Record Solar Output Sends European Energy Prices Into Negative Territory
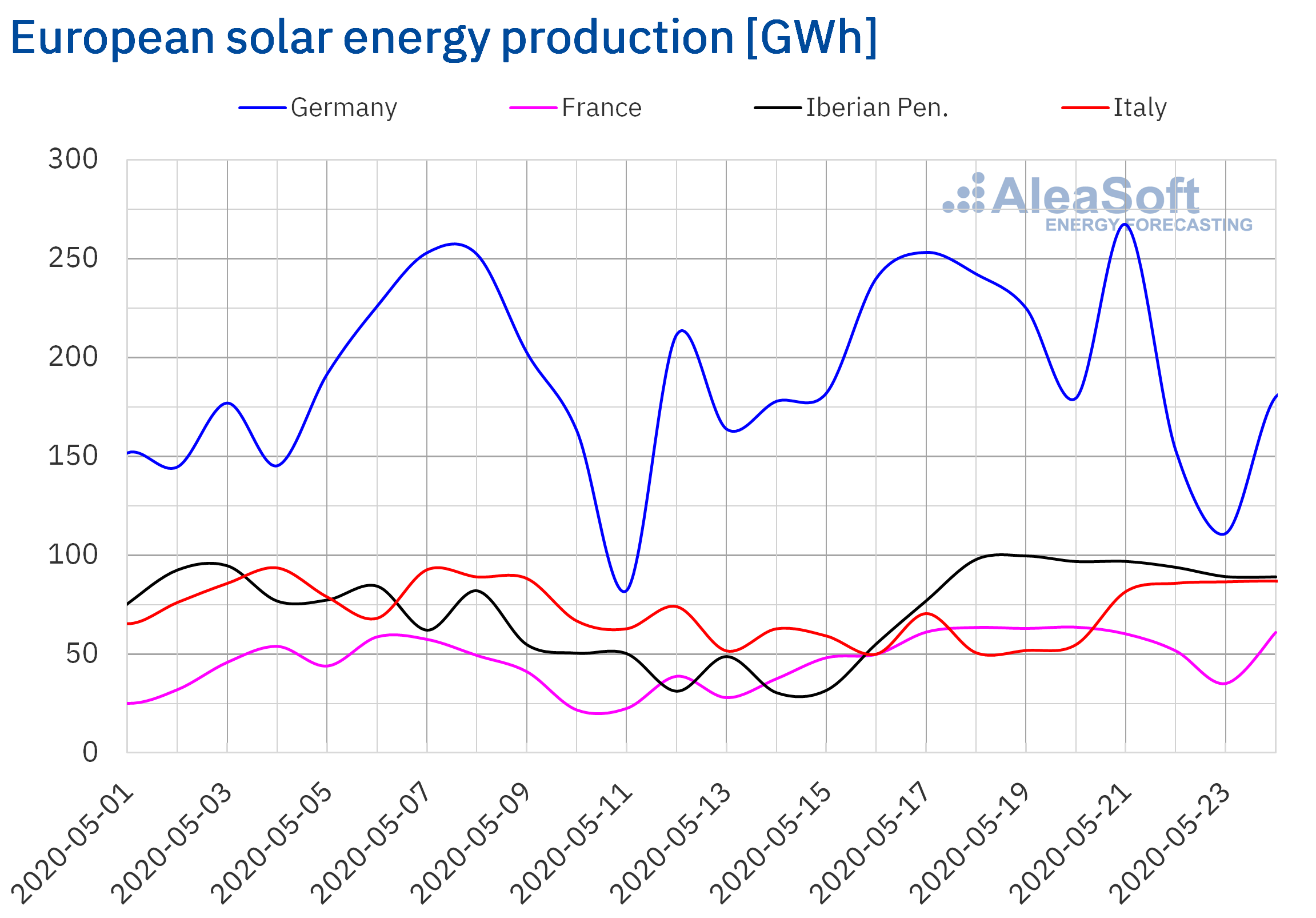
Table of Contents
Unprecedented Solar Power Generation
The surge in solar energy production across Europe is nothing short of remarkable. Several factors have contributed to this record output, pushing electricity prices into negative territory for the first time in many regions.
Factors Contributing to Record Output
-
Ideal Weather Conditions: Extended periods of intense sunshine and clear skies across much of Europe have maximized solar panel efficiency. This prolonged favorable weather pattern has been a crucial factor in the record-breaking solar energy generation.
-
Increased Solar Capacity: Significant investments in recent years have led to a substantial increase in solar power capacity across the continent. New solar farms and residential installations have dramatically boosted overall production capabilities.
-
Reduced Energy Demand: Seasonal factors, such as milder weather reducing the need for heating, have also contributed to the surplus of solar energy. Lower demand combined with high supply is a key driver of negative energy pricing.
-
Specific Country Performance: Germany, Spain, and Italy saw particularly high solar energy output, with Germany reporting a X% increase in solar power generation compared to the same period last year. Specific data on peak production levels should be added here (replace X with actual data).
The Impact of Negative Energy Prices
The unprecedented negative energy prices are having a profound impact on both energy producers and consumers.
