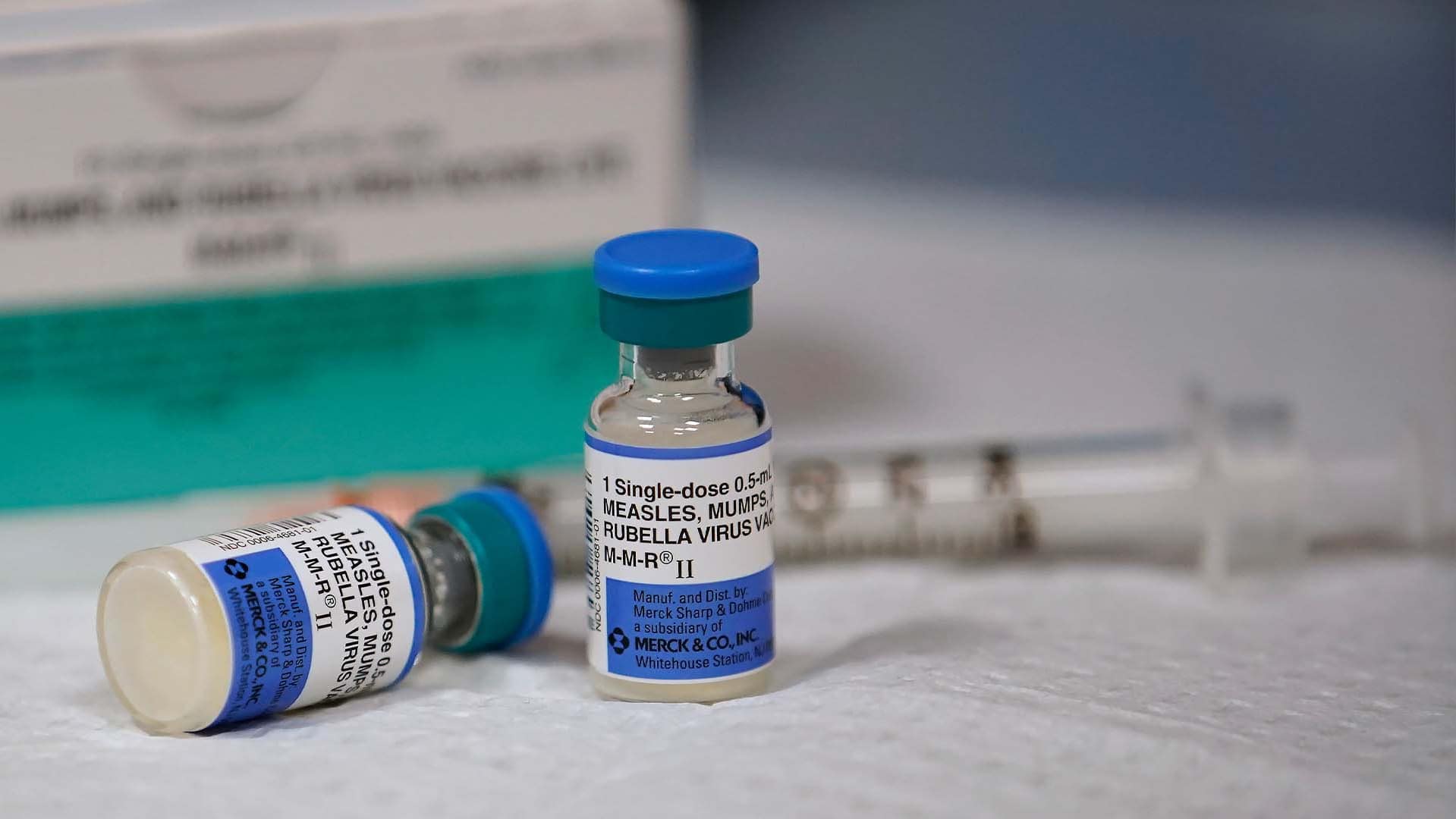
Table of Contents
Understanding the Current Measles Outbreak in Texas
Recent Statistics and Geographic Distribution
The number of reported measles cases in Texas has increased dramatically in recent months. While precise figures fluctuate, data from the Texas Department of State Health Services (DSHS) reveals a concerning trend. Analyzing the Texas measles outbreak map reveals clusters in several counties, particularly in [insert specific counties if available]. This highlights the urgent need for targeted interventions.