Implications for Energy Producers
Negative energy prices represent a significant challenge for traditional power plants reliant on fossil fuels like coal and gas. These plants often have fixed operational costs, meaning they are forced to pay to have their energy taken off the grid during periods of oversupply. This can result in substantial financial losses. To mitigate losses, power plants may:
- Reduce Output: Temporarily scaling back production to avoid further losses.
- Increase Efficiency: Investing in technologies to improve efficiency and reduce operational costs.
- Diversify Production: Exploring renewable energy sources to offset losses from fossil fuel operations.
Benefits for Consumers and Businesses
While challenging for producers, negative energy prices translate into significant benefits for consumers and businesses. During these periods:
- Lower Energy Bills: Consumers and businesses experience a direct reduction in their energy costs, even receiving payments for consuming energy.
- Economic Boost: The savings can stimulate economic activity, boosting businesses and household disposable income.
However, there are challenges:
-
Excess Energy Utilization: Utilizing surplus energy efficiently during periods of negative pricing can be problematic due to a lack of suitable large-scale storage solutions.
-
Examples of Negative Pricing: Specific instances of negative energy pricing, with dates and locations, should be added here to add weight to this point. The financial impact on producers can also be quantified here (replace Y with actual data). For example, "On [date], energy prices in [region] plummeted to -Y €/MWh, resulting in estimated losses of Z million euros for conventional power plants".
Challenges and Opportunities for Grid Management
The influx of intermittent renewable energy sources like solar poses significant challenges for grid management.
Managing Intermittency
The intermittent nature of solar power necessitates advanced grid management strategies. Key challenges include:
- Balancing Supply and Demand: Ensuring a stable electricity supply even when solar output fluctuates due to weather conditions.
- Grid Infrastructure: Upgrading grid infrastructure to handle the increased capacity and rapid changes in energy flow.
- Energy Storage: Developing effective and cost-efficient energy storage solutions (battery storage, pumped hydro) to store excess solar energy for later use.
Future Outlook for Renewable Energy Integration
The record solar output underscores the need for substantial changes in European energy policies and investments. The future holds:
-
Increased Renewable Energy Share: Further expansion of renewable energy sources, particularly solar and wind, is likely.
-
Price Volatility: Energy price fluctuations will likely continue, particularly in the short term, until more advanced grid management systems and storage solutions are in place.
-
Technological Advancements: Advancements in grid technologies and smart grid integration will play a crucial role in improving stability and efficiency.
-
Specific Grid Management Technologies: Detail specific technologies here (e.g., advanced forecasting models, demand-side management systems), explaining their effectiveness in managing the intermittent nature of renewable energy.
Conclusion
The record solar output driving European energy prices into negative territory marks a significant turning point in the European energy landscape. This event underscores the growing importance of renewable energy sources, while simultaneously highlighting the challenges of integrating high levels of intermittent renewables into the existing grid infrastructure. The transition to a predominantly renewable energy system requires careful planning, strategic investment, and a collaborative approach from policymakers, energy producers, and consumers.
Call to Action: The shift towards renewable energy sources, as demonstrated by this unprecedented event, demands a proactive approach to grid management and energy policy. Learn more about the implications of record solar output and the future of European energy markets. Stay informed about the latest developments in solar energy and its impact on European energy prices. Understanding the complexities of this transition is crucial as we move towards a more sustainable energy future.

Featured Posts
-
 Alberto Ardila Olivares Metodo Para Anotar Goles
Apr 29, 2025
Alberto Ardila Olivares Metodo Para Anotar Goles
Apr 29, 2025 -
 The Making Of Oh What A Beautiful World A Willie Nelson Album Story
Apr 29, 2025
The Making Of Oh What A Beautiful World A Willie Nelson Album Story
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Recent Russian Military Activities And Their Implications For Europe
Apr 29, 2025
Recent Russian Military Activities And Their Implications For Europe
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Attorney Generals Transgender Athlete Ban Implications For Minnesota Schools
Apr 29, 2025
Attorney Generals Transgender Athlete Ban Implications For Minnesota Schools
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Louisvilles Early 2025 Disasters Snow Tornadoes And Catastrophic Flooding
Apr 29, 2025
Louisvilles Early 2025 Disasters Snow Tornadoes And Catastrophic Flooding
Apr 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Damon Agrees With Trump Believes Pete Rose Deserves Hall Of Fame Spot
Apr 29, 2025
Damon Agrees With Trump Believes Pete Rose Deserves Hall Of Fame Spot
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Johnny Damon Sides With Trump Advocates For Pete Roses Hall Of Fame Induction
Apr 29, 2025
Johnny Damon Sides With Trump Advocates For Pete Roses Hall Of Fame Induction
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Posthumous Pardon For Pete Rose Understanding Trumps Decision
Apr 29, 2025
Posthumous Pardon For Pete Rose Understanding Trumps Decision
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Snow Fox Operational Status Tuesday February 11th
Apr 29, 2025
Snow Fox Operational Status Tuesday February 11th
Apr 29, 2025 -
 February 11th Snow Fox Updates Delays And Closings
Apr 29, 2025
February 11th Snow Fox Updates Delays And Closings
Apr 29, 2025