- Number of Cases: [Insert most up-to-date number of reported cases].
- Regions Most Affected: [List specific counties or regions with the highest number of cases].
- Age Groups Most Susceptible: While measles can affect anyone, unvaccinated young children and adults are particularly vulnerable.
Symptoms and Transmission of Measles
Measles is a highly contagious viral illness spread through the air via respiratory droplets produced from coughing or sneezing by an infected person. Understanding measles symptoms and transmission is crucial for effective prevention and control.
- Common Symptoms: High fever, cough, runny nose, conjunctivitis (pink eye), and a characteristic Koplik's spots (small white spots inside the mouth) precede the hallmark measles rash.
- Mode of Transmission: Airborne transmission makes measles highly contagious. An infected person can spread the virus from four days before to four days after the rash appears.
- Incubation Period: The incubation period is typically 7-14 days, meaning symptoms can appear up to two weeks after exposure.
Investigating Potential Sources of Infection
Unvaccinated Populations
Low vaccination rates play a significant role in the resurgence of measles. Vaccine hesitancy in Texas, fueled by misinformation and distrust of vaccines, contributes to vulnerable populations.
- Vaccination Rates in Affected Areas: [Insert data on vaccination rates in affected areas, comparing them to statewide averages].
- Reasons for Vaccine Hesitancy: Common concerns include unfounded fears about vaccine safety, distrust in public health authorities, and the spread of misinformation through social media.
Imported Cases and Travel
Imported cases from regions with higher measles incidence contribute to outbreaks. International travel patterns of infected individuals need investigation.
- Recent Travel Patterns: Tracking the travel history of infected individuals can pinpoint potential sources of infection.
- International Connections: Monitoring international travel advisories and identifying potential links to outbreaks in other countries is essential.
Community Clusters and Outbreaks
Identifying specific community clusters where measles has spread rapidly is crucial for targeted interventions.
- Specific Locations: [Mention specific locations, events, or gatherings that may have facilitated the spread of measles].
- Community Spread: Understanding how measles spreads within specific communities can guide public health efforts.
Public Health Response and Prevention Strategies
Current Public Health Measures
Texas health authorities are actively working to contain the outbreak.
- Contact Tracing: DSHS is conducting contact tracing to identify and isolate individuals exposed to measles.
- Vaccination Campaigns: Public health officials are promoting vaccination campaigns to increase MMR vaccination rates.
- Public Health Advisories: Public health advisories are being issued to inform the public about the risks of measles and preventive measures.
The Importance of Vaccination
The MMR (measles, mumps, rubella) vaccine is highly effective in preventing measles.
- MMR Vaccine Effectiveness: The MMR vaccine is over 97% effective in preventing measles infection after two doses.
- Measles Vaccine Safety: The MMR vaccine is one of the safest and most effective vaccines available.
- Addressing Vaccine Myths: Public health campaigns are addressing misinformation and debunking common myths surrounding vaccine safety.
Conclusion
The rising measles cases in Texas highlight the urgent need for increased vaccination rates and proactive public health measures. The outbreak's potential sources, including low vaccination rates, imported cases, and community clusters, underscore the importance of comprehensive strategies. The effectiveness of the MMR vaccine is undeniable, and addressing vaccine hesitancy through education and public health campaigns is paramount. The Texas Department of State Health Services' response, involving contact tracing, vaccination campaigns, and public health advisories, is crucial, yet community participation is essential. The rising measles cases in Texas demand immediate attention. Protect yourself and your community by ensuring you and your loved ones are up-to-date on your MMR vaccinations. Stay informed about the latest updates from Texas health authorities to combat this ongoing challenge. Let's work together to prevent future outbreaks of measles in Texas.
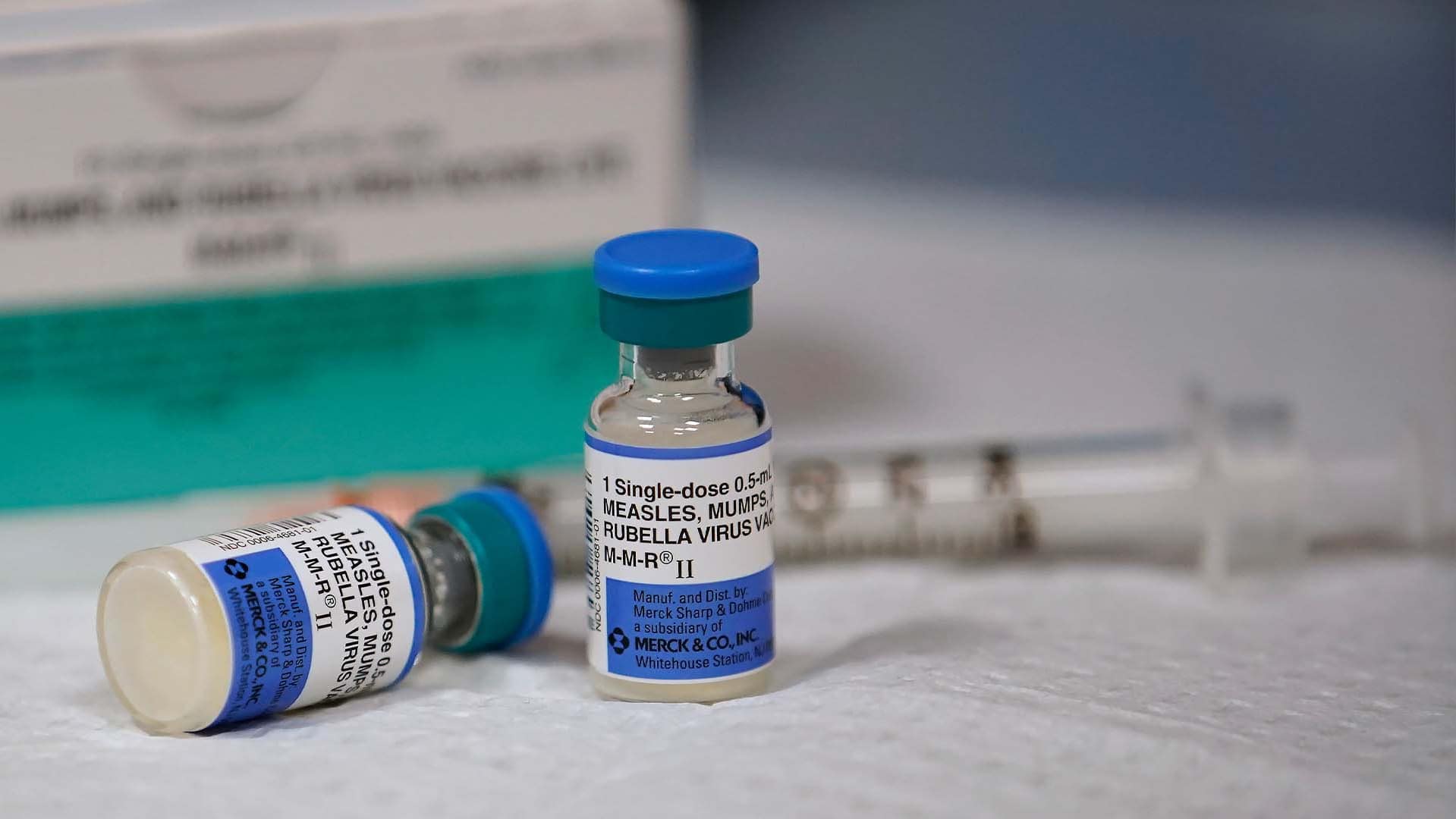
Featured Posts
-
 The Underrated Value Of Middle Managers Boosting Productivity And Morale
May 30, 2025
The Underrated Value Of Middle Managers Boosting Productivity And Morale
May 30, 2025 -
 Oasis Concert Ticket Sales An Audit Of Ticketmasters Practices And Legal Compliance
May 30, 2025
Oasis Concert Ticket Sales An Audit Of Ticketmasters Practices And Legal Compliance
May 30, 2025 -
 Guru Jara A Dalsi Oslavy Jmenin A Vladimir Jako Vudce Svobodneho Sveta V Svete Tomase Koloce
May 30, 2025
Guru Jara A Dalsi Oslavy Jmenin A Vladimir Jako Vudce Svobodneho Sveta V Svete Tomase Koloce
May 30, 2025 -
 Novo Nordisk And Ozempic Challenges And Opportunities In The Weight Loss Market
May 30, 2025
Novo Nordisk And Ozempic Challenges And Opportunities In The Weight Loss Market
May 30, 2025 -
 Combating Measles Persistence Strategies For Improved Vaccination Rates
May 30, 2025
Combating Measles Persistence Strategies For Improved Vaccination Rates
May 30, 2025
